Topic 2.1 The Nuclear Atom
... • this is NOT IB material until indicated • it is very interesting from a geeky-science stand point • it will help you understand and appreciate the structure of the atom • you are not responsible for knowing the information from all thescientists ...
... • this is NOT IB material until indicated • it is very interesting from a geeky-science stand point • it will help you understand and appreciate the structure of the atom • you are not responsible for knowing the information from all thescientists ...
levels of organization and the atom
... atoms are protons, neutrons, and electrons. Strong forces bind protons and neutrons together to form the nucleus, which is at the center of the atom. Here is the atom’s mass. Protons and neutrons have the same mass, 1 atomic mass unit (amu). However, protons are positively charged particles (+) and ...
... atoms are protons, neutrons, and electrons. Strong forces bind protons and neutrons together to form the nucleus, which is at the center of the atom. Here is the atom’s mass. Protons and neutrons have the same mass, 1 atomic mass unit (amu). However, protons are positively charged particles (+) and ...
Atoms - ChemistryatBiotech
... Atoms can lose or gain electrons when bonding to make ionic compounds We keep track of the number of electrons that can be lost or gained with oxidation numbers (also known as charges) Ions are charged particles –when an atom has too many or too few electrons to be neutral No change to the nucleus ...
... Atoms can lose or gain electrons when bonding to make ionic compounds We keep track of the number of electrons that can be lost or gained with oxidation numbers (also known as charges) Ions are charged particles –when an atom has too many or too few electrons to be neutral No change to the nucleus ...
The Basics of Atomic Structure
... Protons + Neutrons (total number of particles in the nucleus) • Atomic mass: the average mass of all known isotopes of the element ...
... Protons + Neutrons (total number of particles in the nucleus) • Atomic mass: the average mass of all known isotopes of the element ...
Lecture 2 - U of L Class Index
... An element is defined by its atomic number. Changing the number of protons in an atom (as in a nuclear reaction) changes the element. While atoms of the same element must have the same atomic number, they may have different mass numbers. If so, they are referred to as isotopes. Most elements have mo ...
... An element is defined by its atomic number. Changing the number of protons in an atom (as in a nuclear reaction) changes the element. While atoms of the same element must have the same atomic number, they may have different mass numbers. If so, they are referred to as isotopes. Most elements have mo ...
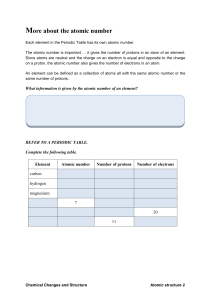
14 more about the atomic number
... Each element in the Periodic Table has its own atomic number. The atomic number is important it gives the number of protons in an atom of an element. Since atoms are neutral and the charge on an electron is equal and opposite to the charge on a proton, the atomic number also gives the number of elec ...
... Each element in the Periodic Table has its own atomic number. The atomic number is important it gives the number of protons in an atom of an element. Since atoms are neutral and the charge on an electron is equal and opposite to the charge on a proton, the atomic number also gives the number of elec ...
Document
... An industrially important element contains 26 electrons and rusts in the presence of air and moisture. Identify the element. ...
... An industrially important element contains 26 electrons and rusts in the presence of air and moisture. Identify the element. ...
and the atomic
... • this is NOT IB material until Rutherford • it is very interesting from a geeky-science stand point • it will help you understand and appreciate the structure of the atom • you are not responsible for knowing the information from all thescientists ...
... • this is NOT IB material until Rutherford • it is very interesting from a geeky-science stand point • it will help you understand and appreciate the structure of the atom • you are not responsible for knowing the information from all thescientists ...
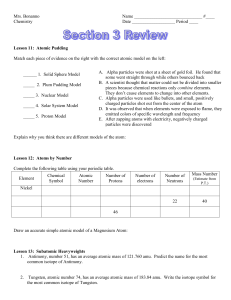
TEST II Study Guide-Atomic Theory Honors Chemistry
... 2. _____________ Using the line spectrum of the hydrogen atom and his knowledge of quantum theory and physics, this scientist proposed an atomic model where electrons orbit the nucleus like planets orbit the sun. 3. Describe the general experiment and their importance from the following scientists: ...
... 2. _____________ Using the line spectrum of the hydrogen atom and his knowledge of quantum theory and physics, this scientist proposed an atomic model where electrons orbit the nucleus like planets orbit the sun. 3. Describe the general experiment and their importance from the following scientists: ...
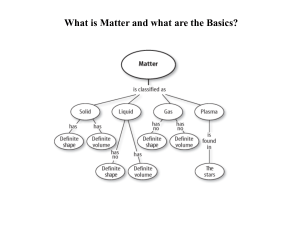
Matter and the Periodic Table
... system of rows and columns on the basis of increasing mass and similar chemical and physical properties. Since the organization exhibited a periodic repetition of similar properties, it became known as the Periodic Table of the Elements. It has become one of modern chemistry's ...
... system of rows and columns on the basis of increasing mass and similar chemical and physical properties. Since the organization exhibited a periodic repetition of similar properties, it became known as the Periodic Table of the Elements. It has become one of modern chemistry's ...
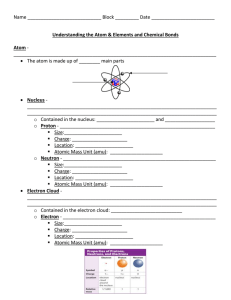
Understanding the Atom GN
... When atoms of the same element have different numbers of neutrons they are called ____________________. Isotope – ________________________________________________________________________ Most elements have ______________________ isotopes. Mass Number - ________________________________________ ...
... When atoms of the same element have different numbers of neutrons they are called ____________________. Isotope – ________________________________________________________________________ Most elements have ______________________ isotopes. Mass Number - ________________________________________ ...
MrsB-Chemistry
... B. A scientist thought that matter could not be divided into smaller pieces because chemical reactions only combine elements. They don’t cause elements to change into other elements. C. Alpha particles were used like bullets, and small, positively charged particles shot out from the center of the at ...
... B. A scientist thought that matter could not be divided into smaller pieces because chemical reactions only combine elements. They don’t cause elements to change into other elements. C. Alpha particles were used like bullets, and small, positively charged particles shot out from the center of the at ...
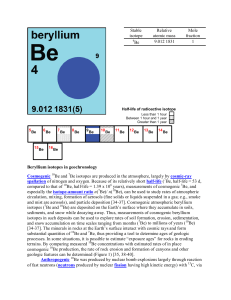
Beryllium isotopes in geochronology Cosmogenic Be and Be
... rocks at three sites on the Level 2 terrace in upper Holtwood Gorge, Pennsylvania, approximately 50 km upstream of Chesapeake Bay [38]. ...
... rocks at three sites on the Level 2 terrace in upper Holtwood Gorge, Pennsylvania, approximately 50 km upstream of Chesapeake Bay [38]. ...
Stable isotope Relative atomic mass Mole fraction Os 183.952 489
... atomic number (Z) – The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. beta decay (β-decay) – radioactive decay process resulting in emission of a beta particle of either positive or negative charge (an electron or positron). [return] electron – elementary particle of matter with a negative electric c ...
... atomic number (Z) – The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. beta decay (β-decay) – radioactive decay process resulting in emission of a beta particle of either positive or negative charge (an electron or positron). [return] electron – elementary particle of matter with a negative electric c ...
Atomic Structure
... b. Credited with the discovery of the neutron c. Credited with the discovery of the electron and the “plum pudding” model of the atom. d. Used the now famous “gold foil” experiment to prove the existence of the nucleus. He also showed most of an atom is empty space! e. Credited with the “planetary” ...
... b. Credited with the discovery of the neutron c. Credited with the discovery of the electron and the “plum pudding” model of the atom. d. Used the now famous “gold foil” experiment to prove the existence of the nucleus. He also showed most of an atom is empty space! e. Credited with the “planetary” ...
What is the history of chemistry and elements
... 2. What is the structure of an atom? 3. How are ions formed from atoms? History 2400 year ago Greek philosophers proposed that everything was made of four basic substances – air, water, fire, and earth. Today chemists know that there are 100+ basic substances, or elements. Everything on Earth ...
... 2. What is the structure of an atom? 3. How are ions formed from atoms? History 2400 year ago Greek philosophers proposed that everything was made of four basic substances – air, water, fire, and earth. Today chemists know that there are 100+ basic substances, or elements. Everything on Earth ...
Atomic Structure: SOL Review #1 Name: Historical Developments 1
... all things made of tiny particles solid sphere model; Atomic Theory: all elements made of atoms, atoms of an element are identical cathode ray tube; discovered electron; plum pudding model oil drop; discovered mass and charge of electron gold foil; discovered nucleus; the atom is mostly empty space ...
... all things made of tiny particles solid sphere model; Atomic Theory: all elements made of atoms, atoms of an element are identical cathode ray tube; discovered electron; plum pudding model oil drop; discovered mass and charge of electron gold foil; discovered nucleus; the atom is mostly empty space ...
Chemistry Midterm Exam 2015 (Study Guide) Unit 1: Measurement
... In the measurement 0.202 L, which digit is the estimated digit? The last 2 How many significant figures are in the measurement 0.0027 kg? 2 How many significant figures are in the measurement 480,500 mg? 4 Express the sum of 7.68 m and 5.0 m using the correct number of significant digits. 12.7 Expre ...
... In the measurement 0.202 L, which digit is the estimated digit? The last 2 How many significant figures are in the measurement 0.0027 kg? 2 How many significant figures are in the measurement 480,500 mg? 4 Express the sum of 7.68 m and 5.0 m using the correct number of significant digits. 12.7 Expre ...
Atomic Structure
... 4 parts of Dalton’s theory: 1. All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms. 2. Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. 3. Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can chemically c ...
... 4 parts of Dalton’s theory: 1. All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms. 2. Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. 3. Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can chemically c ...
Lawrencium

Lawrencium is a synthetic chemical element with chemical symbol Lr (formerly Lw) and atomic number 103. It is named in honor of Ernest Lawrence, inventor of the cyclotron, a device that was used to discover many artificial radioactive elements. A radioactive metal, lawrencium is the eleventh transuranic element and is also the final member of the actinide series. Like all elements with atomic number over 100, lawrencium can only be produced in particle accelerators by bombarding lighter elements with charged particles. Twelve isotopes of lawrencium are currently known; the most stable is 266Lr with a half-life of 11 hours, but the shorter-lived 260Lr (half-life 2.7 minutes) is most commonly used in chemistry because it can be produced on a larger scale.Chemistry experiments have confirmed that lawrencium indeed behaves as a heavier homolog to lutetium in the periodic table, and is a trivalent element. It thus could also be classified as the first of the 7th-period transition metals: however, its electron configuration is anomalous for its position in the periodic table, having an s2p configuration instead of the s2d configuration of its homolog lutetium. This means that lawrencium may be less volatile than expected for its position in the periodic table and have a volatility comparable to that of lead.In the 1950s, 1960s, and 1970s, many claims of the synthesis of lawrencium of varying quality were made from laboratories in the Soviet Union and the United States. The priority of the discovery and therefore the naming of the element was disputed between Soviet and American scientists, and while the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) established lawrencium as the official name for the element and gave the American team credit for the discovery, this was reevaluated in 1997, giving both teams shared credit for the discovery but not changing the element's name.