
Chapter 3 Worksheets / pdf
... In the top left side of the Y shape below, write the characteristics of eukaryotic cells. In the top right side of the Y shape'below, write the characteristics of prokaryotic cells. At the bottom of the. Y shape below, write the characteristics that both , kinds of cells have in common. Then lightly ...
... In the top left side of the Y shape below, write the characteristics of eukaryotic cells. In the top right side of the Y shape'below, write the characteristics of prokaryotic cells. At the bottom of the. Y shape below, write the characteristics that both , kinds of cells have in common. Then lightly ...
Sci 14_Unit C_
... 1. Describe, in general terms, the exchange of matter by the digestive and circulatory systems, the functional relationship between the two systems and the need for a healthy diet and lifestyle • assess the nutrient components of prepared foods by reading labels, and evaluate a variety of popular di ...
... 1. Describe, in general terms, the exchange of matter by the digestive and circulatory systems, the functional relationship between the two systems and the need for a healthy diet and lifestyle • assess the nutrient components of prepared foods by reading labels, and evaluate a variety of popular di ...
Bloodborne Pathogens and Primate Material Blood and other
... persistence of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), HBV, and hepatitis C virus (HCV) within infected individuals in the U.S. population. There also is evidence of accidental transplantation of human tumor cells to healthy recipients which indicates that these cells are potentially hazardous to labora ...
... persistence of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), HBV, and hepatitis C virus (HCV) within infected individuals in the U.S. population. There also is evidence of accidental transplantation of human tumor cells to healthy recipients which indicates that these cells are potentially hazardous to labora ...
Chapter 1 Section 2 Eukaryotic Cells
... lipids- fats and cholesterol (don’t dissolve in water) Two layers of phospholipids Hydrophobic – water fearing Hydrophilic – water loving Control the movement of materials into and out of the cell ...
... lipids- fats and cholesterol (don’t dissolve in water) Two layers of phospholipids Hydrophobic – water fearing Hydrophilic – water loving Control the movement of materials into and out of the cell ...
active transport
... chemical signals that trigger changes in cell activities. The endocrine system is linked to the plasma membrane through the work of hormones. ...
... chemical signals that trigger changes in cell activities. The endocrine system is linked to the plasma membrane through the work of hormones. ...
Introduction to Microbiology
... Introduction to Microbiology Microbiology is the study of microorganisms, a large and diverse group of microscopic organisms which must be viewed with a microscope that exist as single cells or cell clusters; it also includes viruses, which are microscopic but not cellular . ...
... Introduction to Microbiology Microbiology is the study of microorganisms, a large and diverse group of microscopic organisms which must be viewed with a microscope that exist as single cells or cell clusters; it also includes viruses, which are microscopic but not cellular . ...
Six Grade Science Vocabulary
... concentration of white blood cells found in lymph nodes. A network of organs and tissues that collect the fluid that leaks from blood and returns it to blood vessels; includes lymph nodes, lymph vessels, and lymph; the place where certain white blood cells mature. A cell organelle that contains dige ...
... concentration of white blood cells found in lymph nodes. A network of organs and tissues that collect the fluid that leaks from blood and returns it to blood vessels; includes lymph nodes, lymph vessels, and lymph; the place where certain white blood cells mature. A cell organelle that contains dige ...
virtual lab review - Social Circle City Schools
... The “virtual cell” will allow you to get a close-up view of several organelles in 3-D! You will be able to choose certain organelles within the cell and manipulate them by zooming in on the organelle, rotating the image, and dissecting several organelles to view their contents. The intent of the act ...
... The “virtual cell” will allow you to get a close-up view of several organelles in 3-D! You will be able to choose certain organelles within the cell and manipulate them by zooming in on the organelle, rotating the image, and dissecting several organelles to view their contents. The intent of the act ...
Station 1: Cork cells
... Station 5: Muscle cell – smooth muscle This is a muscle cell. Remember that muscle is a tissue made up of several cells all working together. Muscle cells can come in three types: heart muscle, smooth muscle, and skeletal muscle. This is an example of smooth muscle. Smooth muscle is made of single, ...
... Station 5: Muscle cell – smooth muscle This is a muscle cell. Remember that muscle is a tissue made up of several cells all working together. Muscle cells can come in three types: heart muscle, smooth muscle, and skeletal muscle. This is an example of smooth muscle. Smooth muscle is made of single, ...
The Cell
... Function: breaks down nutrients to make energy for the cell. ATP is the energy source. *Why would muscle cells in your legs have more mitochondria than muscles in your abdomen? ...
... Function: breaks down nutrients to make energy for the cell. ATP is the energy source. *Why would muscle cells in your legs have more mitochondria than muscles in your abdomen? ...
PPT 1
... carbohydrate receptors on the cell surface membrane of intestinal epithelial cells. The second part enters the epithelial cells, causing chloride channels to open. • Chloride ions leave the cell and enter the lumen of the small intestine. This raises the water potential of the epithelial cell and lo ...
... carbohydrate receptors on the cell surface membrane of intestinal epithelial cells. The second part enters the epithelial cells, causing chloride channels to open. • Chloride ions leave the cell and enter the lumen of the small intestine. This raises the water potential of the epithelial cell and lo ...
Date - Pearland ISD
... 1. If the concentration of water molecules is greater outside the cell, the solution is called_______________________. 2. In a hypotonic solution, the pressure against the inside of the cell membrane will steadily increase or decrease (circle one). 3. What happens to the cell in the hypotonic soluti ...
... 1. If the concentration of water molecules is greater outside the cell, the solution is called_______________________. 2. In a hypotonic solution, the pressure against the inside of the cell membrane will steadily increase or decrease (circle one). 3. What happens to the cell in the hypotonic soluti ...
File
... molecules (such as glucose) across the cell membrane. Filtration: Because of ________________ pressure, molecules can be forced through membranes by the process of filtration. In the body, ______________ pressure is a type of pressure causing filtration. Where does this occur? Tonicity: A solution ...
... molecules (such as glucose) across the cell membrane. Filtration: Because of ________________ pressure, molecules can be forced through membranes by the process of filtration. In the body, ______________ pressure is a type of pressure causing filtration. Where does this occur? Tonicity: A solution ...
Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes)
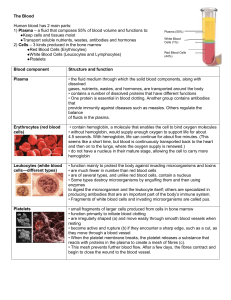
... The Blood Human blood has 2 main parts: 1) Plasma – a fluid that composes 55% of blood volume and functions to: ●Keep cells and tissues moist ●Transport soluble nutrients, wastes, antibodies and hormones 2) Cells – 3 kinds produced in the bone marrow ●Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes) ●White Blood Cell ...
... The Blood Human blood has 2 main parts: 1) Plasma – a fluid that composes 55% of blood volume and functions to: ●Keep cells and tissues moist ●Transport soluble nutrients, wastes, antibodies and hormones 2) Cells – 3 kinds produced in the bone marrow ●Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes) ●White Blood Cell ...
File - Classes with Mrs. Sheetz
... • Vascular plants: -use a system on interconnected tubes to transport water and nutrition -examples: trees, flowers, grasses, bushes, etc. Xylem: transport water & minerals from roots to rest of the plant ...
... • Vascular plants: -use a system on interconnected tubes to transport water and nutrition -examples: trees, flowers, grasses, bushes, etc. Xylem: transport water & minerals from roots to rest of the plant ...
Anatomy Ch 1
... The Nervous System • Function – Directing immediate responses to stimuli, usually by coordinating the activities of other organ systems • Organs – Central Nervous system • Brain • Spinal cord – Peripheral Nervous system ...
... The Nervous System • Function – Directing immediate responses to stimuli, usually by coordinating the activities of other organ systems • Organs – Central Nervous system • Brain • Spinal cord – Peripheral Nervous system ...
1.4 Energy Organelles, Plants and Animals
... nucleus, explain why. Write in complete sentences! Don’t talk during the Catalyst! ...
... nucleus, explain why. Write in complete sentences! Don’t talk during the Catalyst! ...
Cell Organelles
... OBJECTIVE: Students learn the purpose of organelles by researching their function and then use pieces of candy and a legend to visually represent both plant and animal cells. REVIEW: Students first are introduced to the purposes of organelles in both plant and animal cells either through classroom l ...
... OBJECTIVE: Students learn the purpose of organelles by researching their function and then use pieces of candy and a legend to visually represent both plant and animal cells. REVIEW: Students first are introduced to the purposes of organelles in both plant and animal cells either through classroom l ...
Cell Prison analogy[1] - NylandBiology2012-2013
... Cell Membrane/Guards The Guards are like the cell membrane in the way that they control what goes in and what comes out of the prison just like the cell membrane controls goes in and out of the cell. This organelle is found in both the plant and animal cell. ...
... Cell Membrane/Guards The Guards are like the cell membrane in the way that they control what goes in and what comes out of the prison just like the cell membrane controls goes in and out of the cell. This organelle is found in both the plant and animal cell. ...
Document
... • The cytoskeleton, a component of structural functions, is critical to cell structure. • Cells have three types of filaments that are distinguishable by the diameter. • Actin filaments (microfilaments): 5-9 nm diameter with twisted strands. ...
... • The cytoskeleton, a component of structural functions, is critical to cell structure. • Cells have three types of filaments that are distinguishable by the diameter. • Actin filaments (microfilaments): 5-9 nm diameter with twisted strands. ...
3-1
... that contains a lesser concentration of solutes. This means that there is more water in the solution then in the RBC, so water will tend to move into the cell. This causes the cell to swell. This is known as ...
... that contains a lesser concentration of solutes. This means that there is more water in the solution then in the RBC, so water will tend to move into the cell. This causes the cell to swell. This is known as ...
cells
... skin. -Information goes to the brain. -brain sends signals to muscles, skin and blood vessels. - they all work together to help your body perform properly. this system consists of the brain, spinal cord and the nerves. Diet, exercise, drugs, injury, and disease can affect body systems and disrup ...
... skin. -Information goes to the brain. -brain sends signals to muscles, skin and blood vessels. - they all work together to help your body perform properly. this system consists of the brain, spinal cord and the nerves. Diet, exercise, drugs, injury, and disease can affect body systems and disrup ...
PDF
... morphogenesis in the mouse submandibular gland (SMG). They show that the inhibition of heparanase in organ culture decreases SMG branching and that the addition of FGF10, but not other FGFs, rescues branching. Heparanase, they report, releases FGF10 from the basement membrane, where it binds to perl ...
... morphogenesis in the mouse submandibular gland (SMG). They show that the inhibition of heparanase in organ culture decreases SMG branching and that the addition of FGF10, but not other FGFs, rescues branching. Heparanase, they report, releases FGF10 from the basement membrane, where it binds to perl ...
PDF
... morphogenesis in the mouse submandibular gland (SMG). They show that the inhibition of heparanase in organ culture decreases SMG branching and that the addition of FGF10, but not other FGFs, rescues branching. Heparanase, they report, releases FGF10 from the basement membrane, where it binds to perl ...
... morphogenesis in the mouse submandibular gland (SMG). They show that the inhibition of heparanase in organ culture decreases SMG branching and that the addition of FGF10, but not other FGFs, rescues branching. Heparanase, they report, releases FGF10 from the basement membrane, where it binds to perl ...

















![Cell Prison analogy[1] - NylandBiology2012-2013](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008094435_1-6b4378a352221e3c96a92815b0a77167-300x300.png)




