* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download respiratory-system-revision-sheet
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
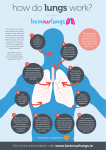
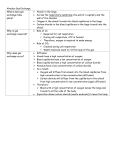
Topic 1.2.3: A HEALTHY, ACTIVE LIFESTYLE & YOUR RESPIRATORY SYSTEM The respiratory system Tidal volume Normal breathing in and out Lung capacity The total volume of air in your lungs after your biggest breath in Vital capacity The maximum you can forcibly breathe in and out The alveoli Small air sacs surrounded by capillaries where diffusion of oxygen and carbon dioxide take place Diffusion The movement of oxygen from the lungs to the capillaries (on cell thick) and carbon dioxide from the capillaries to the lungs to be breathed out Immediate effects Breathing quickens Breathing deepens Oxygen dept To increase the amount of oxygen taken into the lungs each breath To increase the removal of carbon dioxide The extra amount of oxygen required after anaerobic exercise, compared with the amount normally needed when at rest Increased tidal volume Long term effects All of these adaptations means more oxygen can be provided to the working muscles and therefore keep levels of performance of aerobic exercise high Improved efficiency of the lungs Which allows better delivery of oxygen to the working muscles Which means that the body will be able to cope with the demands of exercise Number of alveoli increases This means more oxygen can be absorbed by the capillaries and more carbon dioxide can be taken from them This increases VO2 max – the maximum of oxygen you can take in per minute Capillarisation There is an increase in the number of blood vessels around the alveoli So more oxygen can be absorbed in the blood and be delivered to the working muscles (becomes more efficient) Increased vital capacity Increased lung volume Due to increased tidal volume and vital capacity The effects of Smoking Potential diseases Bronchitis, Emphysema, Lung cancer Damages alveoli The walls break down so less oxygen can be diffused into the capillaries each breath (uptake not intake) Increases blood pressure Effects on exercise Less oxygen uptake means less oxygen to the working muscles therefore less energy made. This means the performer becomes tired and unable to perform to a high ability