Lesson 1
... Inside the Basic Unit of Life A typical cell has numerous membrane-bound organelles, specialized structures that perform specific functions in the cell. ...
... Inside the Basic Unit of Life A typical cell has numerous membrane-bound organelles, specialized structures that perform specific functions in the cell. ...
Cells and Hereditary
... a microscope (there is that instrument again) he found microorganisms everywhere he looked! He found bacteria in the blood of sick animals and humans, much like the soured milk His work led to the first animal vaccination for cholera and anthrax and treatment of rabies in humans, amongst others! ...
... a microscope (there is that instrument again) he found microorganisms everywhere he looked! He found bacteria in the blood of sick animals and humans, much like the soured milk His work led to the first animal vaccination for cholera and anthrax and treatment of rabies in humans, amongst others! ...
Sample Cells
... With a sample capacity of 20 µL, this non-fluorescing fused silica cell is ideal for online monitoring of fluorescent samples. The cell maintains high sensitivity because it has a large aperture for collecting the excitation light to the sample and fluorescence emission from the sample. The flat sid ...
... With a sample capacity of 20 µL, this non-fluorescing fused silica cell is ideal for online monitoring of fluorescent samples. The cell maintains high sensitivity because it has a large aperture for collecting the excitation light to the sample and fluorescence emission from the sample. The flat sid ...
PPT
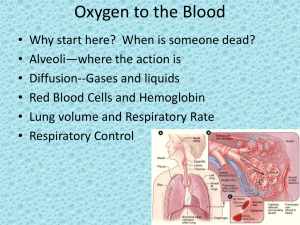
... movement from air (gas) into plasma (liquid) • Mass movement of oxygen into blood works because: – Differences in partial pressures are great – Distance is short – Oxygen is lipid soluble so it passes through membrane and coating (surfactant) – Surface area is huge—remember tennis court ...
... movement from air (gas) into plasma (liquid) • Mass movement of oxygen into blood works because: – Differences in partial pressures are great – Distance is short – Oxygen is lipid soluble so it passes through membrane and coating (surfactant) – Surface area is huge—remember tennis court ...
chpt6(H)syllabus
... Objectives 6-1: The student will be able to explain the main ideas of the cell theory. describe how microscopes aid the study of cells. compare and contrast plant and animal cells. distinguish between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Objectives 6-2: The student will be able to describe th ...
... Objectives 6-1: The student will be able to explain the main ideas of the cell theory. describe how microscopes aid the study of cells. compare and contrast plant and animal cells. distinguish between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Objectives 6-2: The student will be able to describe th ...
The Cell Theory and Membrane Transport
... Active Transport Movement against the concentration gradient. Molecules will move from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration. Requires energy in the form of ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) and protein pumps ...
... Active Transport Movement against the concentration gradient. Molecules will move from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration. Requires energy in the form of ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) and protein pumps ...
Cell Structure Get ready for a little friendly competition….
... ● Genetic material is a single circular molecule of DNA. ● Cell wall is made of polysaccharides connected by short chains of amino acids. ...
... ● Genetic material is a single circular molecule of DNA. ● Cell wall is made of polysaccharides connected by short chains of amino acids. ...
Endocrine System: Practice Questions #1
... Each arrow in the diagram represents a different hormone released by the pituitary gland that stimulates the gland indicated in the diagram. All structures are present in the same organism. ...
... Each arrow in the diagram represents a different hormone released by the pituitary gland that stimulates the gland indicated in the diagram. All structures are present in the same organism. ...
Microstructure Of The Digestive System II
... The function of the intercalated ducts transport of saliva to larger ducts, Primary saliva has the same ionic composition of blood isosmotic. The duct cells actively reabsorb sodium and excrete potassium hypotonic and has a higher concentration of potassium and a lower concentration of sodium ...
... The function of the intercalated ducts transport of saliva to larger ducts, Primary saliva has the same ionic composition of blood isosmotic. The duct cells actively reabsorb sodium and excrete potassium hypotonic and has a higher concentration of potassium and a lower concentration of sodium ...
Eukaryotic Cell - Teachnet UK-home
... •Robert Hooke was the first person to observe cells in 1665. •He looked at thin slices of cork under a very simple microscope. •The cork appeared as little boxes which he called cells. •In 1883 MathiasSchleiden and Theodor Schwann proposed that all plants and animals were composed of cells which wer ...
... •Robert Hooke was the first person to observe cells in 1665. •He looked at thin slices of cork under a very simple microscope. •The cork appeared as little boxes which he called cells. •In 1883 MathiasSchleiden and Theodor Schwann proposed that all plants and animals were composed of cells which wer ...
HOXA9 regulates expression of cancer stem cell markers and
... 服務單位:高雄醫學大學附設中和紀念醫院胃腸內科1 癌症中心2 高雄醫學大學藥學系3 高雄巿立小港醫院內科4 Background: Gastric cancer is one of the most common human cancers. According to Globocan 2000 estimates from World Health Organization (WHO), global gastric cancer incidence and mortality are 950,319 and 714,452 respectively. Nowadays, a growing ...
... 服務單位:高雄醫學大學附設中和紀念醫院胃腸內科1 癌症中心2 高雄醫學大學藥學系3 高雄巿立小港醫院內科4 Background: Gastric cancer is one of the most common human cancers. According to Globocan 2000 estimates from World Health Organization (WHO), global gastric cancer incidence and mortality are 950,319 and 714,452 respectively. Nowadays, a growing ...
Development and Apoptosis
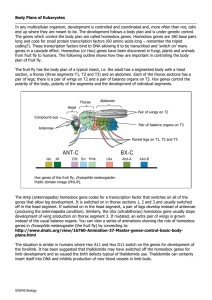
... Body Plans of Eukaryotes In any multicellular organism, development is controlled and coordinated and, more often than not, cells end up where they are meant to be. The development follows a body plan and is under genetic control. The genes which control the body plan are called homeobox genes. Home ...
... Body Plans of Eukaryotes In any multicellular organism, development is controlled and coordinated and, more often than not, cells end up where they are meant to be. The development follows a body plan and is under genetic control. The genes which control the body plan are called homeobox genes. Home ...
Studying gene expression at the level of the single cell
... cells are responsible for the observed phenotypic heterogeneity [2]. Since these pioneering studies, much more was learned about the sources of variability in gene expression between cells and its phenotypic consequences, from bacteria to mammalian cells. Stochasticity in gene expression is not the ...
... cells are responsible for the observed phenotypic heterogeneity [2]. Since these pioneering studies, much more was learned about the sources of variability in gene expression between cells and its phenotypic consequences, from bacteria to mammalian cells. Stochasticity in gene expression is not the ...
AB Biology Summer Assignment (Word)
... 43) Name the two types of vascular tissue found in plants, as well as what they transport. ...
... 43) Name the two types of vascular tissue found in plants, as well as what they transport. ...
Biology Quiz Review – Science 8 Introduction to Cells, Tissues
... 3. When do organisms grow? Organisms grow when they eat more food than their body needs for energy. Their body then may change its form by increasing in size, weight or shape. 4. Where do plants get energy? Animals? Plants get energy from the sun (photosynthesis) and animals get energy from eating ...
... 3. When do organisms grow? Organisms grow when they eat more food than their body needs for energy. Their body then may change its form by increasing in size, weight or shape. 4. Where do plants get energy? Animals? Plants get energy from the sun (photosynthesis) and animals get energy from eating ...
Animal Body System Fill in Notes
... _____________ Group of Cells working together ____________ Group of tissues working together ____________ Group of organs working together Cell Types and Tissue ____________ are specialized for their specific function. Tissues are groups of cells that perform a specific function. Muscle ...
... _____________ Group of Cells working together ____________ Group of tissues working together ____________ Group of organs working together Cell Types and Tissue ____________ are specialized for their specific function. Tissues are groups of cells that perform a specific function. Muscle ...
Motor Neuron - tekkieoldteacher
... • Node of ranvier are the gaps formed between the schwann cell generated by different cells. • Telodendria is the terminal branches of an axon; makes contact with other neurons at synapsesa neural junction used for communication between neurons. • Axonal terminal conducts electrical impulses away fr ...
... • Node of ranvier are the gaps formed between the schwann cell generated by different cells. • Telodendria is the terminal branches of an axon; makes contact with other neurons at synapsesa neural junction used for communication between neurons. • Axonal terminal conducts electrical impulses away fr ...
10AB_grade_1st_quarter
... f. Small particles made up of rRNA and protein molecules which produce proteins g. Filled with enzymes used to break down food into particles that can be used ...
... f. Small particles made up of rRNA and protein molecules which produce proteins g. Filled with enzymes used to break down food into particles that can be used ...
Cell Organelle Flip Book Assignment: Create a flip book of different
... relate structure to function for the components of plant and animal cells. explain the role of cell membranes as a highly selective barrier (passive and active transport). ...
... relate structure to function for the components of plant and animal cells. explain the role of cell membranes as a highly selective barrier (passive and active transport). ...
Name____________________________
... circulatory, digestive, and nervous systems (from chart/outline). See outline on the next page for all body systems. _______________________________________________________________ Vocabulary ...
... circulatory, digestive, and nervous systems (from chart/outline). See outline on the next page for all body systems. _______________________________________________________________ Vocabulary ...
Inside a Cell - WJHS Team 7A
... Cells store water, sugar, and other materials, which they use to function. Cells must also store waste materials until they can be removed. Inside plant and fungus cells are sacs called vacuoles. Vacuoles are enclosed by a membrane and can hold water, waste, and other materials. Vacuoles function wi ...
... Cells store water, sugar, and other materials, which they use to function. Cells must also store waste materials until they can be removed. Inside plant and fungus cells are sacs called vacuoles. Vacuoles are enclosed by a membrane and can hold water, waste, and other materials. Vacuoles function wi ...
(Additional) Review for Animal Systems Test
... capsule. Solutes include glucose, salts, vitamins, nitrogen wastes, and any other substances small enough to pass through the capillary walls. Red blood cells, and proteins remain in the capillaries. The other materials diffuse into the Bowman’s capsule, and then flow into the convoluted tubule. Thi ...
... capsule. Solutes include glucose, salts, vitamins, nitrogen wastes, and any other substances small enough to pass through the capillary walls. Red blood cells, and proteins remain in the capillaries. The other materials diffuse into the Bowman’s capsule, and then flow into the convoluted tubule. Thi ...