The Case Of The Damaged Cell
... mitochondria is enclosed in a vesicle. The lysosmes bump into these vesicles and pour enzymes into them. Useful amino acids and fatty acids are returned to the cytoplasm and waste particles are removed from the cell. Lysosomes also digest food particles, and foreign invaders. The cell can make new o ...
... mitochondria is enclosed in a vesicle. The lysosmes bump into these vesicles and pour enzymes into them. Useful amino acids and fatty acids are returned to the cytoplasm and waste particles are removed from the cell. Lysosomes also digest food particles, and foreign invaders. The cell can make new o ...
1 Objectives Before doing this lab you should understand the
... formation of either gametes (in animals) or spores (in plants). These cells have half the chromosome number of the parent cell. You will study meiosis another day. Where does one find cells undergoing mitosis? Plants and animal differ in this respect. In higher plants the process of forming new cell ...
... formation of either gametes (in animals) or spores (in plants). These cells have half the chromosome number of the parent cell. You will study meiosis another day. Where does one find cells undergoing mitosis? Plants and animal differ in this respect. In higher plants the process of forming new cell ...
CLASS NOTES
... Bowman’s capsule – cup-shaped structure that contains the glomerulus Blood entering the kidney goes through the glomerulus where small molecules such as water, amino acids, salts, glucose, electrolytes, and urea are pushed out of the capillaries into the Bowman’s capsule Urea – a waste product ...
... Bowman’s capsule – cup-shaped structure that contains the glomerulus Blood entering the kidney goes through the glomerulus where small molecules such as water, amino acids, salts, glucose, electrolytes, and urea are pushed out of the capillaries into the Bowman’s capsule Urea – a waste product ...
Cell Analogy Project
... This project will help to develop your understanding of the relationship between the cell’s structure and its function. You will be creating analogies for each of the organelles within the cell. You will also design and construct a cereal box display. This will illustrate the organelles of a typical ...
... This project will help to develop your understanding of the relationship between the cell’s structure and its function. You will be creating analogies for each of the organelles within the cell. You will also design and construct a cereal box display. This will illustrate the organelles of a typical ...
Lab 12
... In mitosis, a cell divides to give two daughter cells, essentially identical to the parent cell. Mitosis results in an equal distribution of hereditary material and usually an equal distribution of the cell contents. All of us began life as single cells. These cells divided by mitosis to become 2, t ...
... In mitosis, a cell divides to give two daughter cells, essentially identical to the parent cell. Mitosis results in an equal distribution of hereditary material and usually an equal distribution of the cell contents. All of us began life as single cells. These cells divided by mitosis to become 2, t ...
Cell Cycle Check
... 9. What is a meristmatic region? Where can you fine one? 10. Compare and contrast DNA in a prokaryotic and a eukaryotic cell. ...
... 9. What is a meristmatic region? Where can you fine one? 10. Compare and contrast DNA in a prokaryotic and a eukaryotic cell. ...
The Excretory System
... waste of cellular metabolism are removed Excretory organs regulate the chemical makeup of blood and other body fluids Helps maintain stable body temperature Excretion is not elimination ...
... waste of cellular metabolism are removed Excretory organs regulate the chemical makeup of blood and other body fluids Helps maintain stable body temperature Excretion is not elimination ...
Human Excretory System
... on the surface of the skin. •This mixture of wastes and water is excreted by perspiration (sweat). •Perspiration functions primarily to regulate body temperature. •Evaporation of sweat cools the body and is another example of how the body maintains homeostasis. Mrs. Degl ...
... on the surface of the skin. •This mixture of wastes and water is excreted by perspiration (sweat). •Perspiration functions primarily to regulate body temperature. •Evaporation of sweat cools the body and is another example of how the body maintains homeostasis. Mrs. Degl ...
Cells: How their discovery led to the cell theory
... Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things. The cells of multicellular organisms are specialized and perform many ...
... Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things. The cells of multicellular organisms are specialized and perform many ...
Organ Systems Overview Rat Dissection and Observation
... Now you will have a chance to observe the size, shape, location, and distribution of some organs and their organ systems. Many of the external and internal structures of the rat are quite similar in structure and function to those of the human. Note that four of the organ systems will not be studied ...
... Now you will have a chance to observe the size, shape, location, and distribution of some organs and their organ systems. Many of the external and internal structures of the rat are quite similar in structure and function to those of the human. Note that four of the organ systems will not be studied ...
No Slide Title
... • No nuclear membrane • No membrane bound organelles • Cell wall • Single loop of DNA ...
... • No nuclear membrane • No membrane bound organelles • Cell wall • Single loop of DNA ...
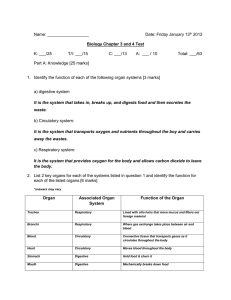
Name: Date: Friday January 13th 2012 Biology Chapter 3 and 4 Test
... 1. Describe the path an apple takes as it goes through your digestive system [5 marks] Food enters the body through the mouth and exits through the anus. In between, it undergoes digestion (from the mouth to the stomach), absorption (from the stomach to the small intestines), and elimination (from t ...
... 1. Describe the path an apple takes as it goes through your digestive system [5 marks] Food enters the body through the mouth and exits through the anus. In between, it undergoes digestion (from the mouth to the stomach), absorption (from the stomach to the small intestines), and elimination (from t ...
Animal Cell - MindMeister
... 7)The rough E.R makes and packages proteins. -A restaurant makes and packages food. 2) The mitochondria is the power house of a cell. -Rough E.R= individual restaurants in food court -The food court is where people get energy while shopping.8)The smooth E.R. is used for storage -Mitochondria=Food Co ...
... 7)The rough E.R makes and packages proteins. -A restaurant makes and packages food. 2) The mitochondria is the power house of a cell. -Rough E.R= individual restaurants in food court -The food court is where people get energy while shopping.8)The smooth E.R. is used for storage -Mitochondria=Food Co ...
Chapter 2 Living Things-Looking Inside Cells
... food and other materials needed by the cell. Vacuoles can also store waste products. Lysosomes- Lysosomes are small, round structures containing chemicals that break down certain materials in the cell. Some chemicals break down large food particles into smaller ones. Lysosomes also break down old ...
... food and other materials needed by the cell. Vacuoles can also store waste products. Lysosomes- Lysosomes are small, round structures containing chemicals that break down certain materials in the cell. Some chemicals break down large food particles into smaller ones. Lysosomes also break down old ...
cell
... All cells have structures which work together to keep the cell alive. Because they cannot move around, plants need cell structures that help them to conserve water and make their own food. Animals don’t need these structures. Animal cells have to be more flexible to allow the animals to move around. ...
... All cells have structures which work together to keep the cell alive. Because they cannot move around, plants need cell structures that help them to conserve water and make their own food. Animals don’t need these structures. Animal cells have to be more flexible to allow the animals to move around. ...
SYSTEM FUNCTIONS MAIN ORGANS Skeletal Muscular Digestive
... 10. The muscular contractions that push food through the digestive system are called ________________________. 11. Physical and chemical digestion begin in the ______________. 12. The ___________________ connects the mouth with the stomach. 13. Small projections called ________________ line the smal ...
... 10. The muscular contractions that push food through the digestive system are called ________________________. 11. Physical and chemical digestion begin in the ______________. 12. The ___________________ connects the mouth with the stomach. 13. Small projections called ________________ line the smal ...
Directed Reading: Diversity of Cells
... ______24. How do eukaryotes compare in size to prokaryotes? a. Eukaryotes have more cells. b. They are about the same size. c. Eukaryotes are about 10 times smaller. d. Eukaryotes are about 10 times larger. ______25. What does a eukaryote have that a prokaryote does not? a. one or more cells b. cell ...
... ______24. How do eukaryotes compare in size to prokaryotes? a. Eukaryotes have more cells. b. They are about the same size. c. Eukaryotes are about 10 times smaller. d. Eukaryotes are about 10 times larger. ______25. What does a eukaryote have that a prokaryote does not? a. one or more cells b. cell ...
MYP Science 9 - cis myp science
... Structure: The cell surface membrane is made up of two layers of phospholipids and is embedded with proteins, such as receptors on the outer surface. Function: The cell membrane separates the contents of the cell from its external environment and regulates the movement of substances in to and out of ...
... Structure: The cell surface membrane is made up of two layers of phospholipids and is embedded with proteins, such as receptors on the outer surface. Function: The cell membrane separates the contents of the cell from its external environment and regulates the movement of substances in to and out of ...
SNL Feeder Cells - Cell Biolabs, Inc.
... Note: For best results begin culture of cells immediately upon receipt. If this is not possible, store at -80ºC until first culture. Store subsequent cultured cells long term in liquid nitrogen. ...
... Note: For best results begin culture of cells immediately upon receipt. If this is not possible, store at -80ºC until first culture. Store subsequent cultured cells long term in liquid nitrogen. ...
how cells reproduce
... 2. Oncogenes3. Carcinogenesis4. Mutations lead to the formation of many forms of cancer. F. Variations on Mitosis: 1. Binary Fission- ...
... 2. Oncogenes3. Carcinogenesis4. Mutations lead to the formation of many forms of cancer. F. Variations on Mitosis: 1. Binary Fission- ...
Name Date ______ Midterm.Review.Fill
... 1. The entire life of a cell from formation to division is called the cell cycle. 2. Entire cells divide to form exact copies of themselves during the process of cell division. 3. Most of a cell’s life is spent in the stage called interphase. During the last part of interphase, the cell’s DNA replic ...
... 1. The entire life of a cell from formation to division is called the cell cycle. 2. Entire cells divide to form exact copies of themselves during the process of cell division. 3. Most of a cell’s life is spent in the stage called interphase. During the last part of interphase, the cell’s DNA replic ...
Chapter 6 learning objectives
... 4. Distinguish between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. 5. Explain why there are both upper and lower limits to cell size. 6. Explain the advantages of compartmentalization in eukaryotic cells. The Nucleus and Ribosomes 7. Describe the structure and function of the nuclear envelope, including the r ...
... 4. Distinguish between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. 5. Explain why there are both upper and lower limits to cell size. 6. Explain the advantages of compartmentalization in eukaryotic cells. The Nucleus and Ribosomes 7. Describe the structure and function of the nuclear envelope, including the r ...
Chapter Six
... 4. Distinguish between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. 5. Explain why there are both upper and lower limits to cell size. 6. Explain the advantages of compartmentalization in eukaryotic cells. The Nucleus and Ribosomes 7. Describe the structure and function of the nuclear envelope, including the r ...
... 4. Distinguish between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. 5. Explain why there are both upper and lower limits to cell size. 6. Explain the advantages of compartmentalization in eukaryotic cells. The Nucleus and Ribosomes 7. Describe the structure and function of the nuclear envelope, including the r ...