10-3 Regulating the Cell Cycle
... • a disorder in which some cells lose the ability to control their own growth • these cells divide uncontrollably resulting in a tumor – tumor – an abnormal growth of tissue, not necessarily cancerous ...
... • a disorder in which some cells lose the ability to control their own growth • these cells divide uncontrollably resulting in a tumor – tumor – an abnormal growth of tissue, not necessarily cancerous ...
cell practice - IHMC Public Cmaps (3)
... A) Firm protective part on the outside of cell membrane (found only in plants) B) center for energy C) green coloring found only in plants that helps plants make food Cytoplasm A) jellylike filling that holds parts in place B) control center C) center for energy Chromosomes A) Holds the information ...
... A) Firm protective part on the outside of cell membrane (found only in plants) B) center for energy C) green coloring found only in plants that helps plants make food Cytoplasm A) jellylike filling that holds parts in place B) control center C) center for energy Chromosomes A) Holds the information ...
Living Cells
... DISCUSSION OF ERROR Discuss any errors that occurred in this lab and how they could be fixed. ...
... DISCUSSION OF ERROR Discuss any errors that occurred in this lab and how they could be fixed. ...
Suggested Stimulation Conditions for
... response. Additionally, responses in cell lines are not always representative of cognate primary cells. ...
... response. Additionally, responses in cell lines are not always representative of cognate primary cells. ...
Foundry Design Kit
... Design flow – it is based on the usage of Cadence licensed software and ensures the library development within a short period of time. • Circuit and layout design (Cadence Virtuoso®); • Extraction of cell schemes from layout with RC-parameters (Cadence Assura); • Characterization of library cells (C ...
... Design flow – it is based on the usage of Cadence licensed software and ensures the library development within a short period of time. • Circuit and layout design (Cadence Virtuoso®); • Extraction of cell schemes from layout with RC-parameters (Cadence Assura); • Characterization of library cells (C ...
Macromolecules to Organelles to Cells
... a. Proteins on the surface and embedded in the cell membrane interact with “lipid bilayer” b. Membrane and proteins control what goes in and out of cell c. Proteins act like pores, channels, pumps and carriers d. Many enzymes in the cell membrane speed up chemical reactions e. Carbohydrate “antenna” ...
... a. Proteins on the surface and embedded in the cell membrane interact with “lipid bilayer” b. Membrane and proteins control what goes in and out of cell c. Proteins act like pores, channels, pumps and carriers d. Many enzymes in the cell membrane speed up chemical reactions e. Carbohydrate “antenna” ...
Study Guide - Issaquah Connect
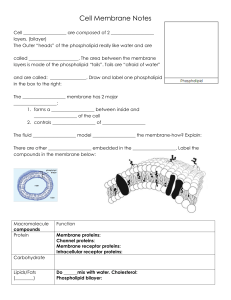
... A cell membrane has other types of molecules embedded in the phospholipid bilayer, List function of each type of molecule in the table below ...
... A cell membrane has other types of molecules embedded in the phospholipid bilayer, List function of each type of molecule in the table below ...
COMPARING CELLS 1: PROKARYOTES vs. EUKARYOTES
... In the Column 1, diagram a single bacterium (prokaryotic cell). Be sure to tell the total magnification, identify the cell, label the cell wall and cytoplasm, and indicate the size of the cell. In Column 2, diagram a single celled Protist (eukaryotic cell). Be sure to tell the total magnification, i ...
... In the Column 1, diagram a single bacterium (prokaryotic cell). Be sure to tell the total magnification, identify the cell, label the cell wall and cytoplasm, and indicate the size of the cell. In Column 2, diagram a single celled Protist (eukaryotic cell). Be sure to tell the total magnification, i ...
7-2 Eukaryotic Cell Structure
... What analogy do your group come up with in order to help remember the function of your organelle? What is at least one other interesting fact about your organelle? ...
... What analogy do your group come up with in order to help remember the function of your organelle? What is at least one other interesting fact about your organelle? ...
Cells: Prokaryote vs Eukaryote
... cell wall: tougher middle layer cell membrane: delicate inner skin ...
... cell wall: tougher middle layer cell membrane: delicate inner skin ...
Cells Alive- Interactive Internet Lesson
... Part D: Plant Cell Model: You need to return to the “cell biology” link to access this page, or hit your back button. Click on “Cell Model”. Click on “take me to animation”. Scroll down and click on “plant cell”. Sketch the chloroplast For this model, you will need to click on the various parts of t ...
... Part D: Plant Cell Model: You need to return to the “cell biology” link to access this page, or hit your back button. Click on “Cell Model”. Click on “take me to animation”. Scroll down and click on “plant cell”. Sketch the chloroplast For this model, you will need to click on the various parts of t ...
Gas exchange
... Key features that make the villi great for exchanging solutes •Big surface area •Very thin layer of cells between blood and dissolved food in intestine (NOT “very thin CELL WALLS) ...
... Key features that make the villi great for exchanging solutes •Big surface area •Very thin layer of cells between blood and dissolved food in intestine (NOT “very thin CELL WALLS) ...
Characterization of a potential new drug in cancer therapy
... • To avoid these processes of being malignant, cells have an intrinsic balance mechanism o Controlled growth and proliferation o Tumour suppressors; cell –cycle arrest, repair, apoptosis ...
... • To avoid these processes of being malignant, cells have an intrinsic balance mechanism o Controlled growth and proliferation o Tumour suppressors; cell –cycle arrest, repair, apoptosis ...
A.P. Bio Chapter 4 Organization of the Cell review sheet
... Chapters 2 and 3 introduced you to the inorganic and organic materials that are critical to an understanding of the cell, the basic unit of life. In this chapter and those that follow, you will see how cells utilize these chemical materials. Because all cells come from preexisting cells, they have s ...
... Chapters 2 and 3 introduced you to the inorganic and organic materials that are critical to an understanding of the cell, the basic unit of life. In this chapter and those that follow, you will see how cells utilize these chemical materials. Because all cells come from preexisting cells, they have s ...
Cell Cycle part 2 - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... chromatids of each chromosome have separated, and the daughter chromosomes are moving to the ends of the cell as their kinetochore microtubules shorten. ...
... chromatids of each chromosome have separated, and the daughter chromosomes are moving to the ends of the cell as their kinetochore microtubules shorten. ...
Practice Exam 4 - IWS2.collin.edu
... b) The glomerulus is correctly described as the proximal end of the proximal convoluted tubule. c) Podocytes are the branching epithelial cells that line the parietal layer of the glomerular capsule. d) The nephron extends from the glomerulus to the collecting ducts. e) The macula densa releases ANP ...
... b) The glomerulus is correctly described as the proximal end of the proximal convoluted tubule. c) Podocytes are the branching epithelial cells that line the parietal layer of the glomerular capsule. d) The nephron extends from the glomerulus to the collecting ducts. e) The macula densa releases ANP ...
Cell Project - WordPress.com
... DNA is organized into structures called chromosomes. The nucleolus is often seen as a large dark spot in the nucleus of a cell. Surrounding the nucleus are two membranes that form a structure called the nuclear envelope. A ribosome is not surrounded by a membrane. Ribosomes are in a cells cytoplasm. ...
... DNA is organized into structures called chromosomes. The nucleolus is often seen as a large dark spot in the nucleus of a cell. Surrounding the nucleus are two membranes that form a structure called the nuclear envelope. A ribosome is not surrounded by a membrane. Ribosomes are in a cells cytoplasm. ...
cell/city project grading rubric
... not clearly represented or stated. -The information/images are organized in a manner that poorly reflects the organization of the cell/city. -The information is less legible and/or lacks direct association the function of cell/city -Less than 60% of the -76-85% of the organelles/cell components orga ...
... not clearly represented or stated. -The information/images are organized in a manner that poorly reflects the organization of the cell/city. -The information is less legible and/or lacks direct association the function of cell/city -Less than 60% of the -76-85% of the organelles/cell components orga ...
Organelles
... cellular proteins • Responds to signals and dictates kinds and amounts of proteins to be synthesized • Most cells are uninucleate • Red blood cells are anucleate • Skeletal muscle cells, bone destruction cells, and some liver cells are multinucleate • Contains 3 different regions: • Nuclear envelope ...
... cellular proteins • Responds to signals and dictates kinds and amounts of proteins to be synthesized • Most cells are uninucleate • Red blood cells are anucleate • Skeletal muscle cells, bone destruction cells, and some liver cells are multinucleate • Contains 3 different regions: • Nuclear envelope ...
File
... Golgi Bodies • Protein “packaging plant” or “shippers” • Coats proteins and other materials so they can move different location inside/outside of cell ...
... Golgi Bodies • Protein “packaging plant” or “shippers” • Coats proteins and other materials so they can move different location inside/outside of cell ...