Heart Physiology /Circulatory System Review
... 5. The first audible beats are produced by the forceful opening of an artery. This is considered to the systole 6. Explain why an athlete must exercise harder or longer to achieve a maximum heart rate than a person who is not as physically fit. Like any muscle, a well-conditioned heart beats more ef ...
... 5. The first audible beats are produced by the forceful opening of an artery. This is considered to the systole 6. Explain why an athlete must exercise harder or longer to achieve a maximum heart rate than a person who is not as physically fit. Like any muscle, a well-conditioned heart beats more ef ...
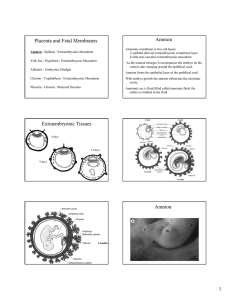
Placenta and Extraembryonic Membranes
... arteries of the uterus and their modification so that, as the embryo grows, they can provide an increasing flow of blood at low pressure to bathe the syncytiotrophoblastic surface of the placenta (see Fig. 7-10). Specialized invasive cytotrophoblastic cells, migrating out from the *Other mammals hav ...
... arteries of the uterus and their modification so that, as the embryo grows, they can provide an increasing flow of blood at low pressure to bathe the syncytiotrophoblastic surface of the placenta (see Fig. 7-10). Specialized invasive cytotrophoblastic cells, migrating out from the *Other mammals hav ...
The anatomy of the heart - Bloomsburg University of
... and extends down to the abdomen. The aorta distributes oxygenated blood to all parts of the body. ...
... and extends down to the abdomen. The aorta distributes oxygenated blood to all parts of the body. ...
Lecture 17: Vascular System Review 3 paired veins drain into the
... o Distal parts join dorsal aortas to form internal carotid arteries- supply middle ears, orbits, brain and its meninges, and pituitary gland Derivatives of the 4th pair of pharyngeal arch arteries o Left 4th pharyngeal arch artery forms part of the arch of aorta Proximal part develops from aortic ...
... o Distal parts join dorsal aortas to form internal carotid arteries- supply middle ears, orbits, brain and its meninges, and pituitary gland Derivatives of the 4th pair of pharyngeal arch arteries o Left 4th pharyngeal arch artery forms part of the arch of aorta Proximal part develops from aortic ...
Chapter 10 The heart Structures
... pulmonary (lung) circuit because it receives blood from the body and pumps it out to the lungs. ...
... pulmonary (lung) circuit because it receives blood from the body and pumps it out to the lungs. ...
Embryonic Adaptations
... involve all three germinal layers and are directed down and in. They undercut the body of the embryo thereby elevating it from the surface of the yolk. The body folds eventually surround the whole body of the embryo but it starts in the head region. Here it is referred to as the head fold. The chori ...
... involve all three germinal layers and are directed down and in. They undercut the body of the embryo thereby elevating it from the surface of the yolk. The body folds eventually surround the whole body of the embryo but it starts in the head region. Here it is referred to as the head fold. The chori ...
Exam 1 Study Guide - Dr. Stuart Sumida
... The return of lymphatic fluid to the venous circulation from most of the body is: a) at the junction of the right subclavian and right jugular veins. b) via the thoracic duct. c) into the cysterna chyli. d) at the junction of the right and left brachiocephalic veins. e) greater when a person is calm ...
... The return of lymphatic fluid to the venous circulation from most of the body is: a) at the junction of the right subclavian and right jugular veins. b) via the thoracic duct. c) into the cysterna chyli. d) at the junction of the right and left brachiocephalic veins. e) greater when a person is calm ...
development - World of Teaching
... has divided to form a 2-celled embryo – The embryo passes down the oviduct by cilia and peristalsis – The zona pellucida has dissolved by the 5th day, when the embryo enters the uterus – The embryo floats free for several days, nourished by fluids from glands in the ...
... has divided to form a 2-celled embryo – The embryo passes down the oviduct by cilia and peristalsis – The zona pellucida has dissolved by the 5th day, when the embryo enters the uterus – The embryo floats free for several days, nourished by fluids from glands in the ...
System+Coloring+Book
... rectum - the lower part of the large intestine, where feces are stored before they are excreted from the body. small intestine - the long, thin winding tube that food goes through after it leaves the stomach. stomach - a sack-like, muscular organ that is attached to the esophagus. When food enters t ...
... rectum - the lower part of the large intestine, where feces are stored before they are excreted from the body. small intestine - the long, thin winding tube that food goes through after it leaves the stomach. stomach - a sack-like, muscular organ that is attached to the esophagus. When food enters t ...
01_Anatomy of the female genital organ[1]
... the right atrium. The foramen ovale is a valvular opening, the valve functioning from the right to left. The left atrial pressure rises and thus closure of the foramen ...
... the right atrium. The foramen ovale is a valvular opening, the valve functioning from the right to left. The left atrial pressure rises and thus closure of the foramen ...
Components of Labor
... • Lengthening of the umbilical cord • Sudden gush of vaginal blood • Change in the shape of the uterus Schultze-shiny and glistening side of placenta fetal surface. (80%) Duncan-looks raw, red irregular with ridges, maternal surface. ...
... • Lengthening of the umbilical cord • Sudden gush of vaginal blood • Change in the shape of the uterus Schultze-shiny and glistening side of placenta fetal surface. (80%) Duncan-looks raw, red irregular with ridges, maternal surface. ...
The Circulatory System – The Heart
... o The femoral artery passes through the femoral triangle to through the thigh ...
... o The femoral artery passes through the femoral triangle to through the thigh ...
The Circulatory System – The Heart
... o The femoral artery passes through the femoral triangle to through the thigh ...
... o The femoral artery passes through the femoral triangle to through the thigh ...
08 Placenta and Fetal Membranes total
... Making the Placenta By 8 weeks - chorionic stem villi over the entire surface of the chorionic sac Those villi associated with the decidua basalis increase in size and more villi form. Enlargement includes further branching of the anchoring villus - chorion frondosum. The villi continue to enlarge d ...
... Making the Placenta By 8 weeks - chorionic stem villi over the entire surface of the chorionic sac Those villi associated with the decidua basalis increase in size and more villi form. Enlargement includes further branching of the anchoring villus - chorion frondosum. The villi continue to enlarge d ...
Placenta and Fetal Membranes
... By 8 weeks - chorionic stem villi over the entire surface of the chorionic sac Those villi associated with the decidua basalis increase in size and more villi form. Enlargement includes further branching of the anchoring villus - chorion frondosum. The villi continue to enlarge during most of gestat ...
... By 8 weeks - chorionic stem villi over the entire surface of the chorionic sac Those villi associated with the decidua basalis increase in size and more villi form. Enlargement includes further branching of the anchoring villus - chorion frondosum. The villi continue to enlarge during most of gestat ...
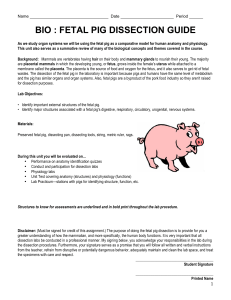
Blood Vessels of the Fetal Pig Dissection
... 4. After you have removed the thymus, there may still be considerable connective tissue around the blood vessels. Use your probes or the tweezers to clean off the vessels so that you can trace them from the heart out into the body. 5. Identify these veins that drain the anterior portion of the feta ...
... 4. After you have removed the thymus, there may still be considerable connective tissue around the blood vessels. Use your probes or the tweezers to clean off the vessels so that you can trace them from the heart out into the body. 5. Identify these veins that drain the anterior portion of the feta ...
bio : fetal pig dissection guide
... BIO : FETAL PIG DISSECTION GUIDE As we study organ systems we will be using the fetal pig as a comparative model for human anatomy and physiology. This unit also serves as a summative review of many of the biological concepts and themes covered in the course. Background: Mammals are vertebrates havi ...
... BIO : FETAL PIG DISSECTION GUIDE As we study organ systems we will be using the fetal pig as a comparative model for human anatomy and physiology. This unit also serves as a summative review of many of the biological concepts and themes covered in the course. Background: Mammals are vertebrates havi ...
Pregnancy and Human Development
... to the immediate vicinity of the oocyte, it weaves its way through the cells of the corona radiata. This journey is assisted by a cellsurface hyaluronidase on the sperm that digests the intercellular cement between the granulosa cells in the immediate area, causing them to fall away from the oocyte ...
... to the immediate vicinity of the oocyte, it weaves its way through the cells of the corona radiata. This journey is assisted by a cellsurface hyaluronidase on the sperm that digests the intercellular cement between the granulosa cells in the immediate area, causing them to fall away from the oocyte ...
File
... • At the end of the seventh week the human heart has reached its final stage of development. • Because the fetus does not use its lungs, most of the blood is diverted to the systemic circulation. This is accomplished by a right to left shunting of blood that occurs between the two atria. • The for ...
... • At the end of the seventh week the human heart has reached its final stage of development. • Because the fetus does not use its lungs, most of the blood is diverted to the systemic circulation. This is accomplished by a right to left shunting of blood that occurs between the two atria. • The for ...
Throat, Thorax, and Visceral Conditions
... to the midthorax. Then divides into left and right bronchial tubes. • Formed by c-shaped rings of hyaline cartilage. • Opens to allow food to pass through, and constricts to expel mucus with coughing. ...
... to the midthorax. Then divides into left and right bronchial tubes. • Formed by c-shaped rings of hyaline cartilage. • Opens to allow food to pass through, and constricts to expel mucus with coughing. ...
Seeley Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 6th
... The primary energy source for the newborn is _______. A. glucose B. glycogen ...
... The primary energy source for the newborn is _______. A. glucose B. glycogen ...
The Mechanism of Labour
... spontaneously/mechanically pushing or still breathing through contractions, how long can the second stage last? Introverted in her behaviour and may adopt alternative Position, bending towards the floor with knees apart Claire Allan ...
... spontaneously/mechanically pushing or still breathing through contractions, how long can the second stage last? Introverted in her behaviour and may adopt alternative Position, bending towards the floor with knees apart Claire Allan ...








![01_Anatomy of the female genital organ[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008603894_1-40f27c4f678b3b3896e93dc1dbdd69d1-300x300.png)