4-BLOOD SUPPLY OF HEART
... Right Coronary Artery Supplies: Right atrium, Right ventricle, part of Left Atrium, Left ventricle & Atrioventricular septum. ...
... Right Coronary Artery Supplies: Right atrium, Right ventricle, part of Left Atrium, Left ventricle & Atrioventricular septum. ...
Female pelvis and fetal skull
... The female pelvis is formed by a pair of hip bones (innominate) bones, the sacrum and the coccyx. The pelvis attaches the lower limbs to the axial skeleton with the strongest ligaments of the body and transmits weight of the upper body to the lower limbs, also it supports the visceral organs of the ...
... The female pelvis is formed by a pair of hip bones (innominate) bones, the sacrum and the coccyx. The pelvis attaches the lower limbs to the axial skeleton with the strongest ligaments of the body and transmits weight of the upper body to the lower limbs, also it supports the visceral organs of the ...
Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System
... Physical factors (age, gender, exercise, and body temperature) influence heart rate Hypocalcemia (reduced levels of ionic calcium) depress the heart Hypercalcemia (> levels of ionic calcium) causes prolonged contraction to point heart ...
... Physical factors (age, gender, exercise, and body temperature) influence heart rate Hypocalcemia (reduced levels of ionic calcium) depress the heart Hypercalcemia (> levels of ionic calcium) causes prolonged contraction to point heart ...
FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
... that cover the ovary and sway, drawing the ovum inside aRer ovula6on ...
... that cover the ovary and sway, drawing the ovum inside aRer ovula6on ...
Blood Vessel Anatomy
... optic chiasma at the base of the brain; this circle unites the ant. & post. blood supplies from the internal carotid & vertebral arteries. E. Arteries of the Shoulder & Upper Extremity - major branches of the ______________ arteries include the 1. _________ A. - continuation of subclavian in the axi ...
... optic chiasma at the base of the brain; this circle unites the ant. & post. blood supplies from the internal carotid & vertebral arteries. E. Arteries of the Shoulder & Upper Extremity - major branches of the ______________ arteries include the 1. _________ A. - continuation of subclavian in the axi ...
Chapter 20
... Special Circulatory Routes Lungs • Low pulmonary blood pressure – flow slower, more time for gas exchange – capillary fluid absorption ...
... Special Circulatory Routes Lungs • Low pulmonary blood pressure – flow slower, more time for gas exchange – capillary fluid absorption ...
Chapter 20
... Special Circulatory Routes Lungs • Low pulmonary blood pressure – flow slower, more time for gas exchange – capillary fluid absorption ...
... Special Circulatory Routes Lungs • Low pulmonary blood pressure – flow slower, more time for gas exchange – capillary fluid absorption ...
Major Concepts of Anatomy and Physiology
... to lower pressure (veins). Respiratory Pump: Breathing muscles help to compress and decompress veins. Chordae Tendinae: Tendonlike fibrous cords that connect the atrioventricular valves of the heart via papillary muscles & provides suction within the heart. Gravity: Helps return blood from the highe ...
... to lower pressure (veins). Respiratory Pump: Breathing muscles help to compress and decompress veins. Chordae Tendinae: Tendonlike fibrous cords that connect the atrioventricular valves of the heart via papillary muscles & provides suction within the heart. Gravity: Helps return blood from the highe ...
Document
... • Failure of the Conduction System of the Heart • The sinuatrial node is the spontaneous source of the cardiac impulse. The atrioventricular node is responsible for picking up the cardiac impulse from the atria. The atrioventricular bundle is the only route by which the cardiac impulse can spread fr ...
... • Failure of the Conduction System of the Heart • The sinuatrial node is the spontaneous source of the cardiac impulse. The atrioventricular node is responsible for picking up the cardiac impulse from the atria. The atrioventricular bundle is the only route by which the cardiac impulse can spread fr ...
Biology 218 – Human Anatomy Lecture Outline Adapted from Martini
... Blood supply to the brain Blood in the vertebral arteries go to the brain via: Left and right vertebral arteries fuse to form the basilar artery Basilar artery branches many times in the area of the pons Basilar artery eventually forms the vessels of the cerebral arterial circle (circle of Willis) B ...
... Blood supply to the brain Blood in the vertebral arteries go to the brain via: Left and right vertebral arteries fuse to form the basilar artery Basilar artery branches many times in the area of the pons Basilar artery eventually forms the vessels of the cerebral arterial circle (circle of Willis) B ...
BIO 218 F 2012 CH 22 Martini Lecture Outline
... Blood supply to the brain Blood in the vertebral arteries go to the brain via: Left and right vertebral arteries fuse to form the basilar artery Basilar artery branches many times in the area of the pons Basilar artery eventually forms the vessels of the cerebral arterial circle (circle of Willis) B ...
... Blood supply to the brain Blood in the vertebral arteries go to the brain via: Left and right vertebral arteries fuse to form the basilar artery Basilar artery branches many times in the area of the pons Basilar artery eventually forms the vessels of the cerebral arterial circle (circle of Willis) B ...
Cardiac Embryology basics DR MADHUSUDAN
... pericardial cavity, forms a common atrium and is incorporated into the pericardial cavity. • The AV junction remains narrow and forms the AV canal, which connects the common atrium and the early embryonic ...
... pericardial cavity, forms a common atrium and is incorporated into the pericardial cavity. • The AV junction remains narrow and forms the AV canal, which connects the common atrium and the early embryonic ...
Materials covered in lecture
... *Note dilated bile ducts. (Low density branching structures anterior to portal veins) ...
... *Note dilated bile ducts. (Low density branching structures anterior to portal veins) ...
4-BLOOD SUPPLY OF HEART [Autosaved]
... from the anterior aortic sinus of the ascending aorta. Runs forward between pulmonary trunk and right auricle. Descends in the right atrioventricular groove between the Right Auricle and the Pulmonary trunk. At the inferior border of the heart it is continuous posteriorly along the atrioventricul ...
... from the anterior aortic sinus of the ascending aorta. Runs forward between pulmonary trunk and right auricle. Descends in the right atrioventricular groove between the Right Auricle and the Pulmonary trunk. At the inferior border of the heart it is continuous posteriorly along the atrioventricul ...
Uterus
... Its major function of uterus is to accept a fertilized ovum which becomes implanted into the endometrium, and derives nourishment. The fertilized ovum becomes an embryo, develops into a fetus If the egg does not embed in the wall of the uterus, a female begins menstruation. ...
... Its major function of uterus is to accept a fertilized ovum which becomes implanted into the endometrium, and derives nourishment. The fertilized ovum becomes an embryo, develops into a fetus If the egg does not embed in the wall of the uterus, a female begins menstruation. ...
vein - SLCC Anatomy
... gives rise to brachiocephalic trunk, left common carotid artery, and left subclavian artery ...
... gives rise to brachiocephalic trunk, left common carotid artery, and left subclavian artery ...
Development of the (supra-) hepatic portion of the inferior caval vein
... during CS13, with the right side being wider than the left. At this stage, the pig embryo differed from the human in that its liver consisted of a single ventromedial lobe overlying the gall bladder and two dorsolateral lobes containing the vitelline conduits. The expanding ventromedial liver lobe s ...
... during CS13, with the right side being wider than the left. At this stage, the pig embryo differed from the human in that its liver consisted of a single ventromedial lobe overlying the gall bladder and two dorsolateral lobes containing the vitelline conduits. The expanding ventromedial liver lobe s ...
Branches of Internal Iliac Artery Posterior Division iliolumbar lateral
... 2. lateral sacral 3. superior gluteal a. largest branch of the internal iliac. b. usually passes between the lumbosacral trunk and the first sacral nerve to leave the pelvis through the greater sciatic foramen above the piriformis. Anterior Division 1. inferior gluteal a. passes between the 2nd and ...
... 2. lateral sacral 3. superior gluteal a. largest branch of the internal iliac. b. usually passes between the lumbosacral trunk and the first sacral nerve to leave the pelvis through the greater sciatic foramen above the piriformis. Anterior Division 1. inferior gluteal a. passes between the 2nd and ...
Decidua capsularis Extraembryonic coelom Placenta
... yolk sac are well formed. The chorionic villi lie in blood-filled intervillous spaces within the endometrium. The embryo is nourished via the umbilical vessels that connect it (through the umbilical cord) to the placenta. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... yolk sac are well formed. The chorionic villi lie in blood-filled intervillous spaces within the endometrium. The embryo is nourished via the umbilical vessels that connect it (through the umbilical cord) to the placenta. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Pig Dissection
... • Open up the plastic bag – – KEEP the outer bag AND the rubber band! – Cut open the inner bag over the sink. Empty pig and contents into sink. THROW AWAY inner bag into the GREEN trash ...
... • Open up the plastic bag – – KEEP the outer bag AND the rubber band! – Cut open the inner bag over the sink. Empty pig and contents into sink. THROW AWAY inner bag into the GREEN trash ...
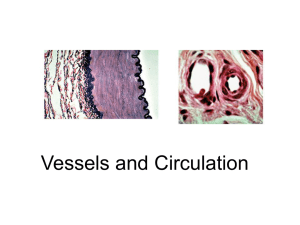
Lecture 19 - Vessels and Circulation
... CO2 and nitrogenous waste (protein break-down product) removal ...
... CO2 and nitrogenous waste (protein break-down product) removal ...













![4-BLOOD SUPPLY OF HEART [Autosaved]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000391496_1-1cc69f66eb9ccd5c1082faab8bb4d060-300x300.png)