Science Fast Facts Cells Animal and plant cells are very similar, ex
... Prokaryotes are the simplest cells. Prokaryotes do not have a nucleus with a membrane or any membrane-bound organelles such as mitochondria. Prokaryotes have DNA floating in the cytoplasm of the cell and reproduce asexually through fission. Eukaryotes are more advanced and all organisms such as pla ...
... Prokaryotes are the simplest cells. Prokaryotes do not have a nucleus with a membrane or any membrane-bound organelles such as mitochondria. Prokaryotes have DNA floating in the cytoplasm of the cell and reproduce asexually through fission. Eukaryotes are more advanced and all organisms such as pla ...
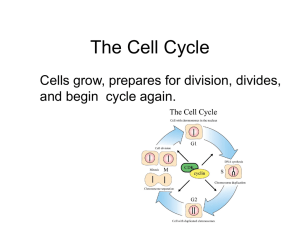
Stages of the cell cycle
... The Cell Cycle Cells grow, prepares for division, divides, and begin cycle again. ...
... The Cell Cycle Cells grow, prepares for division, divides, and begin cycle again. ...
Ch 4 quiz - TESADVBiology
... ____ 14.The nucleus of a cell contains all of the following EXCEPT a.chromosomes. b. mitochondria. c. DNA. d. RNA. ____ 15.Which type of molecule is found in the plasma membrane? a. carbohydrate b. protein c. phospholipid d. All of the above ____ 16.The lipid bilayer of the plasma membrane a.provide ...
... ____ 14.The nucleus of a cell contains all of the following EXCEPT a.chromosomes. b. mitochondria. c. DNA. d. RNA. ____ 15.Which type of molecule is found in the plasma membrane? a. carbohydrate b. protein c. phospholipid d. All of the above ____ 16.The lipid bilayer of the plasma membrane a.provide ...
Title Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α dependent cytoplasmic B7
... B7-H4 expression and treatment of HIF-1 α inhibitor decreased its expression. Furthermore, using B7-H4 promoter-luciferase construct, we found that B7-H4 promoter activity was greatly enhanced under hypoxia compared to normoxia. To investigate the function of hypoxiainduced B7-H4, we used B7-H4 knoc ...
... B7-H4 expression and treatment of HIF-1 α inhibitor decreased its expression. Furthermore, using B7-H4 promoter-luciferase construct, we found that B7-H4 promoter activity was greatly enhanced under hypoxia compared to normoxia. To investigate the function of hypoxiainduced B7-H4, we used B7-H4 knoc ...
Mitosis and Meiosis Crossword
... 1 - These are not visible in the cell during interphase 3 - An Egg has 23 chromosomes. Is it haploid or diploid? 5 - This is when the cell breaks into two 8 - This term describes when genetic segments of information are swapped when the chromosomes are next to each other. 11 - Spindle fiber ...
... 1 - These are not visible in the cell during interphase 3 - An Egg has 23 chromosomes. Is it haploid or diploid? 5 - This is when the cell breaks into two 8 - This term describes when genetic segments of information are swapped when the chromosomes are next to each other. 11 - Spindle fiber ...
Prokaryotic Cells Eukaryotic Cells
... -‐Be able to label at least 10 organelles in a Eukaryotic cell -‐Know how eukaryotic cells obtain energy -‐Be able to compare and contrast Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells (size, age, complexity, struc ...
... -‐Be able to label at least 10 organelles in a Eukaryotic cell -‐Know how eukaryotic cells obtain energy -‐Be able to compare and contrast Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells (size, age, complexity, struc ...
The Inner Life of Cells
... • Multicellular organisms (ie: animals) are made of tissues composed of cells eg. blood, nerves, cartilage, muscle and bone are made up of cells • These cells perform all the functions required for life 3. New cells arise only from pre-existing cells. • Life depends on cells (cells divide and pass o ...
... • Multicellular organisms (ie: animals) are made of tissues composed of cells eg. blood, nerves, cartilage, muscle and bone are made up of cells • These cells perform all the functions required for life 3. New cells arise only from pre-existing cells. • Life depends on cells (cells divide and pass o ...
chapter 4 - Fullfrontalanatomy.com
... What Features Are Shared by All Cells? A. Cells Are Enclosed by a _____________ _______________ B. Cells Use ____________ as a Hereditary Blueprint C. Cells Contain Cytoplasm 1. Contains ___________, __________, and the proteins, __________, _____________________, ___________, ___________, amino aci ...
... What Features Are Shared by All Cells? A. Cells Are Enclosed by a _____________ _______________ B. Cells Use ____________ as a Hereditary Blueprint C. Cells Contain Cytoplasm 1. Contains ___________, __________, and the proteins, __________, _____________________, ___________, ___________, amino aci ...
Homeostasis and Cell Processes
... Homeostasis For your body to stay healthy cells must : 1. Obtain and use energy 2. Make new cells 3. Exchange material 4. Eliminate waste Homeostasis ensures that cells can carry out these tasks ...
... Homeostasis For your body to stay healthy cells must : 1. Obtain and use energy 2. Make new cells 3. Exchange material 4. Eliminate waste Homeostasis ensures that cells can carry out these tasks ...
Name - Humble ISD
... 1. Describe the structure of a “typical cell” 2. Describe the molecular structure and function of the plasma membrane. 3. Describe the structure and function of the following: endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, golgi apparatus, mitochondria, lysosomes, peroxisomes, cytoskeleton (cell fibers, centroso ...
... 1. Describe the structure of a “typical cell” 2. Describe the molecular structure and function of the plasma membrane. 3. Describe the structure and function of the following: endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, golgi apparatus, mitochondria, lysosomes, peroxisomes, cytoskeleton (cell fibers, centroso ...
Anton von Leeuwenhoek
... Parts of the animal cell and definition. Vacuole-cell storage sac for food,waste, and water Mitochondrion –produces energy in a cell Chromosomes-provides direction for cells to follow ...
... Parts of the animal cell and definition. Vacuole-cell storage sac for food,waste, and water Mitochondrion –produces energy in a cell Chromosomes-provides direction for cells to follow ...
Centrioles are self-replicating organelles made up
... Centrioles - Centrioles are self-replicating organelles made up of nine bundles of microtubules and are found only in animal cells. They appear to help in organizing cell division, but aren't essential to the process. Cilia and Flagella - For single-celled eukaryotes, cilia and flagella are essentia ...
... Centrioles - Centrioles are self-replicating organelles made up of nine bundles of microtubules and are found only in animal cells. They appear to help in organizing cell division, but aren't essential to the process. Cilia and Flagella - For single-celled eukaryotes, cilia and flagella are essentia ...
Basic Bio 3
... Respiration This is the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between an organism and its environment. Selective Permeability This is an ability of a plasma membrane to allow some substances to cross across the membrane more easily than others. System This is a group of interdependent organs with si ...
... Respiration This is the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between an organism and its environment. Selective Permeability This is an ability of a plasma membrane to allow some substances to cross across the membrane more easily than others. System This is a group of interdependent organs with si ...
TAKS Obj 2 -BIOLOGY
... Plant Cells have, and Animal Cells don’t • Chloroplasts – organelle responsible for photosynthesis • Cell Walls – a structure outside of the membrane to provide support • Very large vacuoles to store extra water ...
... Plant Cells have, and Animal Cells don’t • Chloroplasts – organelle responsible for photosynthesis • Cell Walls – a structure outside of the membrane to provide support • Very large vacuoles to store extra water ...
Animal Cell
... 2. _____ __________ Forms a boundary that separates the cell from its environment. It controls what comes in and out of the cell. In both plant and animal cells ...
... 2. _____ __________ Forms a boundary that separates the cell from its environment. It controls what comes in and out of the cell. In both plant and animal cells ...
Chapter 9 PowerPoint Lecture
... • In plant cells, the cell wall prevents the cell from being pinched in two. • Instead, a “cell plate” forms between the two nuclei. • Cellulose deposits begin to form at the cell plate, forming a crosswall that divides the parent cell into two daughter cells. ...
... • In plant cells, the cell wall prevents the cell from being pinched in two. • Instead, a “cell plate” forms between the two nuclei. • Cellulose deposits begin to form at the cell plate, forming a crosswall that divides the parent cell into two daughter cells. ...
Mitosis and Meiosis NCSCOS Objective 3.02 Chapter 8.2
... Meiosis is similar to mitosis. In meiosis there are two divisions and the resulting cells have one-half the number of chromosomes of the original cell. In meiosis crossing over or nondisjunction may occur resulting in genetic variation. ...
... Meiosis is similar to mitosis. In meiosis there are two divisions and the resulting cells have one-half the number of chromosomes of the original cell. In meiosis crossing over or nondisjunction may occur resulting in genetic variation. ...