Blood Vessels - IWS2.collin.edu
... externa or adventitia • Areolar or fibrous connective tissue • Supports the vessel • Protects the vessel ...
... externa or adventitia • Areolar or fibrous connective tissue • Supports the vessel • Protects the vessel ...
Chapter 32
... externa or adventitia • Areolar or fibrous connective tissue • Supports the vessel • Protects the vessel ...
... externa or adventitia • Areolar or fibrous connective tissue • Supports the vessel • Protects the vessel ...
Pulmonary semilunar valve
... semilunar aortic valve and then into the aorta. The aorta distributes oxygenated blood to all parts of the body. ...
... semilunar aortic valve and then into the aorta. The aorta distributes oxygenated blood to all parts of the body. ...
Chapter 5 Lecture Notes
... Capillaries connect to veins, and veins return blood to the heart to get rid of carbon dioxide and pick up oxygen. Exhalation—Passive process during which the intercostal muscles and the diaphragm relax The chest decreases in size and positive pressure builds inside the chest cavity. This positive p ...
... Capillaries connect to veins, and veins return blood to the heart to get rid of carbon dioxide and pick up oxygen. Exhalation—Passive process during which the intercostal muscles and the diaphragm relax The chest decreases in size and positive pressure builds inside the chest cavity. This positive p ...
Cross Sectional Anatomy
... Superior vena cava Inferior vena cava Pulmonary artery Pulmonary vein ...
... Superior vena cava Inferior vena cava Pulmonary artery Pulmonary vein ...
Normal Pelvis, types of female pelvis and fetal skull
... Other factors affecting need for C-S include: Fetal size, Force of ...
... Other factors affecting need for C-S include: Fetal size, Force of ...
HEART ANATOMY RESUMED - Sinoe Medical Association
... Sulcus: Depressions on the anterior surface of the heart, used as demarcations for external anatomy. They may be hard to see if fat is present. o Interventricular Sulcus: The demarcation between the left and right ventricles. The Anterior Interventricular Artery is often embedded in this sulcus. o C ...
... Sulcus: Depressions on the anterior surface of the heart, used as demarcations for external anatomy. They may be hard to see if fat is present. o Interventricular Sulcus: The demarcation between the left and right ventricles. The Anterior Interventricular Artery is often embedded in this sulcus. o C ...
Bony pelvis. Fetus as an object of labor
... a vaginal examination, the physician tries to reach the sacral promontory with the middle finger of the examining, hand. The index finger of the free hand marks the point where the lowt border of the pubic symphysis impinges on the examining hand proximal 1 the metacarpophalangeal joint of the index ...
... a vaginal examination, the physician tries to reach the sacral promontory with the middle finger of the examining, hand. The index finger of the free hand marks the point where the lowt border of the pubic symphysis impinges on the examining hand proximal 1 the metacarpophalangeal joint of the index ...
Bony pelvis. Fetus as an object of labor
... a vaginal examination, the physician tries to reach the sacral promontory with the middle finger of the examining, hand. The index finger of the free hand marks the point where the lowt border of the pubic symphysis impinges on the examining hand proximal 1 the metacarpophalangeal joint of the index ...
... a vaginal examination, the physician tries to reach the sacral promontory with the middle finger of the examining, hand. The index finger of the free hand marks the point where the lowt border of the pubic symphysis impinges on the examining hand proximal 1 the metacarpophalangeal joint of the index ...
ORAL CAVITY
... The muscular diaphragm separates the upper from the lower ventrali:>ody cavity. The upper is the thoracic, the lower is the abdominal cavity. We shall study the abdominal area first and later consider the thorax in relation to the study of the heart and circulatory system. With your fingertips locat ...
... The muscular diaphragm separates the upper from the lower ventrali:>ody cavity. The upper is the thoracic, the lower is the abdominal cavity. We shall study the abdominal area first and later consider the thorax in relation to the study of the heart and circulatory system. With your fingertips locat ...
study guide unit 3
... What is the most external and toughest of the meninges? Dura mater What is the web-like middle layer of the three meninges? Arachnoid mater What area of the brain controls logical thought and conscious awareness of the environment? Cerebrum What fissure separates the right and left halves of the cer ...
... What is the most external and toughest of the meninges? Dura mater What is the web-like middle layer of the three meninges? Arachnoid mater What area of the brain controls logical thought and conscious awareness of the environment? Cerebrum What fissure separates the right and left halves of the cer ...
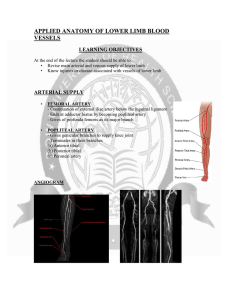
APPLIED ANATOMY OF LOWER LIMB BLOOD VESSELS
... COMPLICATIONS: • Pulmonary embolism • Post DVT limb • Varicose veins ...
... COMPLICATIONS: • Pulmonary embolism • Post DVT limb • Varicose veins ...
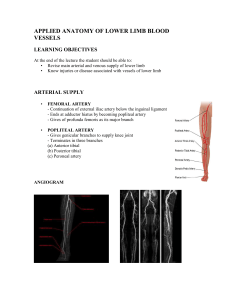
applied anatomy of lower limb blood vessels
... COMPLICATIONS: • Pulmonary embolism • Post DVT limb • Varicose veins ...
... COMPLICATIONS: • Pulmonary embolism • Post DVT limb • Varicose veins ...
MCHENRY WESTERN LAKE COUNTY EMS SYSTEM OPTIONAL
... activated by the SA node before they can fire. This rapid firing causes all the foci to fire faster than their intrinsic rates, a phenomenon known as overdrive-suppression. Thus, in the normal, healthy heart, only the SA node intrinsic rate is observable. If we were then going to evaluate the ECG co ...
... activated by the SA node before they can fire. This rapid firing causes all the foci to fire faster than their intrinsic rates, a phenomenon known as overdrive-suppression. Thus, in the normal, healthy heart, only the SA node intrinsic rate is observable. If we were then going to evaluate the ECG co ...
Lecture Notes
... relax and contract, the heart can do this without any direct stimulus from the nervous system. (Chemoreceptors in the carotid and aortic bodies monitor blood O2, CO2, and pH. Baroreceptors in the carotid sinus and aortic arch respond to increases in blood pressure.) The cardiac muscle cells in the h ...
... relax and contract, the heart can do this without any direct stimulus from the nervous system. (Chemoreceptors in the carotid and aortic bodies monitor blood O2, CO2, and pH. Baroreceptors in the carotid sinus and aortic arch respond to increases in blood pressure.) The cardiac muscle cells in the h ...
Heart
... Describe the unique structure of the atrioventricular valves. Why is this structure necessary? What is the ligamentum arteriosum? What is the fossa ovalis? What were these structures during fetal development? Name the branches off the arch of the aorta. What part of the body do they supply? What is ...
... Describe the unique structure of the atrioventricular valves. Why is this structure necessary? What is the ligamentum arteriosum? What is the fossa ovalis? What were these structures during fetal development? Name the branches off the arch of the aorta. What part of the body do they supply? What is ...
Fetal Pig Dissection Power Point
... • Do NOT cut out the intestines to dissect the urinary system! • Push the intestines to one side and use a scalpel or blunt probe to remove the connective ...
... • Do NOT cut out the intestines to dissect the urinary system! • Push the intestines to one side and use a scalpel or blunt probe to remove the connective ...
Biology 11 - Human Anatomy
... 1. The _______ is a shared structure of the fetus and mother across which nutrients & oxygen diffuse from mother to child and wastes & CO2 diffuse from fetus to mother 2. Paired _________ __________ branch from fetal internal iliac arteries and carry ___oxygenated blood to placenta to pick up oxygen ...
... 1. The _______ is a shared structure of the fetus and mother across which nutrients & oxygen diffuse from mother to child and wastes & CO2 diffuse from fetus to mother 2. Paired _________ __________ branch from fetal internal iliac arteries and carry ___oxygenated blood to placenta to pick up oxygen ...
Pig Dissection - Cypress College A&P
... – SAVE Outer bag – Cut open the inside bag over the sink. Empty pig and contents into sink. THROW AWAY the INSIDE bag into the GREEN trash ...
... – SAVE Outer bag – Cut open the inside bag over the sink. Empty pig and contents into sink. THROW AWAY the INSIDE bag into the GREEN trash ...
Exercise 20
... Two-sided, doublepumping organ. The left side controls the flow of blood to all tissues and cells in the body, where oxygen and nutrients are delivered and wastes are taken away. The right side sends blood to the lungs, where oxygen stored in RBCs is replenished and CO2 is released ...
... Two-sided, doublepumping organ. The left side controls the flow of blood to all tissues and cells in the body, where oxygen and nutrients are delivered and wastes are taken away. The right side sends blood to the lungs, where oxygen stored in RBCs is replenished and CO2 is released ...
Human Life Cycle
... Fertilisation: the process in which the nucleus of a spermatozoon enters the oocyte and fuses with the female pronucleus to produce a zygote. Pronuclei: nucleus of mature germ cells, haploid Zona pellucida: clear, acellular membrane that surrounds the oocyte protecting against ...
... Fertilisation: the process in which the nucleus of a spermatozoon enters the oocyte and fuses with the female pronucleus to produce a zygote. Pronuclei: nucleus of mature germ cells, haploid Zona pellucida: clear, acellular membrane that surrounds the oocyte protecting against ...
Heart - IWS2.collin.edu
... Blood flows to the body Vena cava Superior brings blood from head, neck, arms and superior trunk Inferior brings blood from the rest of the body Blood rich in CO2 Blood flows to the RA ...
... Blood flows to the body Vena cava Superior brings blood from head, neck, arms and superior trunk Inferior brings blood from the rest of the body Blood rich in CO2 Blood flows to the RA ...
Prof. Dr. Mahmoud Al-Dajani
... FETAL PERIOD OF PRENATAL DEVELOPMENT developmental changes are not as dramatic as those that occur during the embryonic period, they are important because they allow the newly formed tissues and organs to function. ► Even though the embryo has been breathing since the third week, by the end of the ...
... FETAL PERIOD OF PRENATAL DEVELOPMENT developmental changes are not as dramatic as those that occur during the embryonic period, they are important because they allow the newly formed tissues and organs to function. ► Even though the embryo has been breathing since the third week, by the end of the ...
(Suprarenal) Glands
... The suprarenal gland is separate from the kidney but enclosed within the renal fascia. The suprarenal gland of the fetus is 10-20 times larger than the adult glands relative to the body weight, and are large compared with the kidneys. This is because of the extensive size of the fetal cortex. Th ...
... The suprarenal gland is separate from the kidney but enclosed within the renal fascia. The suprarenal gland of the fetus is 10-20 times larger than the adult glands relative to the body weight, and are large compared with the kidneys. This is because of the extensive size of the fetal cortex. Th ...
Foetal Membranes
... outer layer) that constitutes the amniotic membranes. • contain the amniotic fluid • A protective layer for the baby insulating him/her from bacteria in the vagina. Rupture of this sac exposes the child to bacteria in the vagina and increases the risk of infection if the infant is not delivered with ...
... outer layer) that constitutes the amniotic membranes. • contain the amniotic fluid • A protective layer for the baby insulating him/her from bacteria in the vagina. Rupture of this sac exposes the child to bacteria in the vagina and increases the risk of infection if the infant is not delivered with ...