Study Guide - Honors Chemistry
... one nucleus is broken into multiple (2 in this case) nuclei by force (an alpha particle is used to break it up) one nucleus is broken into multiple (2 in this case) nuclei on its own. No force is needed. one nucleus is transformed into another nucleus by bombarding a particle into it. A particle may ...
... one nucleus is broken into multiple (2 in this case) nuclei by force (an alpha particle is used to break it up) one nucleus is broken into multiple (2 in this case) nuclei on its own. No force is needed. one nucleus is transformed into another nucleus by bombarding a particle into it. A particle may ...
Isotopes and Ions - Wando High School
... Ions IONS are charged atoms (or groups of atoms) that have a ...
... Ions IONS are charged atoms (or groups of atoms) that have a ...
Salesian High School Elements and atoms Chemistry quiz The
... Most of the alpha particles bounced back Most of the alpha particles went right through the gold foil The electrons bent towards the positive charge Alpha particles are positive and heavy ...
... Most of the alpha particles bounced back Most of the alpha particles went right through the gold foil The electrons bent towards the positive charge Alpha particles are positive and heavy ...
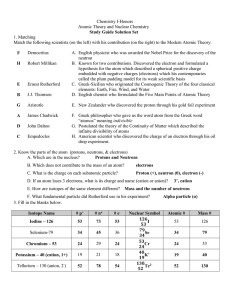
Exemplar exam question – Chapter 2
... The first answer is probably worthy of only 1 mark as it does not make clear that isotopes are different atoms of the same element. The second answer would probably score 0. Although the idea of the same element and different number of neutrons is mentioned, the student has not mentioned different a ...
... The first answer is probably worthy of only 1 mark as it does not make clear that isotopes are different atoms of the same element. The second answer would probably score 0. Although the idea of the same element and different number of neutrons is mentioned, the student has not mentioned different a ...
Measurement of the half-life of
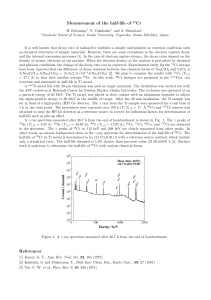
... It is well known that decay rate of radioactive nuclides is usually independent on external conditions such as chemical structures of sample materials. However, there are some exceptions in the electron capture decay and the internal conversion processes [1]. In the case of electron capture decays, ...
... It is well known that decay rate of radioactive nuclides is usually independent on external conditions such as chemical structures of sample materials. However, there are some exceptions in the electron capture decay and the internal conversion processes [1]. In the case of electron capture decays, ...
Intro to Atoms Clicker Questions 1. "atomos" means? 2. Atoms of one
... 2. Atoms of one kind of element _______ be changed into a different element with ordinary chemical means. (can, can’t) 3. Every compound is composed of atoms of different elements combined how? 4. In Thompson's model of the atom, the negatively charged electrons were located how in the atom? 5. In R ...
... 2. Atoms of one kind of element _______ be changed into a different element with ordinary chemical means. (can, can’t) 3. Every compound is composed of atoms of different elements combined how? 4. In Thompson's model of the atom, the negatively charged electrons were located how in the atom? 5. In R ...
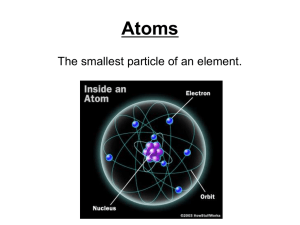
Classifying Atoms
... appears on pages 698–699 of the Appendix. Of the more than 100 known elements listed there, 92 occur naturally on Earth in significant amounts. The rest are synthetic elements produced by scientists. In each row of the periodic table, elements are listed from left to right in order of increasing num ...
... appears on pages 698–699 of the Appendix. Of the more than 100 known elements listed there, 92 occur naturally on Earth in significant amounts. The rest are synthetic elements produced by scientists. In each row of the periodic table, elements are listed from left to right in order of increasing num ...
1 - cloudfront.net
... 13. Why did J. J. Thomson reason that electrons must be a part of the atoms of all elements? 14. Know characteristics regarding the nucleus of an atom. 15. Describe the model of the atom as a result of Rutherford’s discovery of the nucleus. 16. The smallest particle of an element that retains the pr ...
... 13. Why did J. J. Thomson reason that electrons must be a part of the atoms of all elements? 14. Know characteristics regarding the nucleus of an atom. 15. Describe the model of the atom as a result of Rutherford’s discovery of the nucleus. 16. The smallest particle of an element that retains the pr ...
NOTES: 2.1 - Intro to Chemistry
... ATOM: smallest unit of matter that retains the physical and chemical properties of its element ● three subatomic particles: ...
... ATOM: smallest unit of matter that retains the physical and chemical properties of its element ● three subatomic particles: ...
PS 2.2
... the weighted average of the masses of the naturally occurring isotopes of an element. The atomic mass of an element can be found on the periodic table. Since it is an average, it is usually not a whole number. ...
... the weighted average of the masses of the naturally occurring isotopes of an element. The atomic mass of an element can be found on the periodic table. Since it is an average, it is usually not a whole number. ...
Lesson 13 - Highline Public Schools
... weighted average of the masses of the isotopes in a sample of the element. The most common isotope of an element, frequently has a mass that is close to the average atomic mass given in the periodic table. ...
... weighted average of the masses of the isotopes in a sample of the element. The most common isotope of an element, frequently has a mass that is close to the average atomic mass given in the periodic table. ...
Chapter 4 Study Guide Physical Science 1. The word atom comes
... 2. Halogens are very reactive elements located in Group _______of the periodic table. 3. The nucleus of an atom has a(n) ____________________ electric charge. 4. Carbon is found in group ______ of the periodic table. 5. Bohr’s model of the atom compares electrons to ____________________. 6. Elements ...
... 2. Halogens are very reactive elements located in Group _______of the periodic table. 3. The nucleus of an atom has a(n) ____________________ electric charge. 4. Carbon is found in group ______ of the periodic table. 5. Bohr’s model of the atom compares electrons to ____________________. 6. Elements ...
Chapter 3 Chemical Foundations
... Atomic Number, Mass Number, and Nucleus atomic number (Z) = mass number (A) = element symbol (X) = Note: mass number= Therefore …. mass number = ……. A= Z + number of neutrons ….. Number of neutrons = A-Z Note: For any given element on the periodic table: Number of protons = In order to symbolically ...
... Atomic Number, Mass Number, and Nucleus atomic number (Z) = mass number (A) = element symbol (X) = Note: mass number= Therefore …. mass number = ……. A= Z + number of neutrons ….. Number of neutrons = A-Z Note: For any given element on the periodic table: Number of protons = In order to symbolically ...
File
... nucleus of an atom. (The number of protons in the nucleus is the atomic number, which determines the identity of an element.) neutron: a subatomic particle that has no charge and that is located in the nucleus of an atom. electron: a subatomic particle that has a negative charge. element: a substanc ...
... nucleus of an atom. (The number of protons in the nucleus is the atomic number, which determines the identity of an element.) neutron: a subatomic particle that has no charge and that is located in the nucleus of an atom. electron: a subatomic particle that has a negative charge. element: a substanc ...
Atomic Structure
... •Isotope is the same element with different number of ________________________ therefore, the mass number will be different for the same element. All atoms of an element are considered an isotope, some are more common than others. •Ion is same element with a different number of __________________. A ...
... •Isotope is the same element with different number of ________________________ therefore, the mass number will be different for the same element. All atoms of an element are considered an isotope, some are more common than others. •Ion is same element with a different number of __________________. A ...
Chap 7: Around the Room Review
... 3. The atomic number tells us __________. 4. Nitrogen’s atomic number is 7. An isotope of nitrogen containing 7 neutrons would be nitrogen_____. 5. How does the size of a negative ion compare to the size of the atom that formed it? 6. The modern periodic table is organized by _____. 7. Elements in a ...
... 3. The atomic number tells us __________. 4. Nitrogen’s atomic number is 7. An isotope of nitrogen containing 7 neutrons would be nitrogen_____. 5. How does the size of a negative ion compare to the size of the atom that formed it? 6. The modern periodic table is organized by _____. 7. Elements in a ...
Notes
... -the number of protons and neutrons in an atom of an element. •The number of neutrons may vary, but the proton number remains constant. •Written as a subscript next to the element’s symbol ...
... -the number of protons and neutrons in an atom of an element. •The number of neutrons may vary, but the proton number remains constant. •Written as a subscript next to the element’s symbol ...
Chapter 6 Review“The Periodic Table”
... Review“The Periodic Table” 1. How is the number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom calculated? 2. All atoms are neutral, with the number of protons equaling the ___. 3. Isotopes of the same element have different _____. 4. Using the periodic table, determine the number of neutrons in 16O. 5. What ...
... Review“The Periodic Table” 1. How is the number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom calculated? 2. All atoms are neutral, with the number of protons equaling the ___. 3. Isotopes of the same element have different _____. 4. Using the periodic table, determine the number of neutrons in 16O. 5. What ...
atomic number - Thomas C. Cario Middle School
... The periodic table is a chart containing information about the atoms that make up all matter. An element is a substance made up of only one type of atom. The atomic number of an atom is equal to the number of protons in its nucleus. The number of electrons surrounding the nucleus of an atom is equal ...
... The periodic table is a chart containing information about the atoms that make up all matter. An element is a substance made up of only one type of atom. The atomic number of an atom is equal to the number of protons in its nucleus. The number of electrons surrounding the nucleus of an atom is equal ...
IPC Atoms and Periodic Table
... The elements located I the far right column of the Group 18; their outermost energy level is holding the maximum number of electrons possible; stable. ...
... The elements located I the far right column of the Group 18; their outermost energy level is holding the maximum number of electrons possible; stable. ...
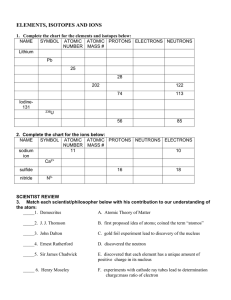
ELEMENTS, ISOTOPES AND IONS
... 1. Complete the chart for the elements and isotopes below: NAME SYMBOL ATOMIC ATOMIC PROTONS ELECTRONS NEUTRONS NUMBER MASS # ...
... 1. Complete the chart for the elements and isotopes below: NAME SYMBOL ATOMIC ATOMIC PROTONS ELECTRONS NEUTRONS NUMBER MASS # ...
Lawrencium

Lawrencium is a synthetic chemical element with chemical symbol Lr (formerly Lw) and atomic number 103. It is named in honor of Ernest Lawrence, inventor of the cyclotron, a device that was used to discover many artificial radioactive elements. A radioactive metal, lawrencium is the eleventh transuranic element and is also the final member of the actinide series. Like all elements with atomic number over 100, lawrencium can only be produced in particle accelerators by bombarding lighter elements with charged particles. Twelve isotopes of lawrencium are currently known; the most stable is 266Lr with a half-life of 11 hours, but the shorter-lived 260Lr (half-life 2.7 minutes) is most commonly used in chemistry because it can be produced on a larger scale.Chemistry experiments have confirmed that lawrencium indeed behaves as a heavier homolog to lutetium in the periodic table, and is a trivalent element. It thus could also be classified as the first of the 7th-period transition metals: however, its electron configuration is anomalous for its position in the periodic table, having an s2p configuration instead of the s2d configuration of its homolog lutetium. This means that lawrencium may be less volatile than expected for its position in the periodic table and have a volatility comparable to that of lead.In the 1950s, 1960s, and 1970s, many claims of the synthesis of lawrencium of varying quality were made from laboratories in the Soviet Union and the United States. The priority of the discovery and therefore the naming of the element was disputed between Soviet and American scientists, and while the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) established lawrencium as the official name for the element and gave the American team credit for the discovery, this was reevaluated in 1997, giving both teams shared credit for the discovery but not changing the element's name.