Key – underlined answers are the correct answers 1) In the diagram
... a) Causes hemoglobin to bind oxygen more tightly (oxygen dissociation curve shifted to the left) b) Causes the urge to breathe c) Occurs in the muscle tissues d) Is caused by high carbon dioxide levels e) Is found in the human left ventricle 42) When there is transposition of the major blood vessels ...
... a) Causes hemoglobin to bind oxygen more tightly (oxygen dissociation curve shifted to the left) b) Causes the urge to breathe c) Occurs in the muscle tissues d) Is caused by high carbon dioxide levels e) Is found in the human left ventricle 42) When there is transposition of the major blood vessels ...
Embryology Complete
... Attached to the uterine wall Placenta: the composite of uterine tissue and chorionic villi Amnion: encases the young embryonic body in a fluid filled chamber that protects the embryo against trauma and temperature extremes Also prevents adhesions during rapid embryonic growth Yolk Sac: no real funct ...
... Attached to the uterine wall Placenta: the composite of uterine tissue and chorionic villi Amnion: encases the young embryonic body in a fluid filled chamber that protects the embryo against trauma and temperature extremes Also prevents adhesions during rapid embryonic growth Yolk Sac: no real funct ...
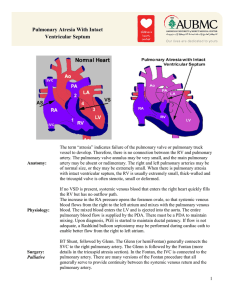
Pulmonary Atresia With Intact Ventricular Septum
... vessel to develop. Therefore, there is no connection between the RV and pulmonary artery. The pulmonary valve annulus may be very small, and the main pulmonary artery may be absent or rudimentary. The right and left pulmonary arteries may be of normal size, or they may be extremely small. When there ...
... vessel to develop. Therefore, there is no connection between the RV and pulmonary artery. The pulmonary valve annulus may be very small, and the main pulmonary artery may be absent or rudimentary. The right and left pulmonary arteries may be of normal size, or they may be extremely small. When there ...
CHAPTER 27 Reproduction and Embryonic Development
... – The amnion, a fluid filled sac that encloses and protects the embryo – The yolk sac, which produces the embryo’s first blood and germ cells – The allantois, which forms part of the umbilical cord – The chorion, which becomes part of the placenta ...
... – The amnion, a fluid filled sac that encloses and protects the embryo – The yolk sac, which produces the embryo’s first blood and germ cells – The allantois, which forms part of the umbilical cord – The chorion, which becomes part of the placenta ...
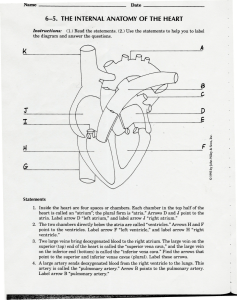
6-5. THE INTERNAL`ANATOMYOF THE HEART
... 6. Two small veins bring oxygen-rich blood from the lungs to the left atrium. These veins are called "pulmonary veins." Find the arrow that points to the pulmonary veins. Label that arrow "pulmonary veins." 7. The bicuspid valve lies between the left atrium and the left ventricle. When it opens, blo ...
... 6. Two small veins bring oxygen-rich blood from the lungs to the left atrium. These veins are called "pulmonary veins." Find the arrow that points to the pulmonary veins. Label that arrow "pulmonary veins." 7. The bicuspid valve lies between the left atrium and the left ventricle. When it opens, blo ...
Fetal Pig Dissection Unit - Grosse Pointe Public School System
... stores bile excreted by the liver and releases it into the small intestine. Stomach - This muscular pouch lies on the left side in the upper abdomen. It is the continuation of the esophagus. Find the esophagus and locate where it pierces the diaphragm to join the stomach. Open the stomach with your ...
... stores bile excreted by the liver and releases it into the small intestine. Stomach - This muscular pouch lies on the left side in the upper abdomen. It is the continuation of the esophagus. Find the esophagus and locate where it pierces the diaphragm to join the stomach. Open the stomach with your ...
Embryology of the Respiratory System
... Oxygenated Blood from Placenta Æ Umbilical vein Æ Branch of Hepatic Portal Vein Æ Ductus venosus Æ Inferior Vena Cava (Mixture with Venous blood) Æ Right atrium Æ Foramen Ovale Æ Left atrium Æ Left ventricle Æ Aorta Æ – Mixture with Venous blood from Pulmonary trunk ...
... Oxygenated Blood from Placenta Æ Umbilical vein Æ Branch of Hepatic Portal Vein Æ Ductus venosus Æ Inferior Vena Cava (Mixture with Venous blood) Æ Right atrium Æ Foramen Ovale Æ Left atrium Æ Left ventricle Æ Aorta Æ – Mixture with Venous blood from Pulmonary trunk ...
Feeding young through mammary glands
... and is able to survive and reproduce on their own one day. ...
... and is able to survive and reproduce on their own one day. ...
Groups
... meatus. In most mammals these parts of the ear help gather and concentrate sound waves. 2. The eye – The eye is protected by the upper and lower eyelids and also by the nictitating membrane, which covers the anterior portion of the eyeball. This membrane can move across the eyeball, helping it to ke ...
... meatus. In most mammals these parts of the ear help gather and concentrate sound waves. 2. The eye – The eye is protected by the upper and lower eyelids and also by the nictitating membrane, which covers the anterior portion of the eyeball. This membrane can move across the eyeball, helping it to ke ...
What are blood types?
... monkeys, a certain blood protein was discovered. This protein is also present in the blood of some people. Other people, however, do not have the protein. • The presence of the protein, or lack of it, is referred to as the Rh (for Rhesus) factor. • If your blood contains the protein, your blood is s ...
... monkeys, a certain blood protein was discovered. This protein is also present in the blood of some people. Other people, however, do not have the protein. • The presence of the protein, or lack of it, is referred to as the Rh (for Rhesus) factor. • If your blood contains the protein, your blood is s ...
Miracle of Life Questions - Carondelet Catholic School
... released from the ____________________. The fertilized egg contains ____________________ from both parents. A cloud of ______________surrounds the egg. These hairs, called ____________________ move the egg along towards the uterus. It takes the egg ____ days to travel of _______________ inches along ...
... released from the ____________________. The fertilized egg contains ____________________ from both parents. A cloud of ______________surrounds the egg. These hairs, called ____________________ move the egg along towards the uterus. It takes the egg ____ days to travel of _______________ inches along ...
The Journey of the Red Blood Cell, by Sophia del Rio
... Imagining ourselves as a group of traveling red blood cells, we are about to embark on a journey through the heart, pointing out structures you need to know for the exam! Beginning on the posterior side of the heart, we drain through the inferior vena cava into the right atrium (RA). We see a ring w ...
... Imagining ourselves as a group of traveling red blood cells, we are about to embark on a journey through the heart, pointing out structures you need to know for the exam! Beginning on the posterior side of the heart, we drain through the inferior vena cava into the right atrium (RA). We see a ring w ...
Document
... are removed from the spermatozoon head, and (b) the acrosome reaction, during which acrosin and trypsin-like substances are released to penetrate the zona pellucida. During fertilization, the spermatozoon must penetrate (a) the corona radiata, (b) the zona pellucida, and (c) the oocyte cell membrane ...
... are removed from the spermatozoon head, and (b) the acrosome reaction, during which acrosin and trypsin-like substances are released to penetrate the zona pellucida. During fertilization, the spermatozoon must penetrate (a) the corona radiata, (b) the zona pellucida, and (c) the oocyte cell membrane ...
Extraembryonic blood vessels form during the early 3rd week
... Critical to restructuring is breakdown of left and right DA between arches 3 and 4. 3rd arches - same fate right and left sides -remain connected at ends to aortic sac & DA -proximal parts form common carotid arteries; distal parts form portion of internal carotid artery (rest from dorsal aorta); ex ...
... Critical to restructuring is breakdown of left and right DA between arches 3 and 4. 3rd arches - same fate right and left sides -remain connected at ends to aortic sac & DA -proximal parts form common carotid arteries; distal parts form portion of internal carotid artery (rest from dorsal aorta); ex ...
Embryology Notes
... • Decision determined that a woman can choose to have an abortion for any reason up until the fetus is viable to live outside of the body without maternal support • Interesting note: Roe actually had the baby and gave it up for adoption • Advantages/benefits of abortion • Some believe that abortion ...
... • Decision determined that a woman can choose to have an abortion for any reason up until the fetus is viable to live outside of the body without maternal support • Interesting note: Roe actually had the baby and gave it up for adoption • Advantages/benefits of abortion • Some believe that abortion ...
Structure and Function of the Normal Heart and Blood
... the alveolar-capillary membrane. Oxygenated blood then enters the left atrium from the lungs via the four pulmonary veins. Blood flows across the open mitral valve and into the left ventricle during diastole and is ejected across the aortic valve and into the aorta during systole. The blood reaches ...
... the alveolar-capillary membrane. Oxygenated blood then enters the left atrium from the lungs via the four pulmonary veins. Blood flows across the open mitral valve and into the left ventricle during diastole and is ejected across the aortic valve and into the aorta during systole. The blood reaches ...
human genome
... •By the end of this period, the fetus can move its arms, legs, mouth, and head. •The fetal brain forms as many as 2 million synaptic connections per second. •By the fifth month, all the brain cells the person will have at birth are present. The fetus now has distinct sleep–wake cycles and periods of ...
... •By the end of this period, the fetus can move its arms, legs, mouth, and head. •The fetal brain forms as many as 2 million synaptic connections per second. •By the fifth month, all the brain cells the person will have at birth are present. The fetus now has distinct sleep–wake cycles and periods of ...
Suprarenal Glands
... • The suprarenal gland of the fetus is 10-20 times larger than the adult glands relative to the body weight, and are large compared with the kidneys. This is because of the extensive size of the fetal cortex. The medulla remains relatively small until after birth. • The suprarenal glands rapidly be ...
... • The suprarenal gland of the fetus is 10-20 times larger than the adult glands relative to the body weight, and are large compared with the kidneys. This is because of the extensive size of the fetal cortex. The medulla remains relatively small until after birth. • The suprarenal glands rapidly be ...
الشريحة 1
... • In some cases where contractions are weak and ineffective • -an oxytocin infusion may be commenced to stimulate adequate contractions and achieve advance of the ...
... • In some cases where contractions are weak and ineffective • -an oxytocin infusion may be commenced to stimulate adequate contractions and achieve advance of the ...
Medical Terminology - Porterville College
... synwith, together • Syndrome – Set of symptoms and signs of disease that occur together to indicate a disease condition ...
... synwith, together • Syndrome – Set of symptoms and signs of disease that occur together to indicate a disease condition ...
Left anterior cardinal vein
... Ductus venosus becomes the ligamentum venosum, attached to the inferior vena cava. Ductus arteriousus becomes ligamentum arteriousum Foramen ovale closes shortly after birth, fuses completely in first year and becomes fossa ovalis The intra-abdominal portions of the umbilical arteries become the med ...
... Ductus venosus becomes the ligamentum venosum, attached to the inferior vena cava. Ductus arteriousus becomes ligamentum arteriousum Foramen ovale closes shortly after birth, fuses completely in first year and becomes fossa ovalis The intra-abdominal portions of the umbilical arteries become the med ...
Heart Anatomy Complete
... Base: broader portion Area where the large vessels exit Is at the top Visceral Pericardium or Epicardium: lies right on the heart muscle itself Parietal Pericardium: outer covering Attached to the diaphragm at the apex Serous fluid is between the two layers (visceral and parietal) to reduce friction ...
... Base: broader portion Area where the large vessels exit Is at the top Visceral Pericardium or Epicardium: lies right on the heart muscle itself Parietal Pericardium: outer covering Attached to the diaphragm at the apex Serous fluid is between the two layers (visceral and parietal) to reduce friction ...
The Foramen of Magendie - Loyola eCommons
... is not intact; it is breaking down by a process of lysiS of the component cells. ...
... is not intact; it is breaking down by a process of lysiS of the component cells. ...
Unit 1 Lecture 2
... tendineae prevent the valve from eversion into the atria. The pulmonary semilunar valve lies in the opening where the pulmonary trunk leaves the right ventricle and the aortic semilunar valve lies at the opening of the left ventricle and the aorta. These two valves prevent blood flow back into the h ...
... tendineae prevent the valve from eversion into the atria. The pulmonary semilunar valve lies in the opening where the pulmonary trunk leaves the right ventricle and the aortic semilunar valve lies at the opening of the left ventricle and the aorta. These two valves prevent blood flow back into the h ...