Questions - World Book Online
... In 490 B.C. who did Sparta and Greece unite against in war? Why did they unite? What was the outcome of the Persian Wars? Why did Sparta and Greece begin fighting each other in 431 B.C? Who won the Peloponnesian War? Who was Alexander the Great? What was the most powerful part of the Greek army? Who ...
... In 490 B.C. who did Sparta and Greece unite against in war? Why did they unite? What was the outcome of the Persian Wars? Why did Sparta and Greece begin fighting each other in 431 B.C? Who won the Peloponnesian War? Who was Alexander the Great? What was the most powerful part of the Greek army? Who ...
Ancient Greece
... the most famous surviving building of Ancient Greece and one of the most famous buildings in the world. The building has stood atop the Acropolis of Athens for nearly 2,500 years and was built to give thanks to Athena, the city's patron goddess, for the salvation of Athens and Greece in the Persian ...
... the most famous surviving building of Ancient Greece and one of the most famous buildings in the world. The building has stood atop the Acropolis of Athens for nearly 2,500 years and was built to give thanks to Athena, the city's patron goddess, for the salvation of Athens and Greece in the Persian ...
The Geography of Greece
... made up of small plains and river valleys surrounded by high mountains. The mountains influenced Greek history, because they separated Greeks from each other. This caused different Greek communities to develop their own ways of life. The small size of these communities encouraged people to be involv ...
... made up of small plains and river valleys surrounded by high mountains. The mountains influenced Greek history, because they separated Greeks from each other. This caused different Greek communities to develop their own ways of life. The small size of these communities encouraged people to be involv ...
The Classical Age of Greece
... Culture • The unique way of life in ancient Greece encouraged creativity and excellence in all pursuits. • From fierce athletic competitions to boldly ambitious education programs, the Greeks aimed for the best in all things. • In this atmosphere, literature flourished. ...
... Culture • The unique way of life in ancient Greece encouraged creativity and excellence in all pursuits. • From fierce athletic competitions to boldly ambitious education programs, the Greeks aimed for the best in all things. • In this atmosphere, literature flourished. ...
Greeks - DuVall School News
... fight the Athenians. These were called the Peloponnesian Wars, and they lasted from 431 - 404 BC. The Spartans won and became the ruling city-state of Greece for a short time. ...
... fight the Athenians. These were called the Peloponnesian Wars, and they lasted from 431 - 404 BC. The Spartans won and became the ruling city-state of Greece for a short time. ...
Greece PPT 2012 - Mr. Mac`s Wikispace!!
... tiny civilizations are known as the Greek Polis’ or City States. ** Greeks civilizations referred to as tribes, orders or Fraternities. ...
... tiny civilizations are known as the Greek Polis’ or City States. ** Greeks civilizations referred to as tribes, orders or Fraternities. ...
Greece Geography study notes
... In Athenian democracy, only free men born in Athens could vote. Women, slaves, and foreigners could not vote. ...
... In Athenian democracy, only free men born in Athens could vote. Women, slaves, and foreigners could not vote. ...
Lesson 1: Early Civilizations of the Aegean Sea
... he was to return dead being carried on his shield. Lesson 5: War tests the Greeks ...
... he was to return dead being carried on his shield. Lesson 5: War tests the Greeks ...
Chapter 4 Study Guide Athens – focused on government and
... Age of Pericles – age of great creativity and learning in Athens Satraps – “defenders of the kingdom” and Persian States Tyrant – rules with total authority Cyrus the Great – King of Persia Hopl ...
... Age of Pericles – age of great creativity and learning in Athens Satraps – “defenders of the kingdom” and Persian States Tyrant – rules with total authority Cyrus the Great – King of Persia Hopl ...
chapter 4 sg - Mr. Vakselis LA/SS Blog
... Age of Pericles – age of great creativity and learning in Athens Satraps – “defenders of the kingdom” and Persian States Tyrant – rules with total authority Cyrus the Great – King of Persia Hoplites – ordinary citizens in the army Parthenon – Workers hauled 20,000 tons of marble and took 15 years to ...
... Age of Pericles – age of great creativity and learning in Athens Satraps – “defenders of the kingdom” and Persian States Tyrant – rules with total authority Cyrus the Great – King of Persia Hoplites – ordinary citizens in the army Parthenon – Workers hauled 20,000 tons of marble and took 15 years to ...
Achievements of Ancient Greece
... achievements and reason why these achievements are so important to our lives today. Government/Law The Greeks developed small, separate communities of people, called “city-states”. Each city-state made their own rules and had their own ruler. As city-states grew in population, citizens demanded a vo ...
... achievements and reason why these achievements are so important to our lives today. Government/Law The Greeks developed small, separate communities of people, called “city-states”. Each city-state made their own rules and had their own ruler. As city-states grew in population, citizens demanded a vo ...
Ancient Greece (Athens vs Sparta)
... According to Buddhist principles, believers can end personal suffering by ...
... According to Buddhist principles, believers can end personal suffering by ...
CHAPTER 5: ANCIENT GREECE
... • Conquered Greece and Crete • They were sea traders • Passed on Egyptian & Mesopotamian influences to later Greeks. • Developed numerous city-states in Greece. ...
... • Conquered Greece and Crete • They were sea traders • Passed on Egyptian & Mesopotamian influences to later Greeks. • Developed numerous city-states in Greece. ...
CHAPTER 5: ANCIENT GREECE
... • Conquered Greece and Crete • They were sea traders • Passed on Egyptian & Mesopotamian influences to later Greeks. • Developed numerous city-states in Greece. ...
... • Conquered Greece and Crete • They were sea traders • Passed on Egyptian & Mesopotamian influences to later Greeks. • Developed numerous city-states in Greece. ...
Answers Ancient Greece test Study guide
... 20. What shows that Greek mythology is part of today’s popular culture? a. Some sports teams are named after figures from Greek mythology. 21. What shows that Greeks strongly influenced our language? a. Many English words and expressions come from Greek mythology. 22. What was the most important asp ...
... 20. What shows that Greek mythology is part of today’s popular culture? a. Some sports teams are named after figures from Greek mythology. 21. What shows that Greeks strongly influenced our language? a. Many English words and expressions come from Greek mythology. 22. What was the most important asp ...
World History Chapter 7 and 8.4 Study Guide The Ancient Greeks
... any of these things. What is your evaluation about the status of women in these two societies? ...
... any of these things. What is your evaluation about the status of women in these two societies? ...
Greek Study Guide - Leon County Schools
... any of these things. What is your evaluation about the status of women in these two societies? ...
... any of these things. What is your evaluation about the status of women in these two societies? ...
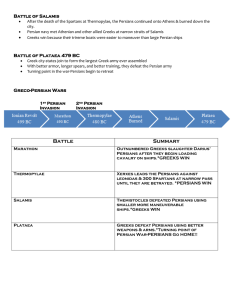
Battle of Salamis After the death of the Spartans at Thermopylae, the
... Greeks win because their trireme boats were easier to maneuver than large Persian ships ...
... Greeks win because their trireme boats were easier to maneuver than large Persian ships ...
Greek Unit Test Review
... D. An outnumbered Greek (Spartan) army tries to take on the Persians at a tight pass. The Greeks will lose but they will allow enough time for the Athenians to get their ships out of port. ...
... D. An outnumbered Greek (Spartan) army tries to take on the Persians at a tight pass. The Greeks will lose but they will allow enough time for the Athenians to get their ships out of port. ...
Cultures of the Mountains and the Sea
... 1. The ______________ was the fundamental political unit in ancient Greece. The ________________ is the public center of a citystate. The ____________________is he highest point in elevation in a Greek city-state. 2. Some city states had a ___________________, rule by a king, queen, or royal family. ...
... 1. The ______________ was the fundamental political unit in ancient Greece. The ________________ is the public center of a citystate. The ____________________is he highest point in elevation in a Greek city-state. 2. Some city states had a ___________________, rule by a king, queen, or royal family. ...
Greek Unit Test Review
... The Greeks will lose but they will allow enough time for the Athenians to get their ships out of port. ...
... The Greeks will lose but they will allow enough time for the Athenians to get their ships out of port. ...
Empires: The Greeks
... of tyrants and their greatest rival, Sparta, to create a new “society of equals.” The program closes on the eve of the new society’s first great test: invasion by the mighty empire of Persia. THE GOLDEN AGE recounts the Greeks’ heroic victory against the mighty Persian empire through the life of The ...
... of tyrants and their greatest rival, Sparta, to create a new “society of equals.” The program closes on the eve of the new society’s first great test: invasion by the mighty empire of Persia. THE GOLDEN AGE recounts the Greeks’ heroic victory against the mighty Persian empire through the life of The ...
The Greco-Persian Wars
... Some Athenians wanted to stay and defend their city-state against the Persians, but the Athenian leader, ________________________, convinced the Athenians to abandon their homes and flee. ...
... Some Athenians wanted to stay and defend their city-state against the Persians, but the Athenian leader, ________________________, convinced the Athenians to abandon their homes and flee. ...
Pontic Greeks
The Pontic Greeks, also known as Pontian Greeks (Greek: Πόντιοι, Ελληνοπόντιοι, Póntioi, Ellinopóntioi; Turkish: Pontus Rumları, Karadeniz Rumlari, Georgian: პონტოელი ბერძნები), are an ethnically Greek group who traditionally lived in the region of Pontus, on the shores of the Black Sea and in the Pontic Alps of northeastern Anatolia. Many later migrated to other parts of Eastern Anatolia, to the former Russian province of Kars Oblast in the Transcaucasus, and to Georgia in various waves between the Ottoman conquest of the Empire of Trebizond in 1461 and the second Russo-Turkish War of 1828-1829. Those from southern Russia, Ukraine, and Crimea are often referred to as ""Northern Pontic [Greeks]"", in contrast to those from ""South Pontus"", which strictly speaking is Pontus proper. Those from Georgia, northeastern Anatolia, and the former Russian Caucasus are in contemporary Greek academic circles often referred to as ""Eastern Pontic [Greeks]"" or as Caucasian Greeks, but also include the Greco-Turkic speaking Urums.Pontic Greeks have Greek ancestry and speak the Pontic Greek dialect, a distinct form of the standard Greek language which, due to the remoteness of Pontus, has undergone linguistic evolution distinct from that of the rest of the Greek world. The Pontic Greeks had a continuous presence in the region of Pontus (modern-day northeastern Turkey), Georgia, and Eastern Anatolia from at least 700 BC until 1922.