* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Gas exchange
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
High-altitude adaptation in humans wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic resistance to malaria wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Regeneration in humans wikipedia , lookup
Organisms at high altitude wikipedia , lookup
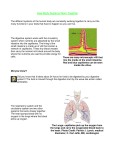
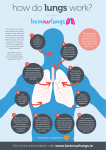
Starter Cells receive the substances they need by diffusion and osmosis Diffusion Oxygen in the blood Net movement is down the concentration gradient Oxygen in the cells Osmosis Water in the soil Net movement is down the concentration gradient Water inside a plant’s roots Obtaining and transporting the materials our bodies need / produce How are organ systems specialised for exchanging substances? How does surface area influence the exchange of food and oxygen? How has the use of artificial aids to breathing developed? How are organ systems specialised for exchanging substances? Which of these have blood, lungs, kidneys or digestive system? How are organ systems specialised for exchanging substances? Which of these have blood, lungs, kidneys or digestive system? As organisms get b…..er or more c……….. , it becomes harder to exchange substances with their surroundings Stretch; note down four of the main “substances” that need to be exchanged and what process each substance is involved in How are organ systems specialised for exchanging substances? Surfaces where gases or dissolved food (solutes) are exchanged are often specialised so exchange is maximised. How are organ systems specialised for exchanging substances? • Villi line the small intestine. Food in intestine How does food get into the blood? Food in intestine When you first start eating digested food diffuses across villi wall into the capillaries. (high to low) How does food get into the blood? Food in intestine When you first start eating digested food diffuses across villi wall into the capillaries. Concentration of food molecules in the blood increases Which of these villi would be better for exchanging solutes? Explain why would one be better? Key features that make the villi great for exchanging solutes •Big surface area •Very thin layer of cells between blood and dissolved food in intestine (NOT “very thin CELL WALLS) •Lots of capillaries to pick up dissolved food The breathing system windpipe Ribs Rib muscles Diaphragm Right Lung Left Lung The breathing system takes air into and out of the body so we can obtain oxygen and get rid of waste carbon dioxide trachea ribcage diaphragm thorax Inhalation (When we breathe out we exhale) Exhalation (When we breathe out we exhale) The Alveoli The air we inhale makes its way into thousands of tiny “air sacs” (alveoli) in the lungs. The outside of the alveoli is covered with capillaries (tiny blood vessels). Air rushes down the t………., through the airways of the lungs and ends up in the a…….… How are the lungs adapted for gas exchange? Each alveolus is surrounded by capillaries which pick up the …………. in each lungful of air you breathe in. The capillaries also bring carbon dioxide (CO2) from ………..cell in the body and let the CO2 out into your lungs so you can breathe it out. Which design would be better for the alveoli to exchange gases with the capillaries of the lungs •Big surface area •Very thin layer of cells •Lots of capillaries Suggest how the changes in the tadpole shown in the drawings help it to survive as it grows larger. You should not refer to movement in your answer. To gain full marks you should refer to structure X. How has the use of artificial aids to breathing developed? Iron Lung Modern Ventillator Draws air into the lung Pushes air into the lung http://www.youtube.com/watch?v= kM30mAEz5bA http://www.youtube.com/watc h?v=V8VIw0fk4X0 The blood now carries this oxygen to the cells of the body. Right Lung Left Lung Blood vessel O2 O2 Blood Body cells Cells Oxygen diffuses from the blood into the cells Carbon dioxide diffuses into the blood from the cells Blood coming from the lungs High concentration Low concentration Body cell Oxygen