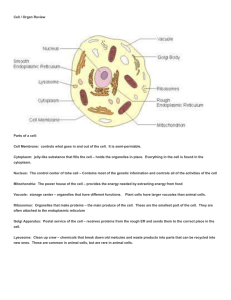
Cell / Organ Review Parts of a cell: Cell Membrane: controls what
... Cytoplasm: jelly-like substance that fills the cell – holds the organelles in place. Everything in the cell is found in the cytoplasm. Nucleus: The control center of tohe cell – Contains most of the genetic information and controls all of the activities of the cell Mitochondria: The power house of t ...
... Cytoplasm: jelly-like substance that fills the cell – holds the organelles in place. Everything in the cell is found in the cytoplasm. Nucleus: The control center of tohe cell – Contains most of the genetic information and controls all of the activities of the cell Mitochondria: The power house of t ...
Cell-Division
... Advantages of being multicellular: • allows organism to be larger • allows for cell differentiation • allows organism to be more complex. Becoming multi-cellular requires the development of specialised organ systems, limited to: • communication between cells (nervous system) • supplying the cells wi ...
... Advantages of being multicellular: • allows organism to be larger • allows for cell differentiation • allows organism to be more complex. Becoming multi-cellular requires the development of specialised organ systems, limited to: • communication between cells (nervous system) • supplying the cells wi ...
Cell Organelle Flashcards
... They supply energy for the cell by breaking down sugar into water and carbon dioxide. Some very active cells that require a lot of energy, like liver cells, may have more than 1000 mitochondria. ...
... They supply energy for the cell by breaking down sugar into water and carbon dioxide. Some very active cells that require a lot of energy, like liver cells, may have more than 1000 mitochondria. ...
Cell Division – Revision Pack (B3)
... Advantages of being multicellular: • allows organism to be larger • allows for cell differentiation • allows organism to be more complex. Becoming multi-cellular requires the development of specialised organ systems, limited to: • communication between cells (nervous system) • supplying the cells wi ...
... Advantages of being multicellular: • allows organism to be larger • allows for cell differentiation • allows organism to be more complex. Becoming multi-cellular requires the development of specialised organ systems, limited to: • communication between cells (nervous system) • supplying the cells wi ...
Cell Structure and Function
... • 1674 – Anton van Leeuwenhoek looked at cells in pond water and blood ...
... • 1674 – Anton van Leeuwenhoek looked at cells in pond water and blood ...
Cancer – Cells Out of Control!
... or they may become invasive and move into neighboring tissue. At some point a tumor may invade a blood vessel or lymph duct. If a cancerous cell from the tumor breaks away and travels to a different part of the body the tumor has metastasized. Once a tumor has gone through metastasis1 it is much mor ...
... or they may become invasive and move into neighboring tissue. At some point a tumor may invade a blood vessel or lymph duct. If a cancerous cell from the tumor breaks away and travels to a different part of the body the tumor has metastasized. Once a tumor has gone through metastasis1 it is much mor ...
Under what conditions do cells gain or lose water - kis
... 1. Did water move into the cell or out of the cell while it was surrounded by hypotonic solution? (think about each cell) ...
... 1. Did water move into the cell or out of the cell while it was surrounded by hypotonic solution? (think about each cell) ...
Eubacteria
... of the cell. Like the cell wall the cell membrane can also provide structure to the cell. mRNA: mRNA or messenger ribonucleic acid is a molecule of RNA that is like a blueprint for a protein product. mRNA is copied from a DNA template, and carries the copied coding information to the ribosome's to m ...
... of the cell. Like the cell wall the cell membrane can also provide structure to the cell. mRNA: mRNA or messenger ribonucleic acid is a molecule of RNA that is like a blueprint for a protein product. mRNA is copied from a DNA template, and carries the copied coding information to the ribosome's to m ...
Prokaryotic cell information - Mrs-Dow
... 2.2.4 State that prokaryotic cells divide by binary fission. Bacterial Reproduction Prokaryotes are much simpler in their organization than are eukaryotes. There are a great many more organelles in eukaryotes, as well as more chromosomes to be moved around during cell division. The typical method of ...
... 2.2.4 State that prokaryotic cells divide by binary fission. Bacterial Reproduction Prokaryotes are much simpler in their organization than are eukaryotes. There are a great many more organelles in eukaryotes, as well as more chromosomes to be moved around during cell division. The typical method of ...
CP Biology
... 65 substance made of only one type of atom that cannot be broken down by chemical means 67 The longest phase mitosis 70 Major biomolecule group that includes sugars and starches 73 The major portion of a ribosome 74 Two non-metals bonded together 75 A mistake in the genetic code 76 The protein that ...
... 65 substance made of only one type of atom that cannot be broken down by chemical means 67 The longest phase mitosis 70 Major biomolecule group that includes sugars and starches 73 The major portion of a ribosome 74 Two non-metals bonded together 75 A mistake in the genetic code 76 The protein that ...
Cells Get Sprayed - Wiley-VCH
... For example, genetically modified bacteria produce human insulin. In future, gene therapy should make it possible to introduce genes into the cells of a diseased organism so that they can address deficiencies to compensate for malfunctions in the body. In order for this to work, foreign (or syntheti ...
... For example, genetically modified bacteria produce human insulin. In future, gene therapy should make it possible to introduce genes into the cells of a diseased organism so that they can address deficiencies to compensate for malfunctions in the body. In order for this to work, foreign (or syntheti ...
OLD BIO Cell
... B. It is selectively permeable so only certain molecules can pass through it. C. It acts more like a fluid than a solid because its molecules are constantly moving. D. Cell membranes surround all animal, plant, and bacterial cells. E. It is a bilayer composed mainly of phospholipids and proteins Cel ...
... B. It is selectively permeable so only certain molecules can pass through it. C. It acts more like a fluid than a solid because its molecules are constantly moving. D. Cell membranes surround all animal, plant, and bacterial cells. E. It is a bilayer composed mainly of phospholipids and proteins Cel ...
Ch. 4 - Ltcconline.net
... 2. Explain why cell size and shape varies. 3. Explain why there are both upper and lower limit to cell size. 4. Distinguish between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. 5. Explain why compartmentalization is important in eukaryotic cells. 6. Compare the structures of plant and animal cells. 7. Describe ...
... 2. Explain why cell size and shape varies. 3. Explain why there are both upper and lower limit to cell size. 4. Distinguish between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. 5. Explain why compartmentalization is important in eukaryotic cells. 6. Compare the structures of plant and animal cells. 7. Describe ...
Cellular Transport – Active Transport Cells Review Questions
... __________________________________ are maintained at a ___________________________________ inside the cell, and ______________________ are maintained at ________________________________________________ inside the cell _________________________________ by protein molecules of the sodium and potassium ...
... __________________________________ are maintained at a ___________________________________ inside the cell, and ______________________ are maintained at ________________________________________________ inside the cell _________________________________ by protein molecules of the sodium and potassium ...
2.1 Organisms – Further questions and answers Q1. Bk Ch2 S2.1
... The microscope was not invented until the 17th century. Until then there was no instrument available to magnify objects as small as cells. Because cells are too small to be seen with the naked eye, biologists were not able to view or describe them. Q3. Bk Ch2 S2.1 FQ3 Study the diagram of the follow ...
... The microscope was not invented until the 17th century. Until then there was no instrument available to magnify objects as small as cells. Because cells are too small to be seen with the naked eye, biologists were not able to view or describe them. Q3. Bk Ch2 S2.1 FQ3 Study the diagram of the follow ...
Gundry Rachel Gundry Bio Lab 1615 April 3, 2012 Summary of
... destruction is the most unknown and scientists still have a lot to learn about this and the role it plays in our system. The second section in the article talks about cancer and what it is and how it happens. Cells go through many cycles of growth, division, and destruction, all of which help to mai ...
... destruction is the most unknown and scientists still have a lot to learn about this and the role it plays in our system. The second section in the article talks about cancer and what it is and how it happens. Cells go through many cycles of growth, division, and destruction, all of which help to mai ...
Lesson 3.1– CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION
... Lesson 3.1– CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION (NB p. 106-108) Explain the cell cycle: It’s the cycle of growth, development and division that all living cells go through. Organize the information about the 2 main phases of the cell cycle. Interphase – longest phase, where cell grows, organelles and DNA a ...
... Lesson 3.1– CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION (NB p. 106-108) Explain the cell cycle: It’s the cycle of growth, development and division that all living cells go through. Organize the information about the 2 main phases of the cell cycle. Interphase – longest phase, where cell grows, organelles and DNA a ...
- cK-12
... 6. During diffusion, which way to molecules move? a) Molecules flow down the concentration gradient. b) Molecules flow against the concentration gradient. c) From an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration. d) none of the above 7. Which best describes an hypertonic solution? a) Th ...
... 6. During diffusion, which way to molecules move? a) Molecules flow down the concentration gradient. b) Molecules flow against the concentration gradient. c) From an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration. d) none of the above 7. Which best describes an hypertonic solution? a) Th ...