(3.3 × 10!4) + (2.52 × 10!2) = (3.3 × 10!4) × (2.52 × 10!2)
... Hypothesis: A tentative explanation or prediction based on experimental observations. Law: A concise verbal or mathematical statement of a behavior or a relation that seems always to be the same under the same conditions. Theory: a well-tested, unifying principle that explains a body of facts and th ...
... Hypothesis: A tentative explanation or prediction based on experimental observations. Law: A concise verbal or mathematical statement of a behavior or a relation that seems always to be the same under the same conditions. Theory: a well-tested, unifying principle that explains a body of facts and th ...
Chemistry: Unit Organizer Name 6-__ Matter has physical properties
... Ability to react: When a substance has the potential to react with acid, oxygen or water; a chemical property. Atom: The smallest unit of matter. ex. a carbon atom Chemical Reaction: a process in which chemical bonds are broken and atoms rearranged. During the process a new substance is formed. Comp ...
... Ability to react: When a substance has the potential to react with acid, oxygen or water; a chemical property. Atom: The smallest unit of matter. ex. a carbon atom Chemical Reaction: a process in which chemical bonds are broken and atoms rearranged. During the process a new substance is formed. Comp ...
The Language of Chemistry
... • Dimensions are given such as mass, time, distance, volume, density, temperature, color specified as a wavelength etc... ...
... • Dimensions are given such as mass, time, distance, volume, density, temperature, color specified as a wavelength etc... ...
Chemistry
... 2. Chemistry: the study of the composition of matter and the energy created by the interaction of matter 3. Matter: anything that has mass & volume 4. Mass: quantity of matter in an object often determined by weighing with a scale ...
... 2. Chemistry: the study of the composition of matter and the energy created by the interaction of matter 3. Matter: anything that has mass & volume 4. Mass: quantity of matter in an object often determined by weighing with a scale ...
Unit 3C Standards for Quiz
... It will be similar to the last exam but there will be at least three questions per standard. Remember that since no calculators are allowed on the standards exam that we will be modeling this in this assessment of progress. Atomic and Molecular Structure 1. The Periodic Table displays the elements i ...
... It will be similar to the last exam but there will be at least three questions per standard. Remember that since no calculators are allowed on the standards exam that we will be modeling this in this assessment of progress. Atomic and Molecular Structure 1. The Periodic Table displays the elements i ...
Chemistry Unit Review
... b. Lead (II) iodide and potassium nitrate are produced when potassium iodide is added to lead (II) nitrate. ...
... b. Lead (II) iodide and potassium nitrate are produced when potassium iodide is added to lead (II) nitrate. ...
atom a very small particle that makes up most kinds of matters and
... upward force exerted on an object immersed in a fluid buoyant force ...
... upward force exerted on an object immersed in a fluid buoyant force ...
Physical Properties
... • Stating that something is hot or cold without specifying a temperature. • Identifying something by smell • No measurements ...
... • Stating that something is hot or cold without specifying a temperature. • Identifying something by smell • No measurements ...
Physical properties
... without using the word "change". Eventually you should be able to look at the formula of a compound and state some chemical property. At this time this is very difficult to do and you are not expected to be able to do it. ...
... without using the word "change". Eventually you should be able to look at the formula of a compound and state some chemical property. At this time this is very difficult to do and you are not expected to be able to do it. ...
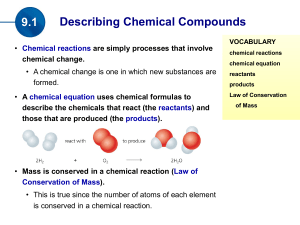
(the products). Mass is conserved in a chemical reaction
... • For example a car rusting is slow; a matchstick burning is fast. • The reaction rate of a chemical reaction is the amount of reactant consumed per unit time or the amount of product formed per unit time. • It is the “speed” of the reaction. ...
... • For example a car rusting is slow; a matchstick burning is fast. • The reaction rate of a chemical reaction is the amount of reactant consumed per unit time or the amount of product formed per unit time. • It is the “speed” of the reaction. ...
Activity 14: Physical and Chemical Properties of Materials
... • A property is a quality or trait that characterizes a material or object. • Physical Properties can be determined without a chemical reaction. • Chemical Properties can only be determined by looking for a reaction. • Chemical Reaction is when a substance changes chemically into another substance. ...
... • A property is a quality or trait that characterizes a material or object. • Physical Properties can be determined without a chemical reaction. • Chemical Properties can only be determined by looking for a reaction. • Chemical Reaction is when a substance changes chemically into another substance. ...
CH 11 Chemical Reaction WS #2 (Pre
... 1. What is the Great Barrier Reef and how was it formed? 2. Define chemical reaction3. How is a chemical reaction different from a physical one? Provide examples to support your explanation. 4. Explain how the appearance of the Statue of Liberty is an example of a chemical reaction: 5. What are stal ...
... 1. What is the Great Barrier Reef and how was it formed? 2. Define chemical reaction3. How is a chemical reaction different from a physical one? Provide examples to support your explanation. 4. Explain how the appearance of the Statue of Liberty is an example of a chemical reaction: 5. What are stal ...
Chapter 2 Chemical Reactions
... Atoms can not be created or destroyed (Law of Conservation of Mass) A reaction can be described several ways: #1. In a sentence every item is a word Copper reacts with chlorine to form copper (II) chloride. ...
... Atoms can not be created or destroyed (Law of Conservation of Mass) A reaction can be described several ways: #1. In a sentence every item is a word Copper reacts with chlorine to form copper (II) chloride. ...