Rat Anatomy - Head, Thoracic, and Abdominal Organs
... The lab books and diagrams available to you are supplemental. You are expected to follow the directions in this lab. You will be held responsible for being able to locate all the structures. You are expected to have exhausted all possibilities in attempting to located structures before asking for as ...
... The lab books and diagrams available to you are supplemental. You are expected to follow the directions in this lab. You will be held responsible for being able to locate all the structures. You are expected to have exhausted all possibilities in attempting to located structures before asking for as ...
Dissection of the Rat
... stomach and rectum. If you are careful you will be able to stretch it out and untangle it so that you can see the relative lengths of the large and the small intestine. Locate the colon, which is the large greenish tube that extends from the small intestine and leads to the anus. The colon is also k ...
... stomach and rectum. If you are careful you will be able to stretch it out and untangle it so that you can see the relative lengths of the large and the small intestine. Locate the colon, which is the large greenish tube that extends from the small intestine and leads to the anus. The colon is also k ...
Digestive system
... upper and lower eyelids. Still farther posterior is the fleshy flap, the pinna, of each ear surrounding the external auditory meatus, which leads to the eardrum. The slash on the right side of the neck was made to inject blue latex into a jugular vein. The blue latex thus fills the veins throughout ...
... upper and lower eyelids. Still farther posterior is the fleshy flap, the pinna, of each ear surrounding the external auditory meatus, which leads to the eardrum. The slash on the right side of the neck was made to inject blue latex into a jugular vein. The blue latex thus fills the veins throughout ...
Mnemonics for TAP Path through male reproductive system: STEVE
... Iliohypogastric [L1] Ilioinguinal [L1] Genitofemoral [L1, L2] Lateral femoral cutaneous [L2, L3] Obturator [L2, L3, L4] Femoral [L2, L3, L4] Which bronchi is more vertical: “Inhale a bite, goes down the right” Contents of spermatic cord: 3 arteries: testicular, cremasteric, artery to vas deferens 2 ...
... Iliohypogastric [L1] Ilioinguinal [L1] Genitofemoral [L1, L2] Lateral femoral cutaneous [L2, L3] Obturator [L2, L3, L4] Femoral [L2, L3, L4] Which bronchi is more vertical: “Inhale a bite, goes down the right” Contents of spermatic cord: 3 arteries: testicular, cremasteric, artery to vas deferens 2 ...
Anatomy of the Respiratory System 2
... TBs is the respiratory zone and from each TB is an acinus. TBs divide into respiratory bronchioles and alveolar ducts. The distance from the TB to the most distal alveolus is only a few millimetres but the respiratory zone makes up most of the lung, its volume about 2.5-3 litres at rest. Because the ...
... TBs is the respiratory zone and from each TB is an acinus. TBs divide into respiratory bronchioles and alveolar ducts. The distance from the TB to the most distal alveolus is only a few millimetres but the respiratory zone makes up most of the lung, its volume about 2.5-3 litres at rest. Because the ...
KAHSSO KINE 2031 Mock Exam SU 2016
... Disclaimer: This test is meant purely for study purposes; it does not necessarily encompass the entirety of the material covered in class, and is not meant to reflect the format and/or difficulty of the actual exam. It should not be your only source of studying. Test created by KAHSSO Peer Tutors ...
... Disclaimer: This test is meant purely for study purposes; it does not necessarily encompass the entirety of the material covered in class, and is not meant to reflect the format and/or difficulty of the actual exam. It should not be your only source of studying. Test created by KAHSSO Peer Tutors ...
4. BLOOD SUPPLY OF HEART 12017-03-24 21
... Descends in the anterior interventricular groove to the apex of the heart (accompanied by the Great cardiac vein) in most individuals it passes around the apex to anastomose with terminal branches of the right coronary , in 1\3 it ends at the apex ) It supplies the right and left ventricles and ante ...
... Descends in the anterior interventricular groove to the apex of the heart (accompanied by the Great cardiac vein) in most individuals it passes around the apex to anastomose with terminal branches of the right coronary , in 1\3 it ends at the apex ) It supplies the right and left ventricles and ante ...
Embryology02-BodyPlanFetalMembranes
... connection from the embryo to the chorion/placenta contains arteries conveying nutrient and oxygenpoor blood to the placenta and a single vein conveying enriched blood back to the fetus Also contains closed off yolk sac During gut development intestinal loops herniate into the umbilical cord and are ...
... connection from the embryo to the chorion/placenta contains arteries conveying nutrient and oxygenpoor blood to the placenta and a single vein conveying enriched blood back to the fetus Also contains closed off yolk sac During gut development intestinal loops herniate into the umbilical cord and are ...
Layers of the Lungs Appendix
... and nutrients they need and carries away waste, such as carbon dioxide. The blood is pumped from the heart through the pulmonary arteries to the lungs so it can release carbon dioxide. Here it collects oxygen, and is pumped back through the pulmonary veins to the left side of the heart. The heart th ...
... and nutrients they need and carries away waste, such as carbon dioxide. The blood is pumped from the heart through the pulmonary arteries to the lungs so it can release carbon dioxide. Here it collects oxygen, and is pumped back through the pulmonary veins to the left side of the heart. The heart th ...
Circulatory System Part 3
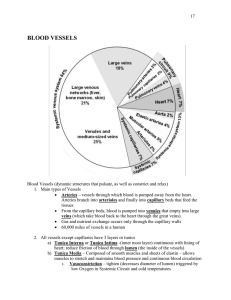
... Blood Vessels (dynamic structures that pulsate, as well as constrict and relax) 1. Main types of Vessels Arteries – vessels through which blood is pumped away from the heart. Arteries branch into arterioles and finally into capillary beds that feed the tissues From the capillary beds, blood is p ...
... Blood Vessels (dynamic structures that pulsate, as well as constrict and relax) 1. Main types of Vessels Arteries – vessels through which blood is pumped away from the heart. Arteries branch into arterioles and finally into capillary beds that feed the tissues From the capillary beds, blood is p ...
The Blood
... This is treated by stopping the transfusion, hydration, and alkalinization of the urine Not every reaction to transfusion is due to infused RBC hemolysis, other less severe reactions can occur ...
... This is treated by stopping the transfusion, hydration, and alkalinization of the urine Not every reaction to transfusion is due to infused RBC hemolysis, other less severe reactions can occur ...
Palpation of the apical impulse
... and great vessels • The pulmonary artery bifurcates quickly into its left and right branches. • The aorta curves upward from the left ventricle to the level of sternal angle, where it arches backward and then down. • On the right, the superior and inferior vena cava empties in the right atrium. ...
... and great vessels • The pulmonary artery bifurcates quickly into its left and right branches. • The aorta curves upward from the left ventricle to the level of sternal angle, where it arches backward and then down. • On the right, the superior and inferior vena cava empties in the right atrium. ...
Types of Nervous Systems
... cells, each with a number of processes radiating from the cell body in all directions The processes of neighboring nerve cells connects to one another to form a continuous network. Called diffuse type because primitive nerve cells (neuries or protoneurons) non-polar; nerve impulses are conducted i ...
... cells, each with a number of processes radiating from the cell body in all directions The processes of neighboring nerve cells connects to one another to form a continuous network. Called diffuse type because primitive nerve cells (neuries or protoneurons) non-polar; nerve impulses are conducted i ...
Anatomy Blue Boxes Exam 1 Esophagus and Stomach Pgs 254
... Anomalies of Liver: can have accessory hepatic ducts (in 5% population and not troublesome) Accessory ducts run from right lobe of liver to anterior gallbladder Extrahepatic Biliary Atresia: most common form is obliteration of bile ducts Could result from failure of remodeling process at hepatic hil ...
... Anomalies of Liver: can have accessory hepatic ducts (in 5% population and not troublesome) Accessory ducts run from right lobe of liver to anterior gallbladder Extrahepatic Biliary Atresia: most common form is obliteration of bile ducts Could result from failure of remodeling process at hepatic hil ...
The Human Heart Essay Research Paper Biology
... circulation of the blood”. It is divided into four cavities; two atria and two ventricles. The left atrium receives oxygenated blood from the lungs. From there the blood passes to the left ventricle, which forces it via the aorta, through the arteries to supply the tissues of the body. The right atr ...
... circulation of the blood”. It is divided into four cavities; two atria and two ventricles. The left atrium receives oxygenated blood from the lungs. From there the blood passes to the left ventricle, which forces it via the aorta, through the arteries to supply the tissues of the body. The right atr ...
- Circle of Docs
... Chambers of the heart - the heart is divided into two receiving chambers, atria, and two pumping chambers, ventricles A. right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from the body (via the superior and inferior vena cava) and the heart (via the coronary sinus, mostly); its interior has 1. sinus venarum ...
... Chambers of the heart - the heart is divided into two receiving chambers, atria, and two pumping chambers, ventricles A. right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from the body (via the superior and inferior vena cava) and the heart (via the coronary sinus, mostly); its interior has 1. sinus venarum ...
Disclosure Zoltan Turi MD, MSCAI
... Level of anticoagulation Sheath size Left atrial pressure Presence and compliance of pericardium Use of echo guidance Most important ...
... Level of anticoagulation Sheath size Left atrial pressure Presence and compliance of pericardium Use of echo guidance Most important ...
Fraternal Birth Order and the Maternal Immune Hypothesis of Male
... Blanchard and Bogaert (1996b) conjectured that the high fraternal birth order of homosexual men may reflect a maternal immune reaction, which is provoked only by male fetuses and which becomes stronger after each pregnancy with a male fetus. This hypothesis rests partly on the argument that a woman’ ...
... Blanchard and Bogaert (1996b) conjectured that the high fraternal birth order of homosexual men may reflect a maternal immune reaction, which is provoked only by male fetuses and which becomes stronger after each pregnancy with a male fetus. This hypothesis rests partly on the argument that a woman’ ...
Gastro40-HALabPracticalReview
... the aorta. Can see the superior mesenteric artery anterior (or ventral) to the body of the pancreas. The superior mesenteric vein is to the right of the artery. In this view, can see that that superior mesenteric vessels are immediately anterior (or ventral) to the uncinate process of the pancreas, ...
... the aorta. Can see the superior mesenteric artery anterior (or ventral) to the body of the pancreas. The superior mesenteric vein is to the right of the artery. In this view, can see that that superior mesenteric vessels are immediately anterior (or ventral) to the uncinate process of the pancreas, ...
Unit One: Introduction to Physiology: The Cell and General Physiology
... systemic arterial blood supplied mostly by the bronchial arteries b. Low pressure high flow circulation that supplies venous blood to the aveolar capillaries where oxygen is added and carbon dioxide is removed. ...
... systemic arterial blood supplied mostly by the bronchial arteries b. Low pressure high flow circulation that supplies venous blood to the aveolar capillaries where oxygen is added and carbon dioxide is removed. ...
Educational Topic 63: Osteopathy in Obstetrics
... reports having had a tonsillectomy when asked about surgical history. The only medication she is taking is a prenatal vitamin with DHA. Her BP is 110/68, pulse 78, respirations 16, height 5’3”, and weight is 218lb. Physical exam is benign but noted are large, pendulous breasts without masses/skin ch ...
... reports having had a tonsillectomy when asked about surgical history. The only medication she is taking is a prenatal vitamin with DHA. Her BP is 110/68, pulse 78, respirations 16, height 5’3”, and weight is 218lb. Physical exam is benign but noted are large, pendulous breasts without masses/skin ch ...
Document
... Of all 24 ribs, the first seven pairs are often labeled as "true." These bones are connected to the costal cartilage, while the five other "false" sets do not. Three of those connect to non-costal cartilage, and two are deemed to be "floating," which means they only connect to the spine. ...
... Of all 24 ribs, the first seven pairs are often labeled as "true." These bones are connected to the costal cartilage, while the five other "false" sets do not. Three of those connect to non-costal cartilage, and two are deemed to be "floating," which means they only connect to the spine. ...
Which of the following places on the diaphragm are weak? a
... 18. Which chamber of the fetal heart is supplied with blood by means of the oval foramen? a) Left atrium b) Right atrium ...
... 18. Which chamber of the fetal heart is supplied with blood by means of the oval foramen? a) Left atrium b) Right atrium ...
Gross Anatomy Lungs
... • Consists of segmental bronchus , a segmental branch of the pulmonary artery ,and a segment of the lung tissue, surrounded by a delicate connective tissue septum. • It is drained by the intersegmental part of the pulmonary vein • Refers to the portion of the lung supplied by each segmental bronchu ...
... • Consists of segmental bronchus , a segmental branch of the pulmonary artery ,and a segment of the lung tissue, surrounded by a delicate connective tissue septum. • It is drained by the intersegmental part of the pulmonary vein • Refers to the portion of the lung supplied by each segmental bronchu ...
Lecture 1
... -connect arterioles and venules -network of microscopic vessels (one cell thick) = capillary bed -site of exchange: gases, nutrients, wastes -can be closed off when not needed ...
... -connect arterioles and venules -network of microscopic vessels (one cell thick) = capillary bed -site of exchange: gases, nutrients, wastes -can be closed off when not needed ...