Macroanatomy of the Azygos Vein: A Comparative Description
... from the lower three posterior intercostal veins, a common trunk formed by the left ascending lumbar and subcostal veins, and by esophageal and mediastinal tributaries. It was ascended anterior of the vertebral column to the eighth thoracic level then crossed the vertebral column posterior to the ao ...
... from the lower three posterior intercostal veins, a common trunk formed by the left ascending lumbar and subcostal veins, and by esophageal and mediastinal tributaries. It was ascended anterior of the vertebral column to the eighth thoracic level then crossed the vertebral column posterior to the ao ...
Dissector Bold terms 3
... -Sigmoid colon (ends in pelvic cavity at 3rd sacral vertebral level) -Rectum (located in pelvis) -Lesser omentum (hepatogastric ligament/ hepatoduodenal ligament) -Round ligament of the liver (ligamentum teres hepatis): umbilical vein -Transverse mesocolon (phrenicocolic ligament) ...
... -Sigmoid colon (ends in pelvic cavity at 3rd sacral vertebral level) -Rectum (located in pelvis) -Lesser omentum (hepatogastric ligament/ hepatoduodenal ligament) -Round ligament of the liver (ligamentum teres hepatis): umbilical vein -Transverse mesocolon (phrenicocolic ligament) ...
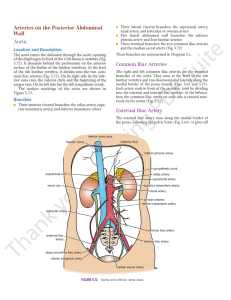
Arteries
... • Formed when capillary beds unite – Smallest postcapillary venules – Very porous; allow fluids and WBCs into tissues – Consist of endothelium and a few pericytes ...
... • Formed when capillary beds unite – Smallest postcapillary venules – Very porous; allow fluids and WBCs into tissues – Consist of endothelium and a few pericytes ...
full text pdf
... hilum, they are placed anterior to the arterial branches, which are located anterior to the bronchi [1.2]. According to [3 and 5], within the lung parenchyma, the pulmonary veins have an independent traject, as they move towards the pulmonary hilum. According to [6], the superior right pulmonary vei ...
... hilum, they are placed anterior to the arterial branches, which are located anterior to the bronchi [1.2]. According to [3 and 5], within the lung parenchyma, the pulmonary veins have an independent traject, as they move towards the pulmonary hilum. According to [6], the superior right pulmonary vei ...
Slide 1
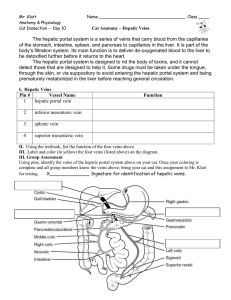
... gastric vein, right gastric vein, and cystic veins. Splenic vein: This vein leaves the hilum of the spleen and passes to the right in the splenicorenal ligament. It unites with the superior mesenteric vein behind the neck of the pancreas to form the portal vein . It receives the short gastric, left ...
... gastric vein, right gastric vein, and cystic veins. Splenic vein: This vein leaves the hilum of the spleen and passes to the right in the splenicorenal ligament. It unites with the superior mesenteric vein behind the neck of the pancreas to form the portal vein . It receives the short gastric, left ...
Arteries - Princeton ISD
... during breathing suck blood toward the heart by squeezing local veins Muscular “pump” – contraction of skeletal muscles “milk” blood toward the heart ...
... during breathing suck blood toward the heart by squeezing local veins Muscular “pump” – contraction of skeletal muscles “milk” blood toward the heart ...
Surgical and angiographic anatomy of the posterior
... bands or rarely it might lie within a sulcus in the posterior clinoid process. During manipulations and dissection of the artery this variations should be kept in mind. An important anatomical landmark in surgical anatomy of the PComA is the oculomotor nerve, which enters the dura lateral to the pos ...
... bands or rarely it might lie within a sulcus in the posterior clinoid process. During manipulations and dissection of the artery this variations should be kept in mind. An important anatomical landmark in surgical anatomy of the PComA is the oculomotor nerve, which enters the dura lateral to the pos ...
Tributaries of the hepatic portal vein
... The left gastroepiploic vein (v. gastroepiploica sinistra) receives branches from the antero-superior and posteroinferior surfaces of the stomach and from the greater omentum; it runs from right to left along the greater curvature of the stomach and ends in the commencement of the lienal vein. The p ...
... The left gastroepiploic vein (v. gastroepiploica sinistra) receives branches from the antero-superior and posteroinferior surfaces of the stomach and from the greater omentum; it runs from right to left along the greater curvature of the stomach and ends in the commencement of the lienal vein. The p ...
Superficial Veins of Upper Limbs
... (a) Diagram of veins in a forearm showing the antecubital fossa area where blood samples are taken, (b) Venous blood sample being taken from a vein in the antecubital fossa using a venepuncture vacuum system. ...
... (a) Diagram of veins in a forearm showing the antecubital fossa area where blood samples are taken, (b) Venous blood sample being taken from a vein in the antecubital fossa using a venepuncture vacuum system. ...
Common Iliac Arteries External Iliac Artery EMBRYOLOGIC NOTES
... body below the diaphragm to the right atrium of the heart. It is formed by the union of the common iliac veins behind the right common iliac artery at the level of the 5th lumbar vertebra (Fig. 5.72). It ascends on the right side of the aorta, pierces the central tendon of the diaphragm at the level ...
... body below the diaphragm to the right atrium of the heart. It is formed by the union of the common iliac veins behind the right common iliac artery at the level of the 5th lumbar vertebra (Fig. 5.72). It ascends on the right side of the aorta, pierces the central tendon of the diaphragm at the level ...
Posterior abdominal wall
... gastric vein, right gastric vein, and cystic veins. Splenic vein: This vein leaves the hilum of the spleen and passes to the right in the splenicorenal ligament. It unites with the superior mesenteric vein behind the neck of the pancreas to form the portal vein . It receives the short gastric, left ...
... gastric vein, right gastric vein, and cystic veins. Splenic vein: This vein leaves the hilum of the spleen and passes to the right in the splenicorenal ligament. It unites with the superior mesenteric vein behind the neck of the pancreas to form the portal vein . It receives the short gastric, left ...
PPT
... gastric vein, right gastric vein, and cystic veins. Splenic vein: This vein leaves the hilum of the spleen and passes to the right in the splenicorenal ligament. It unites with the superior mesenteric vein behind the neck of the pancreas to form the portal vein . It receives the short gastric, left ...
... gastric vein, right gastric vein, and cystic veins. Splenic vein: This vein leaves the hilum of the spleen and passes to the right in the splenicorenal ligament. It unites with the superior mesenteric vein behind the neck of the pancreas to form the portal vein . It receives the short gastric, left ...
Inferior Mesenteric Vein
... gastric vein, right gastric vein, and cystic veins. Splenic vein: This vein leaves the hilum of the spleen and passes to the right in the splenicorenal ligament. It unites with the superior mesenteric vein behind the neck of the pancreas to form the portal vein . It receives the short gastric, left ...
... gastric vein, right gastric vein, and cystic veins. Splenic vein: This vein leaves the hilum of the spleen and passes to the right in the splenicorenal ligament. It unites with the superior mesenteric vein behind the neck of the pancreas to form the portal vein . It receives the short gastric, left ...
Misc Anatomy - Notes For ANZCA Primary Exam
... • @ lowest corner of fossa splits into: ‣ anterior tibial artery ‣ posterior tibial artery Anterior Tibial Artery • passes through opening at top of interosseous membrane ⟹ into ant compartment • runs down on ant aspect of IO membrane • passes under extensor retinaculum between EHL & EDL • on top of ...
... • @ lowest corner of fossa splits into: ‣ anterior tibial artery ‣ posterior tibial artery Anterior Tibial Artery • passes through opening at top of interosseous membrane ⟹ into ant compartment • runs down on ant aspect of IO membrane • passes under extensor retinaculum between EHL & EDL • on top of ...
intestine rectum aorta vena cava
... The teniae coli, thickened bands of smooth muscle represenAng most of the longitudinal coat, begin at the base of the appendix as the thick longitudinal layer of the appendix separates into three bands. ...
... The teniae coli, thickened bands of smooth muscle represenAng most of the longitudinal coat, begin at the base of the appendix as the thick longitudinal layer of the appendix separates into three bands. ...
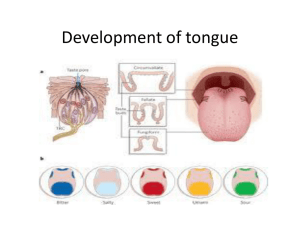
Development of tongue
... Tongue muscles originate from the mesoderm. The tongue muscle develops before masticatory muscles and is completed by birth. Masticatory muscles :originate from loose masses of the mesoderm. These muscles develop late and are not complete even at birth. Masticatory muscles develop muscle fibers wit ...
... Tongue muscles originate from the mesoderm. The tongue muscle develops before masticatory muscles and is completed by birth. Masticatory muscles :originate from loose masses of the mesoderm. These muscles develop late and are not complete even at birth. Masticatory muscles develop muscle fibers wit ...
21-7 The Systemic Circuit
... to his retirement from corporate work. His blood pressure was >180/115 on three separate days. Further examination showed normal to low plasma renin activity, elevated total peripheral resistance (TPR), cardiac output (CO) of 7.2 L/min (normal approx 5L/min), x-ray evidence of left ventricular hyper ...
... to his retirement from corporate work. His blood pressure was >180/115 on three separate days. Further examination showed normal to low plasma renin activity, elevated total peripheral resistance (TPR), cardiac output (CO) of 7.2 L/min (normal approx 5L/min), x-ray evidence of left ventricular hyper ...
Development of the human knee joint
... specimens they examined, signs of chondrification were evident during O’Rahilly stage 21. Walmsley (1940) reported the earliest signs of chondrification in 30-mm embryos, whereas McDermott (1943) distinguished this phenomenon during fetal development at 9 and 10 weeks. The epiphysis of the femur and ...
... specimens they examined, signs of chondrification were evident during O’Rahilly stage 21. Walmsley (1940) reported the earliest signs of chondrification in 30-mm embryos, whereas McDermott (1943) distinguished this phenomenon during fetal development at 9 and 10 weeks. The epiphysis of the femur and ...
Azygos vein cannulation - The Southwest Respiratory and Critical
... the distal port of CVC showed an oxygen saturation of 94%. Connection of the CVC to a pressure transducer revealed venous wave forms with a pressure of 7 mmHg. The CVC was noted to be in the superior vena cava with the tip turned medially in the chest x-ray (Figure 1). Although return of spontaneous ...
... the distal port of CVC showed an oxygen saturation of 94%. Connection of the CVC to a pressure transducer revealed venous wave forms with a pressure of 7 mmHg. The CVC was noted to be in the superior vena cava with the tip turned medially in the chest x-ray (Figure 1). Although return of spontaneous ...
Triple arterial blood supply to the liver and double cystic arteries: A
... lateral lobe is supplied by the left EA, originating from LGA; the central lobe is supplied by the middle EA from the CT; and the right lateral lobe is supplied by the right EA from the SMA. The three aforementioned embryonic arteries (left, middle and right) anastomose in the hepatic hilum. The cen ...
... lateral lobe is supplied by the left EA, originating from LGA; the central lobe is supplied by the middle EA from the CT; and the right lateral lobe is supplied by the right EA from the SMA. The three aforementioned embryonic arteries (left, middle and right) anastomose in the hepatic hilum. The cen ...
electrical anatomy of the atrial chambers
... So as to account fully for any threedimensional structure, it is always necessary to account for its three orthogonal planes. In this context, the heart has its own sets of orthogonal planes, two in the long and one in the short axes (Figure 1). It does not help the clinician, however, to use the in ...
... So as to account fully for any threedimensional structure, it is always necessary to account for its three orthogonal planes. In this context, the heart has its own sets of orthogonal planes, two in the long and one in the short axes (Figure 1). It does not help the clinician, however, to use the in ...
Caput medusa sign
... AXIAL NON FUSION: The 3 segments that are constitutive of the BAs remain discontinuous: CAUDAL ‘‘vertebral’’ segment that supplies the PICAs only; INTERMEDIATE ‘‘trigeminal’’ segment that supplies the AICA, ASCA, and the pontine perforators ; CRANIAL ‘‘carotid’’ segment that supplies the PCAs Right ...
... AXIAL NON FUSION: The 3 segments that are constitutive of the BAs remain discontinuous: CAUDAL ‘‘vertebral’’ segment that supplies the PICAs only; INTERMEDIATE ‘‘trigeminal’’ segment that supplies the AICA, ASCA, and the pontine perforators ; CRANIAL ‘‘carotid’’ segment that supplies the PCAs Right ...
The morphogenesis of human sphincter urethrae muscle
... (Braus and Elze 1924),a dorsally open arch or a horseshoeshapedformation, particularly in the upper portion of the sphincter(Henle 1866; Oerlich 1980),were described. In terms of clinical urology the male m. sphincterurethrae envelops the membranous as well as a portion of the prostatic part of the ...
... (Braus and Elze 1924),a dorsally open arch or a horseshoeshapedformation, particularly in the upper portion of the sphincter(Henle 1866; Oerlich 1980),were described. In terms of clinical urology the male m. sphincterurethrae envelops the membranous as well as a portion of the prostatic part of the ...
Blood Flow
... • Delivery of O2 and nutrients to, and removal of wastes from, tissue cells • Gas exchange (lungs) • Absorption of nutrients (digestive tract) • Urine formation (kidneys) ...
... • Delivery of O2 and nutrients to, and removal of wastes from, tissue cells • Gas exchange (lungs) • Absorption of nutrients (digestive tract) • Urine formation (kidneys) ...
Labeled diagram of the foramen magnum
... Draw an arrow and write a label on Diagram 2 to indicate the. Look at the skulls and determine the position of the foramen magnum – is its position on the anatomy of the inferior skull including: the foramen magnum, occipital condyles, mastoid. .. Labeled diagrams will be very important in a physiol ...
... Draw an arrow and write a label on Diagram 2 to indicate the. Look at the skulls and determine the position of the foramen magnum – is its position on the anatomy of the inferior skull including: the foramen magnum, occipital condyles, mastoid. .. Labeled diagrams will be very important in a physiol ...