* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PP-Alveolar gas exchange Notes
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
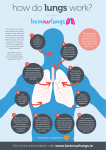
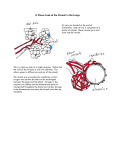
Alveolar Gas Exchange Where does gas exchange take place? Why is gas exchange required? Why does gas exchange occur? Alveoli in the lungs Across the respiratory membrane-the wall of a capillary and the wall of the alveolus Oxygen in the alveoli travels into blood capillaries in the lungs Carbon dioxide in the blood capillaries in the lungs travels into the alveoli Role of O2 Required for cell respiration During cell respiration, ATP is formed Therefore, oxygen is required to make energy Role of CO2 Created during cell respiration Waste molecule-need to rid the body of the gas Diffusion: Alveoli have a high concentration of oxygen Blood capillaries have a low concentration of oxygen Blood capillaries have a high concentration of carbon dioxide Alveolus have a low concentration of carbon dioxide As a result: Oxygen will diffuse from alveoli into the blood capillaries from high concentration to low concentration (diffusion) Carbon dioxide will diffuse from the capillaries to the alveoli from high concentration to low concentration (again diffusion) Therefore: Blood with a high concentration of oxygen leaves the lungs and travels to all the cells of the body Expiration allows carbon dioxide (waste molecule) to leave the body