A View of the Cell
... structures called organelles – Many are surrounded by membranes – Each has a specific function in the cell ...
... structures called organelles – Many are surrounded by membranes – Each has a specific function in the cell ...
Stem-Cell Treatments Enrichment LESSON 2
... the central nervous system could not repair itself. Damage to this human body system was thought to be permanent. New research, however, has opened the door to treating injuries and diseases of the central nervous system. Some of this research focuses on embryonic stem (ES) cells. ...
... the central nervous system could not repair itself. Damage to this human body system was thought to be permanent. New research, however, has opened the door to treating injuries and diseases of the central nervous system. Some of this research focuses on embryonic stem (ES) cells. ...
Cell division and mitosis
... Shortest phase of mitosis Centrioles are at poles Chromosomes line up in the middle along equator Spindle fibers attach to chromosomes on the centromere ...
... Shortest phase of mitosis Centrioles are at poles Chromosomes line up in the middle along equator Spindle fibers attach to chromosomes on the centromere ...
Nociceptin mediated microvascular inflammation during sepsis
... predictor of disease outcome in head and neck cancer than that of the cancer cells themselves. The stroma is composed of a number of cell types, including fibroblasts, endothelial cells, immune cells and neurones. Communication between these cells by secreted factors is known to be a key factor in d ...
... predictor of disease outcome in head and neck cancer than that of the cancer cells themselves. The stroma is composed of a number of cell types, including fibroblasts, endothelial cells, immune cells and neurones. Communication between these cells by secreted factors is known to be a key factor in d ...
CELLS
... •Eukaryotic chromosomal DNA in the nucleus is wound on nucleosome cores whereas prokaryotic DNA is “naked”—i.e., there are no nucleosomes or other proteins on which the DNA is wound. •Most eukaryotic cells are diploid, receiving a set of chromosomes from each parent. Thus their chromosomes occur in ...
... •Eukaryotic chromosomal DNA in the nucleus is wound on nucleosome cores whereas prokaryotic DNA is “naked”—i.e., there are no nucleosomes or other proteins on which the DNA is wound. •Most eukaryotic cells are diploid, receiving a set of chromosomes from each parent. Thus their chromosomes occur in ...
Facilitated Diffusion - BellevilleBiology.com
... 6. Of the cells that moved the dye…Did they move the dye in or out? 7. If active transport was used to move the dye, out via what mechanism did the dye get in? ...
... 6. Of the cells that moved the dye…Did they move the dye in or out? 7. If active transport was used to move the dye, out via what mechanism did the dye get in? ...
Regulation of the Cell Cycle / Cancer
... • Mutated proto-oncogenes are called oncogenes are tumor-promoting • Oncogenes are found in most cancer cells found in malignant tumors • Tumor-suppressing genes help keep cancers from developing in two ways: 1. Preventing cell division until DNA is repaired 2. Cell suicide ...
... • Mutated proto-oncogenes are called oncogenes are tumor-promoting • Oncogenes are found in most cancer cells found in malignant tumors • Tumor-suppressing genes help keep cancers from developing in two ways: 1. Preventing cell division until DNA is repaired 2. Cell suicide ...
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Guiding Questions: What are the
... Characteristics of Eukaryotic Cells (eukaryotes) ...
... Characteristics of Eukaryotic Cells (eukaryotes) ...
The Cell
... All living things are made up of cells. 2. __________________________________________________________ All cells come from pre-existing cells. 3. __________________________________________________________ ...
... All living things are made up of cells. 2. __________________________________________________________ All cells come from pre-existing cells. 3. __________________________________________________________ ...
IHS-9.1_The Structure outline_JM
... Nucleolus – inside of the nucleus, important in cell reproduction. RNA & proteins are mfg. in the nucleolus Chromatin – in the nucleus & makes DNA deoxyribonucleic acid. The chromatin condenses to form a rod-like structure called chromosomes. The human has 46 or 23 pairs. Chromosomes contain about 1 ...
... Nucleolus – inside of the nucleus, important in cell reproduction. RNA & proteins are mfg. in the nucleolus Chromatin – in the nucleus & makes DNA deoxyribonucleic acid. The chromatin condenses to form a rod-like structure called chromosomes. The human has 46 or 23 pairs. Chromosomes contain about 1 ...
ANSWERS Cell Part or Organelle Is It Found In An Animal Cell? Is It
... Cell Membrane Cell Wall Chloroplast Lysosome Vacuole nucleus Cytoplasm mitochondrion Golgi Bodies Nuclear Membrane Nucleolus Ribosome ...
... Cell Membrane Cell Wall Chloroplast Lysosome Vacuole nucleus Cytoplasm mitochondrion Golgi Bodies Nuclear Membrane Nucleolus Ribosome ...
01 - TeacherWeb
... a. a group of cells that work together to perform a specific job b. a group of tissues that belong to different systems c. a group of tissues that work together to perform a specific job d. a body structure, such as muscles or lungs _____ 8. The benefits of being multicellular include a. small size, ...
... a. a group of cells that work together to perform a specific job b. a group of tissues that belong to different systems c. a group of tissues that work together to perform a specific job d. a body structure, such as muscles or lungs _____ 8. The benefits of being multicellular include a. small size, ...
Cell Junctions - LincolnLions.org
... movement by detecting changes and responding with nerve impulses. Ex: Brain and spinal cord ...
... movement by detecting changes and responding with nerve impulses. Ex: Brain and spinal cord ...
cell cycle and mitosis powerpoint 2015
... • The chromosomes continue to move until they are in two groups • Each side has own copy of DNA ...
... • The chromosomes continue to move until they are in two groups • Each side has own copy of DNA ...
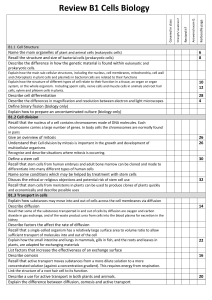
GCSE Cells Topic Learning Checklist
... Explain how to prepare an uncontaminated culture (biology only) B1.2 Cell division Recall that the nucleus of a cell contains chromosomes made of DNA molecules. Each ...
... Explain how to prepare an uncontaminated culture (biology only) B1.2 Cell division Recall that the nucleus of a cell contains chromosomes made of DNA molecules. Each ...
8th grade Review TOPIC: Characteristics of Life Do Now: What is the
... Notes: (found on Ms. Harris’s Carey website) ...
... Notes: (found on Ms. Harris’s Carey website) ...
Cell
... A structure made up of different kinds of TISSUES that all work together to perform the same JOB. ...
... A structure made up of different kinds of TISSUES that all work together to perform the same JOB. ...