3 Normal Early Pregnancy (First Trimester)
... appears as a circular echogenic structure bordering directly on the decidua. High-resolution color Doppler imaging can define maternal blood vessels between the decidua and chorion (Figs. 3.3, 3.4). By establishing this connection with the maternal circulation, the embryo secures the nutritional sup ...
... appears as a circular echogenic structure bordering directly on the decidua. High-resolution color Doppler imaging can define maternal blood vessels between the decidua and chorion (Figs. 3.3, 3.4). By establishing this connection with the maternal circulation, the embryo secures the nutritional sup ...
323Lecture14 - Dr. Stuart Sumida
... into inferior vena cava. (As body wall structures, they DON NOT dump into hepatic portal system. ...
... into inferior vena cava. (As body wall structures, they DON NOT dump into hepatic portal system. ...
Prenatal Development Timeline
... Aortic arches 4 and 6 Artery from the common iliac artery feeds each lower limb bud Atrioventricular bundle Cardiac contractions still under myogenic control Celiac artery, superior and inferior mesenteric arteries Circulatory system "well established" Common iliac arteries (right and left, from dor ...
... Aortic arches 4 and 6 Artery from the common iliac artery feeds each lower limb bud Atrioventricular bundle Cardiac contractions still under myogenic control Celiac artery, superior and inferior mesenteric arteries Circulatory system "well established" Common iliac arteries (right and left, from dor ...
Left Coronary Artery
... Pulmonary trunk. At the inferior border of the heart it continues posteriorly along the atrioventricular groove . Anastomoses with the left coronary artery in the posterior interventricular groove. ...
... Pulmonary trunk. At the inferior border of the heart it continues posteriorly along the atrioventricular groove . Anastomoses with the left coronary artery in the posterior interventricular groove. ...
Heart Anatomy
... Ramifies on the lowest part of the pulmonary conus and upper part of the right ventricle. Commonly anastomosis with branches from the left coronary artery to form annulus of vieussenis. ...
... Ramifies on the lowest part of the pulmonary conus and upper part of the right ventricle. Commonly anastomosis with branches from the left coronary artery to form annulus of vieussenis. ...
Emergency Ultrasound of the Abdominal Aorta
... Aneurysms enlarge at an average rate of 0.4 cm per year, with a high individual variability Threshold for rupture tends to occur at greater than 5.0 cm in size (22% risk of rupture within 2 years) Risk of rupture is estimated at 1-3% per year for aneurysms 4-5 cm; 6-11% per year for aneurysms 5-7 cm ...
... Aneurysms enlarge at an average rate of 0.4 cm per year, with a high individual variability Threshold for rupture tends to occur at greater than 5.0 cm in size (22% risk of rupture within 2 years) Risk of rupture is estimated at 1-3% per year for aneurysms 4-5 cm; 6-11% per year for aneurysms 5-7 cm ...
right and left brachiocephalic veins
... vena cava (SC ); the azygos vein; arch of the aorta and the descending thoracic aorta; pulmonary trunk, right and left pulmonary arteries and ligamentum arteriosum connecting the aortic arch and left pulmonary artery noting the course of the left recurrent laryngeal nerve hooking below the ligamentu ...
... vena cava (SC ); the azygos vein; arch of the aorta and the descending thoracic aorta; pulmonary trunk, right and left pulmonary arteries and ligamentum arteriosum connecting the aortic arch and left pulmonary artery noting the course of the left recurrent laryngeal nerve hooking below the ligamentu ...
Incompetent Cervix and Cerclage
... the bag of waters that surrounds the baby ruptures. The result is usually miscarriage or delivery of a premature baby. An incompetent cervix may be the result of a birth defect. If a woman’s mother took the drug diethylstilbestrol (DES) during pregnancy, it may have caused an abnormality in the cerv ...
... the bag of waters that surrounds the baby ruptures. The result is usually miscarriage or delivery of a premature baby. An incompetent cervix may be the result of a birth defect. If a woman’s mother took the drug diethylstilbestrol (DES) during pregnancy, it may have caused an abnormality in the cerv ...
9/30/09 Abdomen Continued Ureters: They are muscular ducts
... comes off of the diaphragm. The kidneys receive 20-25% of Cardiac Output at rest and thus, the most active tissue in the body. Each of those arteries enters the hilum (a doorway) and divides into 5 segmental arteries. The right renal artery is lower than the left renal artery due to space (this is b ...
... comes off of the diaphragm. The kidneys receive 20-25% of Cardiac Output at rest and thus, the most active tissue in the body. Each of those arteries enters the hilum (a doorway) and divides into 5 segmental arteries. The right renal artery is lower than the left renal artery due to space (this is b ...
Histological Organization of Blood Vessels
... In areas such as the brain, heart, and stomach, a continuous, rich flow of blood is required In these areas, more than one artery supplies a specific area These arteries (collateral arteries) typically fuse forming an arterial anastomosis If one arteriole is blocked, the other one will suppl ...
... In areas such as the brain, heart, and stomach, a continuous, rich flow of blood is required In these areas, more than one artery supplies a specific area These arteries (collateral arteries) typically fuse forming an arterial anastomosis If one arteriole is blocked, the other one will suppl ...
Thorax Thorax -Thorax is the Superior part of trunk betw neck and
... the thorax from front to back and any fracture will occur usually right in front of this. -Rib fracture in infants and children are rare, due to the ribs elasticity -Fractured ribs are very painful due to movement during ventilation, most of the time they can’t be seen on x-ray -Ribs 1 and 2 (due to ...
... the thorax from front to back and any fracture will occur usually right in front of this. -Rib fracture in infants and children are rare, due to the ribs elasticity -Fractured ribs are very painful due to movement during ventilation, most of the time they can’t be seen on x-ray -Ribs 1 and 2 (due to ...
the heart
... arch of the aorta, thoracic duct, trachea, esophagus, thymus, vagus, leB recurrent laryngeal, and phrenic nerves. The superior vena cava (SVC) returns blood from all structures superior to the diaphragm, except the lungs and heart. The arch of the aorta (aor5c arch), the curved con2nua2on of ...
... arch of the aorta, thoracic duct, trachea, esophagus, thymus, vagus, leB recurrent laryngeal, and phrenic nerves. The superior vena cava (SVC) returns blood from all structures superior to the diaphragm, except the lungs and heart. The arch of the aorta (aor5c arch), the curved con2nua2on of ...
mediastinum - Yeditepe University Pharma Anatomy
... Provide the anchoring attachment (origin) of many of the muscles that move and maintain the position of the upper limbs relative to the trunk, as well as provide the attachments for muscles of the abdomen, neck, back, and respiration. The thorax is one of the most dynamic regions of the body. ...
... Provide the anchoring attachment (origin) of many of the muscles that move and maintain the position of the upper limbs relative to the trunk, as well as provide the attachments for muscles of the abdomen, neck, back, and respiration. The thorax is one of the most dynamic regions of the body. ...
Cardiac Anatomy
... ventricular output reaches the lungs. The blood follows the descending aorta and returns to the placenta via the umbilical arteries. By the third month, the heart and major vessels are formed. However, the transition to the adult circulation occurs shortly after birth, when the umbilical cord is cut ...
... ventricular output reaches the lungs. The blood follows the descending aorta and returns to the placenta via the umbilical arteries. By the third month, the heart and major vessels are formed. However, the transition to the adult circulation occurs shortly after birth, when the umbilical cord is cut ...
4.3.3 Go With The Flow
... 4. Bring the strand forward to the fold of the elbow (antecubital region). Angle the strand to run along the medial side of the radius down towards the palm. The strand running along the radius represents the radial artery. 5. Curve the strand back around so it begins traveling up the medial side o ...
... 4. Bring the strand forward to the fold of the elbow (antecubital region). Angle the strand to run along the medial side of the radius down towards the palm. The strand running along the radius represents the radial artery. 5. Curve the strand back around so it begins traveling up the medial side o ...
Fetal Pig I External and Ventral Body Cavity Anatomy Introduction to
... All students are required to wash their hands, tools and bench with soap and water after they have completed the dissection activities. Razor blades are always disposed of in the biohazard container. Used razor blades and scalpel blades must be disposed of in the biohazard container. It is important ...
... All students are required to wash their hands, tools and bench with soap and water after they have completed the dissection activities. Razor blades are always disposed of in the biohazard container. Used razor blades and scalpel blades must be disposed of in the biohazard container. It is important ...
Physical Therapy Intervention of Low Back Pain
... Physical therapy examination ? Must take a good history to have a clear clinical presentation ? Where is the pain – back ( central / symmetrical, unilateral / asymmetrical) Is the pain in the back, thigh or referred to below the knee ? When did it start - Is it acute, sub-acute, chronic ? Is the pai ...
... Physical therapy examination ? Must take a good history to have a clear clinical presentation ? Where is the pain – back ( central / symmetrical, unilateral / asymmetrical) Is the pain in the back, thigh or referred to below the knee ? When did it start - Is it acute, sub-acute, chronic ? Is the pai ...
Blood Supply of Barin
... Nearly half of the admissions to many busy neurologic services are because of strokes. Cerebrovascular disease is the third most common cause of death. ...
... Nearly half of the admissions to many busy neurologic services are because of strokes. Cerebrovascular disease is the third most common cause of death. ...
EZMP1640 Arterial and Veneo Arterial and
... to this termination. The internal carotid arteries (ICAs) can be traced from the point where they enter the petrous portion of the temporal bone via the carotid canal and travel medially and anteriorly to emerge on the superior margin of the foramen lacerum. lacerum. It is here that each ICA lies wi ...
... to this termination. The internal carotid arteries (ICAs) can be traced from the point where they enter the petrous portion of the temporal bone via the carotid canal and travel medially and anteriorly to emerge on the superior margin of the foramen lacerum. lacerum. It is here that each ICA lies wi ...
12 c h a p t e r The Circulatory System
... than those in the right ventricle. These chordae tendineae and papillary muscles keep the bicuspid valve from inverting into the left atrium when the left ventricle contracts. The opening by which the aorta leaves the left ventricle is closed by a semilunar valve called the aortic semilunar valve (s ...
... than those in the right ventricle. These chordae tendineae and papillary muscles keep the bicuspid valve from inverting into the left atrium when the left ventricle contracts. The opening by which the aorta leaves the left ventricle is closed by a semilunar valve called the aortic semilunar valve (s ...
Angiology_SLDC
... ***All of the blood drained from the internal organs, lower extremities and hepatic portal circulation eventually drains into the inferior vena cava which in turn empties into the right atrium of the heart ...
... ***All of the blood drained from the internal organs, lower extremities and hepatic portal circulation eventually drains into the inferior vena cava which in turn empties into the right atrium of the heart ...
Midwifery 1 150363
... -Mammory glands are composed of glandular tissue and a variable amount of fat. They are also have a complex secretory product called breast milk. Breast milk travels through a passageway called the Lactiferous duct, which travels from the alveoli to the nipple. The nipple is a centrally located proj ...
... -Mammory glands are composed of glandular tissue and a variable amount of fat. They are also have a complex secretory product called breast milk. Breast milk travels through a passageway called the Lactiferous duct, which travels from the alveoli to the nipple. The nipple is a centrally located proj ...
I. Introduction
... 11. Chordae tendinae are fibrous strings and function to prevent cusps of A-V valves from swinging back into atria. 12. Papillary muscles are located in ventricular walls and contract when the ventricles contract. 13. The right ventricle receives blood from the right atrium. 14. The right ventricle ...
... 11. Chordae tendinae are fibrous strings and function to prevent cusps of A-V valves from swinging back into atria. 12. Papillary muscles are located in ventricular walls and contract when the ventricles contract. 13. The right ventricle receives blood from the right atrium. 14. The right ventricle ...
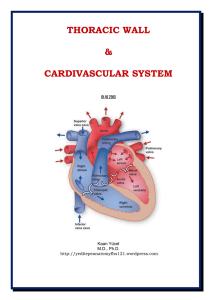
Dr.Kaan Yücel yeditepeanatomyfhs121.wordpress.com Thoracic
... six minutes without blood travelling in our vessels. You can see the heart as a self-adjusting suction and pressure pump, function of which is to send blood to all parts of the body. 2.1. The two sides of the heart: right heart & left heart The right side of the heart (right heart) receives poorly o ...
... six minutes without blood travelling in our vessels. You can see the heart as a self-adjusting suction and pressure pump, function of which is to send blood to all parts of the body. 2.1. The two sides of the heart: right heart & left heart The right side of the heart (right heart) receives poorly o ...