Blood Vessel Lab
... IV. Fetal circulation - Figure 21.30, page 794 in your text Fetal circulation (circulation of the unborn) is different than circulation after birth. The fetus does not use its lung to breathe; it depends on its mother for oxygenation of its blood. The fetus is connected to its mother’s circulation ...
... IV. Fetal circulation - Figure 21.30, page 794 in your text Fetal circulation (circulation of the unborn) is different than circulation after birth. The fetus does not use its lung to breathe; it depends on its mother for oxygenation of its blood. The fetus is connected to its mother’s circulation ...
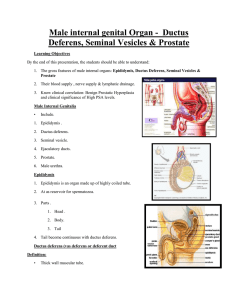
Male internal genital Organ - Ductus Deferens, Seminal Vesicles
... 6. Reaching the base of urinary bladder. 7.Medial to seminal vesicle. 8. Approaches the opposite duct. 9. Reaches base of prostate 10. At base of prostate ductus deferens is joined at an acute angle by : ...
... 6. Reaching the base of urinary bladder. 7.Medial to seminal vesicle. 8. Approaches the opposite duct. 9. Reaches base of prostate 10. At base of prostate ductus deferens is joined at an acute angle by : ...
SECTION 2 Blood Supply Lymphatics Innervation
... During pregnancy, there is marked hypertrophy of the uterine vasculature, which is supplied principally from the uterine and ovarian arteries (see Fig. 2-9). The uterine artery, a main branch of the internal iliac artery—previously called the hypogastric artery—enters the base of the broad ligament ...
... During pregnancy, there is marked hypertrophy of the uterine vasculature, which is supplied principally from the uterine and ovarian arteries (see Fig. 2-9). The uterine artery, a main branch of the internal iliac artery—previously called the hypogastric artery—enters the base of the broad ligament ...
Abdomen
... enters the lienorenal ligament . 53. Structure that is divided into the proper hepatic and gastroduodenal ...
... enters the lienorenal ligament . 53. Structure that is divided into the proper hepatic and gastroduodenal ...
Dr. Fullerton in Austin Woman Magazine
... with an anesthetic into an injured area to cause mild inflammation. The body responds by sending healing and growth factors to the area, thus enhancing the healing process. The process is very effective on injuries to the ligaments, tendons and cartilage-fibrous tissues, which tend to heal poorly du ...
... with an anesthetic into an injured area to cause mild inflammation. The body responds by sending healing and growth factors to the area, thus enhancing the healing process. The process is very effective on injuries to the ligaments, tendons and cartilage-fibrous tissues, which tend to heal poorly du ...
maxillary artery
... 2. The maxillary artery and the superficial temporal artery are the terminal branches of the external carotid artery. 3. The pterygopalatine fossa is a cone-shaped paired depression deep to the infratemporal fossa. The pterygopalatine fossa is located between the pterygoid process and the maxillary ...
... 2. The maxillary artery and the superficial temporal artery are the terminal branches of the external carotid artery. 3. The pterygopalatine fossa is a cone-shaped paired depression deep to the infratemporal fossa. The pterygopalatine fossa is located between the pterygoid process and the maxillary ...
31-Aorta& IVC
... It is formed by the union of the common iliac artery at the level of the 5th lumbar vertebra. So, it conveys most of the blood from the body below the diaphragm and drains into the right atrium of the heart. It ascends on the right side of the aorta. It pierces the central tendon of the diaphragm at ...
... It is formed by the union of the common iliac artery at the level of the 5th lumbar vertebra. So, it conveys most of the blood from the body below the diaphragm and drains into the right atrium of the heart. It ascends on the right side of the aorta. It pierces the central tendon of the diaphragm at ...
Chapter 21: Immune System
... • congenital or mechanically stressed from prolonged standing or pregnancy ...
... • congenital or mechanically stressed from prolonged standing or pregnancy ...
Overview and Review of the Pelvis and Perineum Three
... presence closes off lesser sciatic notch to become lesser sciatic foramen. Most, but not all of obturator foramen is covered over by obturator membrane. Smaller foramen is left. ...
... presence closes off lesser sciatic notch to become lesser sciatic foramen. Most, but not all of obturator foramen is covered over by obturator membrane. Smaller foramen is left. ...
Chapter 3
... INTRODUCTION • Developmental anatomy is the study of the sequence of events from the fertilization of a secondary oocyte to the formation of an adult organism. • Embryology is the study of development from fertilization to the fetal period. • Obstetrics is the branch of medicine that deals with the ...
... INTRODUCTION • Developmental anatomy is the study of the sequence of events from the fertilization of a secondary oocyte to the formation of an adult organism. • Embryology is the study of development from fertilization to the fetal period. • Obstetrics is the branch of medicine that deals with the ...
MC - WordPress.com
... branches of the internal thoracic artery. II. The sensory fibers in the lower five intercostal nerves supply the skin of the lateral thoracic and anterior abdominal walls. a. If only (I) is correct b. If only (II) is correct c. If both (I) and (II) are correct d. If neither (I) nor (II) is correct 7 ...
... branches of the internal thoracic artery. II. The sensory fibers in the lower five intercostal nerves supply the skin of the lateral thoracic and anterior abdominal walls. a. If only (I) is correct b. If only (II) is correct c. If both (I) and (II) are correct d. If neither (I) nor (II) is correct 7 ...
Abdomen. Liver Part 2
... (part of the medial segment is the quadrate lobe). This fissure may be identified by three landmarks on ultrasound: left hepatic vein (superior portion) anterior turn of the left portal vein (middle ...
... (part of the medial segment is the quadrate lobe). This fissure may be identified by three landmarks on ultrasound: left hepatic vein (superior portion) anterior turn of the left portal vein (middle ...
Anatomy of a Frog Reading
... The Circulatory System The frog heart is the only organ contained within the coelom that has its own protective covering. This covering is the pericardium. (Humans have one, too.) There are two upper chambers of the heart, the right atrium and the left atrium. The frog heart, however, has only one l ...
... The Circulatory System The frog heart is the only organ contained within the coelom that has its own protective covering. This covering is the pericardium. (Humans have one, too.) There are two upper chambers of the heart, the right atrium and the left atrium. The frog heart, however, has only one l ...
cross-sectional-anatomy-liver-part-2
... (part of the medial segment is the quadrate lobe). This fissure may be identified by three landmarks on ultrasound: left hepatic vein (superior portion) anterior turn of the left portal vein (middle ...
... (part of the medial segment is the quadrate lobe). This fissure may be identified by three landmarks on ultrasound: left hepatic vein (superior portion) anterior turn of the left portal vein (middle ...
Arteries to the Neck, Head, and Brain
... parathyroid glands, larynx, trachea, esophagus, and pharynx ...
... parathyroid glands, larynx, trachea, esophagus, and pharynx ...
عرض تقديمي من PowerPoint
... recess is very lucent (i.e., dark) on an x-ray when the lung expands fully to fill it; at expiration, however, the lung recedes upward and the diaphragm and chest wall move near to each other once again, and the lucency disappears. ...
... recess is very lucent (i.e., dark) on an x-ray when the lung expands fully to fill it; at expiration, however, the lung recedes upward and the diaphragm and chest wall move near to each other once again, and the lucency disappears. ...
Blood Supply of Brain and Spinal Cord
... internal carotid artery just before it divides into its terminal branches - the anterior and middle cerebral arteries The anterior cerebral artery forms the anterolateral portion of the Circle of Willis, while the middle cerebral artery does not contribute to the circle The right and left posterior ...
... internal carotid artery just before it divides into its terminal branches - the anterior and middle cerebral arteries The anterior cerebral artery forms the anterolateral portion of the Circle of Willis, while the middle cerebral artery does not contribute to the circle The right and left posterior ...
D. hepatic artery
... brachial cephalic trunk axillary artery arch of the aorta ascending aorta descending aorta ...
... brachial cephalic trunk axillary artery arch of the aorta ascending aorta descending aorta ...
D. hepatic artery
... brachial cephalic trunk axillary artery arch of the aorta ascending aorta descending aorta ...
... brachial cephalic trunk axillary artery arch of the aorta ascending aorta descending aorta ...
Brief description of non ear region anatomy of Bothriogenys, DUPC
... oriented such that the lateral margin is slightly more anterior than the medial margin. No significant preglenoid process exists. Superior to the glenoid fossa is a large supraglenoid foramen (~ 2 mm in diameter), which, on the right side only, has a second, smaller foramen adjacent to it (Fig. 2.2) ...
... oriented such that the lateral margin is slightly more anterior than the medial margin. No significant preglenoid process exists. Superior to the glenoid fossa is a large supraglenoid foramen (~ 2 mm in diameter), which, on the right side only, has a second, smaller foramen adjacent to it (Fig. 2.2) ...
Congenital Interruption of the Inferior Vena Cava
... a normal right superior vena cava; it communicated with the left atrium via a fossa ovalis defect. The dilated main pulmonary artery divided into a large left and a small right branch, which supplied the upper lobe of the right lung only. The right middle and lower lobes were perfused by a vessel ar ...
... a normal right superior vena cava; it communicated with the left atrium via a fossa ovalis defect. The dilated main pulmonary artery divided into a large left and a small right branch, which supplied the upper lobe of the right lung only. The right middle and lower lobes were perfused by a vessel ar ...
Additional file 1
... Medulloblastomas are traditionally approached by the transvermian route by splitting the inferior vermis. After opening the dura, the arachnoid over the cisterna magna and foramen of Magendie are opened. The tonsils with the posterior inferior cerebellar artery (PICA) are retracted to expose the inf ...
... Medulloblastomas are traditionally approached by the transvermian route by splitting the inferior vermis. After opening the dura, the arachnoid over the cisterna magna and foramen of Magendie are opened. The tonsils with the posterior inferior cerebellar artery (PICA) are retracted to expose the inf ...
Extra Embryonic Membranes E
... diseases such as diphtheria, scarlet fever, small pox and measles. The antibodies which have developed in the blood of mother against these diseases are passed to the foetal placenta. Similarly Rh antibody also pass through placenta. Blood proteins cannot pass through the placenta because they are l ...
... diseases such as diphtheria, scarlet fever, small pox and measles. The antibodies which have developed in the blood of mother against these diseases are passed to the foetal placenta. Similarly Rh antibody also pass through placenta. Blood proteins cannot pass through the placenta because they are l ...
3 Normal Early Pregnancy (First Trimester)
... appears as a circular echogenic structure bordering directly on the decidua. High-resolution color Doppler imaging can define maternal blood vessels between the decidua and chorion (Figs. 3.3, 3.4). By establishing this connection with the maternal circulation, the embryo secures the nutritional sup ...
... appears as a circular echogenic structure bordering directly on the decidua. High-resolution color Doppler imaging can define maternal blood vessels between the decidua and chorion (Figs. 3.3, 3.4). By establishing this connection with the maternal circulation, the embryo secures the nutritional sup ...