SUMMARY TERMS-Thoracic Cavity
... the SA node and passes them to the R. and L. AV bundles Sinoatrial (SA) node-can be found in the superior part of the Cristae terminalis; consist of Purkinje fibers; pacemaker of the heart; automatic depolarization initiates impulses at 70/min; impulse spreads through atria to the AV node; electrica ...
... the SA node and passes them to the R. and L. AV bundles Sinoatrial (SA) node-can be found in the superior part of the Cristae terminalis; consist of Purkinje fibers; pacemaker of the heart; automatic depolarization initiates impulses at 70/min; impulse spreads through atria to the AV node; electrica ...
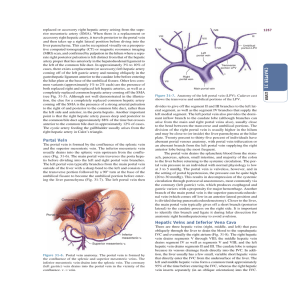
CHAPTER 31 Portal Vein Hepatic Veins and Inferior
... replaced or accessory right hepatic artery arising from the superior mesenteric artery (SMA). When there is a replacement or accessory right hepatic artery, it travels posterior to the portal vein and then takes up a right lateral position before diving into the liver parenchyma. This can be recogni ...
... replaced or accessory right hepatic artery arising from the superior mesenteric artery (SMA). When there is a replacement or accessory right hepatic artery, it travels posterior to the portal vein and then takes up a right lateral position before diving into the liver parenchyma. This can be recogni ...
The Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels and Circulation
... Fluid moves No net movement into capillary of fluid ...
... Fluid moves No net movement into capillary of fluid ...
Complete Pig Manual
... Locate the following parts of the head: Snout - The snout of the pig has a blunt tip, ending with a disc-like, pliable but firm structure composed of cartilage. The tip of the nose is also strengthened by bone. This permits the pig to use the snout to push, lift weights and dig. External Nares - The ...
... Locate the following parts of the head: Snout - The snout of the pig has a blunt tip, ending with a disc-like, pliable but firm structure composed of cartilage. The tip of the nose is also strengthened by bone. This permits the pig to use the snout to push, lift weights and dig. External Nares - The ...
Liver& biliary
... The posteroinferior or visceral surface is irregular in shape. It lies in contact with the abdominal part of the esophagus (1 ); stomach; duodenum; right colic flexure; right kidney; suprarenal gland ( 2 ) and the gallbladder. The porta hepatis ( hilum of the liver ) lies on this surface. It lies be ...
... The posteroinferior or visceral surface is irregular in shape. It lies in contact with the abdominal part of the esophagus (1 ); stomach; duodenum; right colic flexure; right kidney; suprarenal gland ( 2 ) and the gallbladder. The porta hepatis ( hilum of the liver ) lies on this surface. It lies be ...
Gastro17-GITractPt1
... but last year there were 20 questions from the Gross Anatomy lectures. Also, there will be a lot of changes on this year’s test. This year there will be more questions given in the form of clinical applications. So, pay close attention to the clinical examples given in the lectures. Understand that ...
... but last year there were 20 questions from the Gross Anatomy lectures. Also, there will be a lot of changes on this year’s test. This year there will be more questions given in the form of clinical applications. So, pay close attention to the clinical examples given in the lectures. Understand that ...
Reproduction - Male
... Prevention of bacteria and other large molecular substances from dam to young. The secretion of certain hormones; HCG (woman) and PMSG (mare), and ...
... Prevention of bacteria and other large molecular substances from dam to young. The secretion of certain hormones; HCG (woman) and PMSG (mare), and ...
Aortic pathology
... Splenic A; SA- is on its way to the spleen, tortuous and difficult to visualize, courses superior to Panc. Supplies spleen , panc, lt side of greater curvature. LGA (Lt. Gastric A.) - Usually not seen on US. Courses superior and to the left. Supplies left side of the lesser curvature and eventually ...
... Splenic A; SA- is on its way to the spleen, tortuous and difficult to visualize, courses superior to Panc. Supplies spleen , panc, lt side of greater curvature. LGA (Lt. Gastric A.) - Usually not seen on US. Courses superior and to the left. Supplies left side of the lesser curvature and eventually ...
The Goofy anatomist`s thorax
... with sensory nerves. Also…Can’t be B, because the intercostal nerves supply the costal and peripheral diaphragmatic pleurae and the intercostal muscles. Can’t be C, because the phrenic nerve supplies the mediastinal and diaphragmatic pleurae and the muscular diaphragm. Can’t be D, because the viscer ...
... with sensory nerves. Also…Can’t be B, because the intercostal nerves supply the costal and peripheral diaphragmatic pleurae and the intercostal muscles. Can’t be C, because the phrenic nerve supplies the mediastinal and diaphragmatic pleurae and the muscular diaphragm. Can’t be D, because the viscer ...
Matthew Smuck, MD
... – Listen - Claudication with activity, not while standing – Feel - localized gluteal tenderness, no other provocation – Feel - normal neuro, diminished pedal pulses on the right ...
... – Listen - Claudication with activity, not while standing – Feel - localized gluteal tenderness, no other provocation – Feel - normal neuro, diminished pedal pulses on the right ...
Thorax
... collaterals (arrowheads). -After stent placement, extending from the left subclavian vein into the superior vena cava, the patient felt better within a day, and was back to baseline at 27 days (Panel C), the venogram (Panel D) -14 months after the procedure and chemotherapy, remains free of symptoms ...
... collaterals (arrowheads). -After stent placement, extending from the left subclavian vein into the superior vena cava, the patient felt better within a day, and was back to baseline at 27 days (Panel C), the venogram (Panel D) -14 months after the procedure and chemotherapy, remains free of symptoms ...
ID_113_Topographical anatomy and oper_English_sem_
... It ends at the confluence of the right subclavian and brachiocephalic veins In most of its course it lies behind the esophagus It contains valves Which of the following statements is correct in relation to thoracic splanchnic nerves? Their fibers relay in the sympathetic ganglion chain They are part ...
... It ends at the confluence of the right subclavian and brachiocephalic veins In most of its course it lies behind the esophagus It contains valves Which of the following statements is correct in relation to thoracic splanchnic nerves? Their fibers relay in the sympathetic ganglion chain They are part ...
Abdominal Cavity III
... gastrointestinal tract, spleen, pancreas, gallbladder - all delivered to liver • Portal vein is formed by junction of splenic vein & superior mesenteric vein - posterior to pancreas – splenic vein • small splenic vein • short gastric vein • left gastroepiploic vein ...
... gastrointestinal tract, spleen, pancreas, gallbladder - all delivered to liver • Portal vein is formed by junction of splenic vein & superior mesenteric vein - posterior to pancreas – splenic vein • small splenic vein • short gastric vein • left gastroepiploic vein ...
Major arteries of the body
... from each part. List major arteries and their distribution in the head & neck, thorax, abdomen and upper & lower extremities. List main pulse points. ...
... from each part. List major arteries and their distribution in the head & neck, thorax, abdomen and upper & lower extremities. List main pulse points. ...
Jon Storm-Mathisen - Universitetet i Oslo
... You must know a fair number of names to able to communicate.. ..but don’t get lost in details The real challenge is to establish ones own internal three-dimensional pictures Therefore: spend ample time with prosected specimens, models and microscopic slides ...
... You must know a fair number of names to able to communicate.. ..but don’t get lost in details The real challenge is to establish ones own internal three-dimensional pictures Therefore: spend ample time with prosected specimens, models and microscopic slides ...
Peripheral Vascular Anatomy
... Behind the sternoclavicular joint in the internal jugular vein to become the brachiocephalic vein (innominate) Commencing from the axillary vein medially it receives flow from the external jugular vein, progressing anterior to the anterior scalene muscle which separtates the SCV and artery. It cross ...
... Behind the sternoclavicular joint in the internal jugular vein to become the brachiocephalic vein (innominate) Commencing from the axillary vein medially it receives flow from the external jugular vein, progressing anterior to the anterior scalene muscle which separtates the SCV and artery. It cross ...
Major arteries of the body
... At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: Define the word ‘artery’ and understand the general principles of the arterial system. Define arterial anastomosis and describe its significance. Define end arteries and give examples. Describe the aorta and its divisions & list the branches ...
... At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: Define the word ‘artery’ and understand the general principles of the arterial system. Define arterial anastomosis and describe its significance. Define end arteries and give examples. Describe the aorta and its divisions & list the branches ...
2-Copy of MAJOR ARTERIES OF BODY-PROF AHMED
... At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: Define the word ‘artery’ and understand the general principles of the arterial system. Define arterial anastomosis and describe its significance. Define end arteries and give examples. Describe the aorta and its divisions & list the branches ...
... At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: Define the word ‘artery’ and understand the general principles of the arterial system. Define arterial anastomosis and describe its significance. Define end arteries and give examples. Describe the aorta and its divisions & list the branches ...
Arteries and Veins Worksheet
... 4) The hepatic portal vein drains the digestive tract organs and carries this blood through the liver before it enters the systemic circulation. The hepatic veins drain the liver. 5) The internal iliac vein drains blood from the rectum and tissue of the bladder. 6) The common iliac vein which is for ...
... 4) The hepatic portal vein drains the digestive tract organs and carries this blood through the liver before it enters the systemic circulation. The hepatic veins drain the liver. 5) The internal iliac vein drains blood from the rectum and tissue of the bladder. 6) The common iliac vein which is for ...
4 BloodVessels
... True capillaries – exchange vessels o Oxygen and nutrients cross to cells o Carbon dioxide and metabolic waste products cross into blood ...
... True capillaries – exchange vessels o Oxygen and nutrients cross to cells o Carbon dioxide and metabolic waste products cross into blood ...
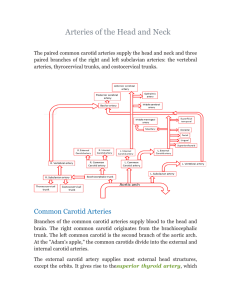
Arteries of the Head and Neck
... branches of the subclavian artery. Two bronchial arteries on the left and one on the right deliver systemic blood to the lung structures, including the visceral pleura, esophagus, and bronchi of lungs. Blood is also delivered to the esophagus by the four or five esophageal arteries. Numerous small m ...
... branches of the subclavian artery. Two bronchial arteries on the left and one on the right deliver systemic blood to the lung structures, including the visceral pleura, esophagus, and bronchi of lungs. Blood is also delivered to the esophagus by the four or five esophageal arteries. Numerous small m ...