Bilateral double testicular arteries: a case report and review of the
... As regards the embryological development of the gonads, the latter ones are supplied from mesonephric arteries originated from the lateral aspect of aorta. In particular, nine pairs of lateral mesonephric arteries exist, constituting a cranial group from the first and second mesonephric artery arisi ...
... As regards the embryological development of the gonads, the latter ones are supplied from mesonephric arteries originated from the lateral aspect of aorta. In particular, nine pairs of lateral mesonephric arteries exist, constituting a cranial group from the first and second mesonephric artery arisi ...
17-Vascular anatomy of lower limb2017-01-12 19
... o It enters the anterior compartment of the leg through an opening in the upper part of the interosseous membrane). Where it descends with (company with) the Deep Peroneal nerve. o It supplies structures in the Anterior Compartment of the Leg & Dorsum of foot. o In its upper part, it is Deep. In its ...
... o It enters the anterior compartment of the leg through an opening in the upper part of the interosseous membrane). Where it descends with (company with) the Deep Peroneal nerve. o It supplies structures in the Anterior Compartment of the Leg & Dorsum of foot. o In its upper part, it is Deep. In its ...
The forensic and surgical importance of anatomical variation. The
... development of the azygos vein and the lungs, there is a possibility for supernumerary pulmonary lobes to develop such as the lobe of the azygos vein [4]. ...
... development of the azygos vein and the lungs, there is a possibility for supernumerary pulmonary lobes to develop such as the lobe of the azygos vein [4]. ...
An unusual popliteal vein and its clinical
... The variable pattern of popliteal vein formation presented in this case strengthens the previous research by ...
... The variable pattern of popliteal vein formation presented in this case strengthens the previous research by ...
this PDF file
... The Council for Postgraduate Study of the Faculty of Medicine in Niš at this time gave permission to investigate the fetal material. The arteries of fetuses were injected with Micropaque or latex through the left cardiac ventricle or through the common carotid artery. All fetuses were fixed in 10% f ...
... The Council for Postgraduate Study of the Faculty of Medicine in Niš at this time gave permission to investigate the fetal material. The arteries of fetuses were injected with Micropaque or latex through the left cardiac ventricle or through the common carotid artery. All fetuses were fixed in 10% f ...
Bilateral absence of ovarian artery in a Tanzanian female cadaver: a
... vaginal fornix. Once the vessel reaches the cervix, it ascends along the lateral margin of the uterus to reach the uterine tube where it curves laterally and anastomoses with the ovarian artery [2]. It occasionally supplies branches that may be designated as superior vesical, inferior vesical, urete ...
... vaginal fornix. Once the vessel reaches the cervix, it ascends along the lateral margin of the uterus to reach the uterine tube where it curves laterally and anastomoses with the ovarian artery [2]. It occasionally supplies branches that may be designated as superior vesical, inferior vesical, urete ...
Origins of the Segmental Arteries in the Aorta
... G). Each segmental artery ran upward to reach the middle region of the corresponding vertebral body, so the ascending course was more apparent in the upper thoracic region. As a result of the location of the origin, the arteries in the upper thoracic level, the third to sixth, ran upward markedly to ...
... G). Each segmental artery ran upward to reach the middle region of the corresponding vertebral body, so the ascending course was more apparent in the upper thoracic region. As a result of the location of the origin, the arteries in the upper thoracic level, the third to sixth, ran upward markedly to ...
Veins of the Head and neck
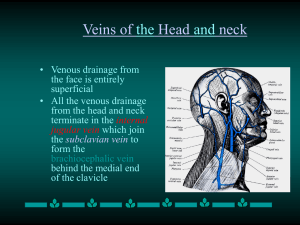
... • Venous drainage from the face is entirely superficial • All the venous drainage from the head and neck terminate in the internal jugular vein which join the subclavian vein to form the brachiocephalic vein behind the medial end of the clavicle ...
... • Venous drainage from the face is entirely superficial • All the venous drainage from the head and neck terminate in the internal jugular vein which join the subclavian vein to form the brachiocephalic vein behind the medial end of the clavicle ...
[ PDF ] - journal of evidence based medicine and
... INTRODUCTION: The clavicle (collar bone) is an unusual long bone which has many unique embryologic features. It is the first bone to ossify and intramembranous in origin.[1] It is a horizontally placed, ‘f’ shaped, tubular bone that connects the appendicular and axial skeletons. It was described tha ...
... INTRODUCTION: The clavicle (collar bone) is an unusual long bone which has many unique embryologic features. It is the first bone to ossify and intramembranous in origin.[1] It is a horizontally placed, ‘f’ shaped, tubular bone that connects the appendicular and axial skeletons. It was described tha ...
Anatomical variation in position, direction, and number of nutrient
... bone. In this study, all the clavicles had at least one nutrient foramen.[7] Total number of foramina in clavicles was 82, and we observed that most of the clavicles (52%) had two foramina. Most of the foramina were in middle 1/3rd region (72%) and in 66.1% clavicles. Also, most of the nutrient fora ...
... bone. In this study, all the clavicles had at least one nutrient foramen.[7] Total number of foramina in clavicles was 82, and we observed that most of the clavicles (52%) had two foramina. Most of the foramina were in middle 1/3rd region (72%) and in 66.1% clavicles. Also, most of the nutrient fora ...
Specific characteristics of innervation of gluteal muscles in the
... the methods of ordinary and fine preparation under the control of binocular loupe and morphometry. Only those cases when the cause of death was not associated with pathology of the pelvic cavity organs, pelvic cavity muscles and vascular-nervous formations of gluteal area were studied. Investigation ...
... the methods of ordinary and fine preparation under the control of binocular loupe and morphometry. Only those cases when the cause of death was not associated with pathology of the pelvic cavity organs, pelvic cavity muscles and vascular-nervous formations of gluteal area were studied. Investigation ...
Specific characteristics of innervation of gluteal muscles in the
... the area of buttocks and thighs, dermatolipectomy of the buttocks, endoprosthetics of the buttocks with lipofillings, liposaction, deliverance from stretchings and other contour plastics) and reconstructiverestorations plastics of the defects of the perineum and sacrococcygeal area demands from the ...
... the area of buttocks and thighs, dermatolipectomy of the buttocks, endoprosthetics of the buttocks with lipofillings, liposaction, deliverance from stretchings and other contour plastics) and reconstructiverestorations plastics of the defects of the perineum and sacrococcygeal area demands from the ...
multiple vascular variations in a single cadaver:ac ase
... superior mesenteric artery. The accessory renal arteries also seen frequently (1,2,3), especially on the left. They usually enter above or below the renal hilum; if below, the accessory renal arteries crosses anterior to the ureter and on the right side, usually also anterior to the inferior vena ca ...
... superior mesenteric artery. The accessory renal arteries also seen frequently (1,2,3), especially on the left. They usually enter above or below the renal hilum; if below, the accessory renal arteries crosses anterior to the ureter and on the right side, usually also anterior to the inferior vena ca ...
Abnormality of the Foramen Spinosum due to a Variation in the
... regarding the origin, position, and intracranial branches8,9 and several anomalies of this artery6,10–12 have been reported for more than three decades; before that, embryological studies had been conducted to improve knowledge of possible anatomic variations of this important arterial segment.13 Li ...
... regarding the origin, position, and intracranial branches8,9 and several anomalies of this artery6,10–12 have been reported for more than three decades; before that, embryological studies had been conducted to improve knowledge of possible anatomic variations of this important arterial segment.13 Li ...
Veins - Dr. Par Mohammadian
... Venous System: Venules • Formed when capillary beds unite – Smallest postcapillary venules: very porous; allow fluids and WBCs into tissues – Consist of endothelium and a few pericytes ...
... Venous System: Venules • Formed when capillary beds unite – Smallest postcapillary venules: very porous; allow fluids and WBCs into tissues – Consist of endothelium and a few pericytes ...
Where There Is Blood, There Is a Way
... is most commonly an acquired condition, typically caused by malignancy, benign conditions such as mediastinal fibrosis, and iatrogenic causes such as venous catheterization. In the event of chronic occlusion, collateral pathways must develop to maintain venous drainage. The major collateral pathways ...
... is most commonly an acquired condition, typically caused by malignancy, benign conditions such as mediastinal fibrosis, and iatrogenic causes such as venous catheterization. In the event of chronic occlusion, collateral pathways must develop to maintain venous drainage. The major collateral pathways ...
2-MAJOR ARTERIES OF BODY-PROF AHMED
... Principal arteries of the human body: 1 internal carotid artery, 2 external carotid artery, 3 common carotid artery, 4 arch of the aorta, 5 descending aorta, 6 pulmonary vein, 7 left coronary artery, 8 celiac artery, 9 splenic artery, 10 left gastric artery, 11 inferior mesenteric artery, 12 abd ...
... Principal arteries of the human body: 1 internal carotid artery, 2 external carotid artery, 3 common carotid artery, 4 arch of the aorta, 5 descending aorta, 6 pulmonary vein, 7 left coronary artery, 8 celiac artery, 9 splenic artery, 10 left gastric artery, 11 inferior mesenteric artery, 12 abd ...
2-Major arteries of the body
... Principal arteries of the human body: 1 internal carotid artery, 2 external carotid artery, 3 common carotid artery, 4 arch of the aorta, 5 descending aorta, 6 pulmonary vein, 7 left coronary artery, 8 celiac artery, 9 splenic artery, 10 left gastric artery, 11 inferior mesenteric artery, 12 abdo ...
... Principal arteries of the human body: 1 internal carotid artery, 2 external carotid artery, 3 common carotid artery, 4 arch of the aorta, 5 descending aorta, 6 pulmonary vein, 7 left coronary artery, 8 celiac artery, 9 splenic artery, 10 left gastric artery, 11 inferior mesenteric artery, 12 abdo ...
Blood supply of Head and neck
... Internal Carotid Artery Begins at the level of upper border of thyroid cartilage No branches in the neck Through carotid canal enters into cranial cavity Supplies brain, eyes, forehead and part of the nose ...
... Internal Carotid Artery Begins at the level of upper border of thyroid cartilage No branches in the neck Through carotid canal enters into cranial cavity Supplies brain, eyes, forehead and part of the nose ...
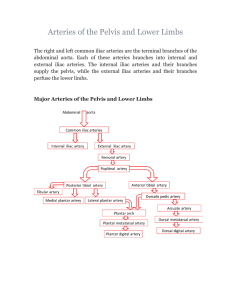
Arteries of the Pelvis and Lower Limbs
... The external iliac arteries become the femoral arteries; Branches supply the anterior abdominal wall muscles, round ligament of uterus in females, and cremaster muscles in males ...
... The external iliac arteries become the femoral arteries; Branches supply the anterior abdominal wall muscles, round ligament of uterus in females, and cremaster muscles in males ...
Vascular Anatomy of the Lower Limbs
... (The artery of lateral compartment of the leg ) which gives: A- Nutrient artery to the fibula. B- perforating branch ( to lower part of front of the leg ) C- shares in anastomosis around the ankle joint. D- Muscular branches to the muscles of the lateral and posterior compartments of the leg. 2- Nut ...
... (The artery of lateral compartment of the leg ) which gives: A- Nutrient artery to the fibula. B- perforating branch ( to lower part of front of the leg ) C- shares in anastomosis around the ankle joint. D- Muscular branches to the muscles of the lateral and posterior compartments of the leg. 2- Nut ...
chapter 4 - Jack Stern`s Home Page
... The pectoralis major is a muscle of the upper limb that has migrated onto the anterior surface of the thoracic wall. Its origin starts at about the midpoint of the anterior surface of the clavicle and extends medially along this bone toward the sternoclavicular joint. Crossing the anterior surface o ...
... The pectoralis major is a muscle of the upper limb that has migrated onto the anterior surface of the thoracic wall. Its origin starts at about the midpoint of the anterior surface of the clavicle and extends medially along this bone toward the sternoclavicular joint. Crossing the anterior surface o ...
No. 17 - 辽宁医学院
... 4) The systemic veins can be divided into the superficial and deep veins. The superficial veins, which lie just beneath the skin (in the superficial fascia, in the hypodermis, immediately under the skin), return blood from the skin and the subcutaneous regions to the deep veins.They freely anasto ...
... 4) The systemic veins can be divided into the superficial and deep veins. The superficial veins, which lie just beneath the skin (in the superficial fascia, in the hypodermis, immediately under the skin), return blood from the skin and the subcutaneous regions to the deep veins.They freely anasto ...





![[ PDF ] - journal of evidence based medicine and](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/003813610_1-51f9cf52dc3dd7ae680a3b0bd55821af-300x300.png)