* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Respiratory system - simonbaruchcurriculum
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Organisms at high altitude wikipedia , lookup
Gaseous signaling molecules wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic resistance to malaria wikipedia , lookup
Regeneration in humans wikipedia , lookup
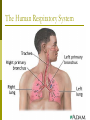
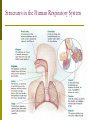
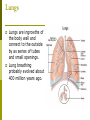
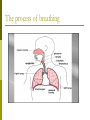
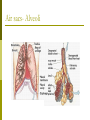
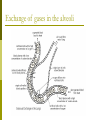
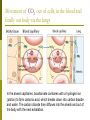
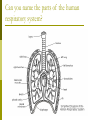
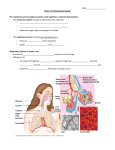
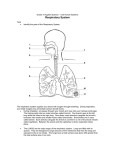
Why do we have a respiratory system? 1. Movement of an oxygen-containing medium (air) so it contacts a moist membrane overlying blood vessels. (ie the role of Breathing) 2. Diffusion of oxygen from the medium into the blood. (ie the role of alveoli) Transport of oxygen to the tissues and cells of the body. (ie the role of the red blood cells in the arteries) 3. 4. Diffusion of oxygen from the blood into cells. (ie the role red blood cells in the capillary beds) 5. Carbon dioxide follows a reverse path. (ie the role of the red blood cells/Plasma in the veins) The Human Respiratory System Structures in the Human Respiratory System Lungs Lungs are ingrowths of the body wall and connect to the outside by as series of tubes and small openings. Lung breathing probably evolved about 400 million years ago. Gas exchange in the Lungs The diaphragm is the muscle that controls the breathing process. As the diaphragm flattens it causes the chest to expand and air is sucked into the lungs. When the diaphragm relaxes, the chest collapses and the air in the lungs is forced out. Control of Respiration Muscular contraction and relaxation controls the rate of expansion and constriction of the lungs. These muscles are stimulated by nerves that carry messages from the part of the brain that controls breathing, the medulla. Two systems control breathing: an automatic response and a voluntary response. The process of breathing The figures in Breathing Gas exchange occurs in the alveolus where the thin laminar blood flow and inspired air are separated only by a thin tissue layer. Gas exchange takes 0.25 seconds or 1/3 of the total transit time of a red cell. The entire blood volume of the body passes through the lungs each minute in the resting state, that is 5 liters per minute. The total surface area of the lung is about 80 meters square, equivalent to the size of a tennis court. Air sacs- Alveoli Exchange of gases in the alveoli Movement of CO2 out of cells, in the blood and finally out body via the lungs In the alveoli capillaries, bicarbonate combines with a hydrogen ion (proton) to form carbonic acid, which breaks down into carbon dioxide and water. The carbon dioxide then diffuses into the alveoli and out of the body with the next exhalation. Can you name the parts of the human respiratory system? Lung disorders Respiratory quiz