Types of Arteries
... All medium and large arteries have deep locations accompanied by deep veins ...
... All medium and large arteries have deep locations accompanied by deep veins ...
XCA LIVER - WordPress.com
... major hepatic and portal veins should be easily seen in the normal liver. The hepatic veins are most prominent closest to the diaphragm. The right, middle, and left Hepatic Veins converge to enter the IVC. The Hepatic Veins have thin, smooth walls which only produce a bright echo when the sound beam ...
... major hepatic and portal veins should be easily seen in the normal liver. The hepatic veins are most prominent closest to the diaphragm. The right, middle, and left Hepatic Veins converge to enter the IVC. The Hepatic Veins have thin, smooth walls which only produce a bright echo when the sound beam ...
peripheral vascular surgery - A
... the rest of the body via vessels called arteries Arterial blood is going away from the heart Arteries are large vessels originating with the AORTA that come directly out of the heart Arteries divide into smaller braches as they reach their destination in the body Arteries→arterioles→capillar ...
... the rest of the body via vessels called arteries Arterial blood is going away from the heart Arteries are large vessels originating with the AORTA that come directly out of the heart Arteries divide into smaller braches as they reach their destination in the body Arteries→arterioles→capillar ...
left common carotid artery
... anterior aspect of the forearm. In front of the elbow it gives off a large branch, the median cubital vein, which slants upwards and medially to join the basilic vein. After crossing the elbow joint the cephalic vein passes up the lateral aspect of the arm and in front of the shoulder joint to end i ...
... anterior aspect of the forearm. In front of the elbow it gives off a large branch, the median cubital vein, which slants upwards and medially to join the basilic vein. After crossing the elbow joint the cephalic vein passes up the lateral aspect of the arm and in front of the shoulder joint to end i ...
left common carotid artery
... and medially and lies in a groove in the mastoid process of the temporal bone. Anteriorly only a thin plate of bone separates the sinus from the air cells in the mastoid process of the temporal bone. Inferiorly it continues as the internal jugular vein. The internal jugular veins begin at the jugula ...
... and medially and lies in a groove in the mastoid process of the temporal bone. Anteriorly only a thin plate of bone separates the sinus from the air cells in the mastoid process of the temporal bone. Inferiorly it continues as the internal jugular vein. The internal jugular veins begin at the jugula ...
Right Ventricle
... Right Ventricle: Features : Trabeculae carneae is of three types: 1) Ridges : which are fixed elevations 2) Bridges: having two fixed ends, but with a free centre. 3) Pillars/Papillary Muscles: one end attached to the ventricular wall, and the other end connected to the cusps of the tricuspid valve ...
... Right Ventricle: Features : Trabeculae carneae is of three types: 1) Ridges : which are fixed elevations 2) Bridges: having two fixed ends, but with a free centre. 3) Pillars/Papillary Muscles: one end attached to the ventricular wall, and the other end connected to the cusps of the tricuspid valve ...
Chorion
... – Secreted by trophoblast cells; later chorion – Prompts corpus luteum to continue secretion of progesterone and estrogen – Promotes placental development via its autocrine growth factor activity – hCG levels rise until end of second month, then decline as placenta begins to secrete progesterone and ...
... – Secreted by trophoblast cells; later chorion – Prompts corpus luteum to continue secretion of progesterone and estrogen – Promotes placental development via its autocrine growth factor activity – hCG levels rise until end of second month, then decline as placenta begins to secrete progesterone and ...
Mediastinum2008-12-31 04:212.4 MB
... 1- Ascending aorta It begins at the base of the left ventricle and runs upward and forward to come to lie behind the right half of the sternum at the level of the sternal angle, where it becomes continuous with the arch of the aorta. It lies within the fibrous pericardium and is enclosed with the pu ...
... 1- Ascending aorta It begins at the base of the left ventricle and runs upward and forward to come to lie behind the right half of the sternum at the level of the sternal angle, where it becomes continuous with the arch of the aorta. It lies within the fibrous pericardium and is enclosed with the pu ...
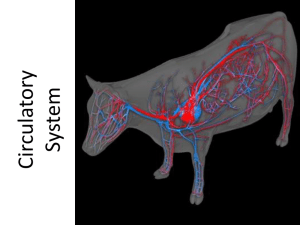
Follow the Circulatory System
... E. Follow the path of a blood cell through the circulatory system ...
... E. Follow the path of a blood cell through the circulatory system ...
Anatomy
... fissure for the ligamentum teres also separates the medial and lateral segments. The medial segment is also called the quadrate lobe. In the widely used Couinaud (or "French") system, the functional lobes are further divided into a total of eight subsegments based on a transverse plane through the ...
... fissure for the ligamentum teres also separates the medial and lateral segments. The medial segment is also called the quadrate lobe. In the widely used Couinaud (or "French") system, the functional lobes are further divided into a total of eight subsegments based on a transverse plane through the ...
Embryology04-CardiovascularSystem
... foramen ovale • Also shunted from pulmonary outflow via ductus arteriorsus ...
... foramen ovale • Also shunted from pulmonary outflow via ductus arteriorsus ...
File
... The systemic circulation Includes the arteries and arterioles that carry blood containing oxygen and nutrients from the left ventricle to systemic capillaries throughout the body, plus the venules and veins that carry blood ...
... The systemic circulation Includes the arteries and arterioles that carry blood containing oxygen and nutrients from the left ventricle to systemic capillaries throughout the body, plus the venules and veins that carry blood ...
Unit 10 Comfort and Discomfort
... a chemical factors: b Physical factors: temperature, incision, c pathological factors: diseases d. Emotional factors: ...
... a chemical factors: b Physical factors: temperature, incision, c pathological factors: diseases d. Emotional factors: ...
Anatomy 3: heart, pericardium, coronary vessels
... o sternopericardial ligaments sternum o Tunica adventitia of vessels (continuous) and pretracheal fascia o Pericardiophrenic ligament central tendon Serous Pericardium Mesothelium- simple squamous epithelium on layer of subserosal CT 2 layers: parietal and visceral (epicardium of heart) o Pari ...
... o sternopericardial ligaments sternum o Tunica adventitia of vessels (continuous) and pretracheal fascia o Pericardiophrenic ligament central tendon Serous Pericardium Mesothelium- simple squamous epithelium on layer of subserosal CT 2 layers: parietal and visceral (epicardium of heart) o Pari ...
Lesson 3 - Mammals - Mother Teresa Regional School
... some of the better known marsupials. Their young are born at an early stage of development, and they usually continue to develop in a pouch on the mother’s body. Marsupials have a very short gestation period. Ex: opossums have a gestation period of 13 days. ...
... some of the better known marsupials. Their young are born at an early stage of development, and they usually continue to develop in a pouch on the mother’s body. Marsupials have a very short gestation period. Ex: opossums have a gestation period of 13 days. ...
heart and blood vessels ppt
... • All 3 tunics are present in small veins • Medium sized veins: collect blood from small veins and deliver to large viens • Large veins: contain valves ...
... • All 3 tunics are present in small veins • Medium sized veins: collect blood from small veins and deliver to large viens • Large veins: contain valves ...
BIO 218 F 2012 CH 21 Martini Lecture Outline
... The Right Ventricle Receives deoxygenated blood from the right atrium Blood enters the ventricle by passing through the tricuspid valve (right atrioventricular valve – right AV valve) The valve is connected to papillary muscles via chordae tendineae Since there are three cusps to the valve, the chor ...
... The Right Ventricle Receives deoxygenated blood from the right atrium Blood enters the ventricle by passing through the tricuspid valve (right atrioventricular valve – right AV valve) The valve is connected to papillary muscles via chordae tendineae Since there are three cusps to the valve, the chor ...
3_Bilaminar Embryo_(week2)
... o Duplication of male haplotype following monospermic fertiliazation of an ovum o Polyspermy (dispermic fertilization of ovum) o W/only paternal chromosomes, fetus will degenerate; h/w trophoblast persists & proliferates o Multivesicular mass w/diffuse hydropic villi fill uterine lumen o Symptoms: v ...
... o Duplication of male haplotype following monospermic fertiliazation of an ovum o Polyspermy (dispermic fertilization of ovum) o W/only paternal chromosomes, fetus will degenerate; h/w trophoblast persists & proliferates o Multivesicular mass w/diffuse hydropic villi fill uterine lumen o Symptoms: v ...
Clinical Anatomy of the Pelvis
... It is generally agreed that episiotomy is indicated when descent of the fetus is arrested or protracted, when instrumentation is necessary (e.g., use of obstetrical forceps), or to expedite delivery when there are signs of fetal distress. However, routine prophylactic episiotomy is widely debated an ...
... It is generally agreed that episiotomy is indicated when descent of the fetus is arrested or protracted, when instrumentation is necessary (e.g., use of obstetrical forceps), or to expedite delivery when there are signs of fetal distress. However, routine prophylactic episiotomy is widely debated an ...
Internal Anatomy and Organization of the Heart
... The Right Ventricle Receives deoxygenated blood from the right atrium Blood enters the ventricle by passing through the tricuspid valve Right atrioventricular valve—right AV valve Blood leaves the ventricle by passing through the pulmonary valve Leads to the pulmonary trunk, then to the ri ...
... The Right Ventricle Receives deoxygenated blood from the right atrium Blood enters the ventricle by passing through the tricuspid valve Right atrioventricular valve—right AV valve Blood leaves the ventricle by passing through the pulmonary valve Leads to the pulmonary trunk, then to the ri ...
Lung Anatomy - Learning
... remain separate – such that three veins leave the right lung and enter the left atrium • The left pulmonary veins may unite and enter the left atrium as a single vessel ...
... remain separate – such that three veins leave the right lung and enter the left atrium • The left pulmonary veins may unite and enter the left atrium as a single vessel ...
Thoracic Cavity Pleural sac Visceral pleura Invests the lung and
... 2 fissures - horizontal, oblique Left lung 2 lobes ...
... 2 fissures - horizontal, oblique Left lung 2 lobes ...
Coronary circulation mgmc
... are provided almost aerobically with little capacity for anaerobic metabolism. • During resting condition, 70 to 80 % of oxygen carried by coronary blood is extracted by the myocardium. • Extraction cant increase on stress but the cardiac output / coronary flow can increase ...
... are provided almost aerobically with little capacity for anaerobic metabolism. • During resting condition, 70 to 80 % of oxygen carried by coronary blood is extracted by the myocardium. • Extraction cant increase on stress but the cardiac output / coronary flow can increase ...
BIOL 218 F 2011 Lecture Outline Ch 21
... The AV bundle travels along the interventricular septum and then divides to form the right and left bundle branches ...
... The AV bundle travels along the interventricular septum and then divides to form the right and left bundle branches ...