* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Cell
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
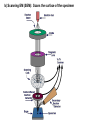
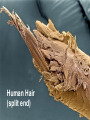
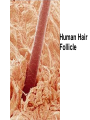
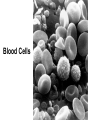
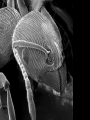
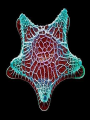
The Cell I. Cell Theory A. Famous Scientists 1. Anton von Leeuwenhoek (1665): A Dutch businessman who used the microscope to examine the quality of the cloth he traded. a) He was the first person to see microorganisms in a drop _______________________ of water. _______________________ b) He called them ____________ animalcules. I. Cell Theory A. Famous Scientists 1. Robert Hooke (1674): An English physicist who used the microscope to look at a thin slice of cork. cork is a) He discovered that _____________ made of many small chambers. ____________________________ cells after b) He called them ________ monastery rooms. ________________________ c) Hooke’s work inspired other scientists to search for cells elsewhere. 3. Mathias Schleiden (1823): A German botonist – plant specialist. all plants are a) He discovered that _____________ made up of cells. ____________________________ 4. Theodore Schwann (1839): Another German scientist all animals are a) He discovered that _____________ Sideburns made up of cells. ____________________________ Not to be confused with… cells cells 5. Rudolf Virchow (1855): A German physicist who realized that all cells come from pre-existing cells. B. The discoveries made by these scientists led to the formation of the cell theory: The cell is the basic unit of structure and function in living things. 1. __________________________________________________________ All living things are made up of cells. 2. __________________________________________________________ All cells come from pre-existing cells. 3. __________________________________________________________ Exceptions… II. Microscopy light microscope was invented in the 1600s and A. The ________________ opened a whole new world to biologists. B. Magnification: How much larger an object appears C. Resolving Power (resolution): Measure of clarity/detail of an image Ex. What appears to be one star, may actually be two stars when viewed with a high-resolution telescope. D. Light Microscope (LM) 1. Produce image by focusing light on specimen. 2. Resolution is limited by wavelength of visible light a) LMs can resolve objects ≥ 0.2 µm (micrometer… 10-6meter) b) Clear magnification up to 1,000X 3. Dead or live specimens 4. Various dyes can be used to improve visibility a) Lugol’s Iodine solution – stains starch in plant cells b) Methylene Blue – stains animal cells Light Microscope Parts Body Tube Revolving Nosepiece Eyepiece (Ocular Lens) Arm Objective Lens Stage Stage Clips Diaphragm Light Source Coarse Adjustment Fine Adjustment Base E. Electron Microscope (EM) 1. Uses electromagnets to focus a beam of electrons on/through a specimen. 2. Much shorter wavelength than visible light: a) Higher magnification b) Resolve objects ≥ 0.1 nm (nanometer… 10-9meter) First EM was built by Ernst Ruska & Max Knoll at Berlin Tech in the late 1920’s Vladimir Zworykin (seated) & James Hillier Demonstrate an early electron microscope. This model stood 10 feet high and weighed half a ton! 3. Two types of Electron Microscopes: a) Transmission EM (TEM): Aims electron beam through a thin section of the specimen b) Scanning EM (SEM): Scans the surface of the specimen Cilia in rabbit trachea Table Salt Human Hair (split end) Human Hair Follicle Blood Cells Pollen Fly’s Eye Spinnerets Of a spider Diatoms