BDS Ist YEAR EXAMINATION 2008-09
... Tributaries of Portal Vein. Structures transmitted through lesser sciatic foramen. Boundaries of epiploic foramen. Branches of Femoral Artery. Openings present in left atrium. Muscles in front of thigh. ...
... Tributaries of Portal Vein. Structures transmitted through lesser sciatic foramen. Boundaries of epiploic foramen. Branches of Femoral Artery. Openings present in left atrium. Muscles in front of thigh. ...
Chapter 20 Blood Vessels
... 6. hepatic portal vein leading into the liver which in turn is drained by the 7. hepatic veins into the inferior vena cava VII Fetal circulation A. Reasons for differences 1. lungs not functioning 2. maternal regulation of blood content of wastes & nutrients B. Fetal blood flow patterns 1. blood ent ...
... 6. hepatic portal vein leading into the liver which in turn is drained by the 7. hepatic veins into the inferior vena cava VII Fetal circulation A. Reasons for differences 1. lungs not functioning 2. maternal regulation of blood content of wastes & nutrients B. Fetal blood flow patterns 1. blood ent ...
Exam 3 study guide Lecture 1 Animal Structure and Function Most
... insect leg as insect grows larger? Lungs Internal sacs Unlike insect tracheal system lungs do not contact entire body Circulatory system draws oxygen from lungs to tissues Found in snails, a few fishes, spiders, vertebrates Structure of the mammalian lung - main structure need to know is alveoli and ...
... insect leg as insect grows larger? Lungs Internal sacs Unlike insect tracheal system lungs do not contact entire body Circulatory system draws oxygen from lungs to tissues Found in snails, a few fishes, spiders, vertebrates Structure of the mammalian lung - main structure need to know is alveoli and ...
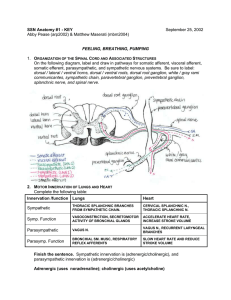
Anatomy Workshop #1
... 1. ORGANIZATION OF THE SPINAL CORD AND ASSOCIATED STRUCTURES On the following diagram, label and draw in pathways for somatic afferent, visceral afferent, somatic efferent, parasympathetic, and sympathetic nervous systems. Be sure to label: ...
... 1. ORGANIZATION OF THE SPINAL CORD AND ASSOCIATED STRUCTURES On the following diagram, label and draw in pathways for somatic afferent, visceral afferent, somatic efferent, parasympathetic, and sympathetic nervous systems. Be sure to label: ...
HIGH YIELD EMBRYOLOGY 2012
... Dextrocardia: right-sided heart; situs inversus involves all organs in the body cavity Ectopia cordis: ventral wall defect where the heart is on the outside of the thorax Sudden infant death syndrome: possibly caused by abnormalities in the cardiac conducting system? Atrial septal defects (ASD) - ca ...
... Dextrocardia: right-sided heart; situs inversus involves all organs in the body cavity Ectopia cordis: ventral wall defect where the heart is on the outside of the thorax Sudden infant death syndrome: possibly caused by abnormalities in the cardiac conducting system? Atrial septal defects (ASD) - ca ...
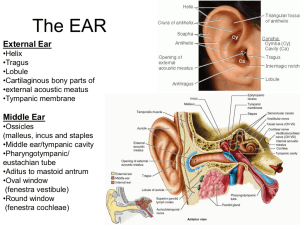
The EAR - Ipswich-Year2-Med-PBL-Gp-2
... • L coronary artery supplies L atrium and ventricle, most of IV septum including Bundle of His and Branches and small part of R ventricle (none of R atrium) A cross-section of the right and left ventricles demonstrates the most common pattern of distribution of blood from the RCA (red) and LCA (pink ...
... • L coronary artery supplies L atrium and ventricle, most of IV septum including Bundle of His and Branches and small part of R ventricle (none of R atrium) A cross-section of the right and left ventricles demonstrates the most common pattern of distribution of blood from the RCA (red) and LCA (pink ...
17. Egg Membranes Placenta `10
... Yolk Sac • 1st extra embryonic membrane to form • mediates nutrition • derived from endodermal cells that grow over yolk to enclose it ...
... Yolk Sac • 1st extra embryonic membrane to form • mediates nutrition • derived from endodermal cells that grow over yolk to enclose it ...
Document
... tube distal to the larynx differentiates into the epithelium and glands of the trachea and to the pulmonary epithelium. The cartilage, connective tissue and muscles ...
... tube distal to the larynx differentiates into the epithelium and glands of the trachea and to the pulmonary epithelium. The cartilage, connective tissue and muscles ...
Exam 3 study guide Lecture 1 Animal Structure and Function Most
... Example of closed circulatory system: Earthworm Compare and contrast open vs. closed Open less effective at circulating all the fluid Doesn’t matter if metabolism is slow, e.g., clams Insects use trachael system to supply oxygen and get rid of carbon dioxide Closer look at closed circulatory system ...
... Example of closed circulatory system: Earthworm Compare and contrast open vs. closed Open less effective at circulating all the fluid Doesn’t matter if metabolism is slow, e.g., clams Insects use trachael system to supply oxygen and get rid of carbon dioxide Closer look at closed circulatory system ...
Neurosonography Part Three
... Schematic representation of the cerebral ventricular system. Note that lateral ventricles encompass the frontal horns (F.H.), body, posterior horns ( P.H .), and temporal horns (T.H.). The cerebrospinal fluid flows (1) from the lateral ventricles to the third ventricle (closed arrow) via the short ...
... Schematic representation of the cerebral ventricular system. Note that lateral ventricles encompass the frontal horns (F.H.), body, posterior horns ( P.H .), and temporal horns (T.H.). The cerebrospinal fluid flows (1) from the lateral ventricles to the third ventricle (closed arrow) via the short ...
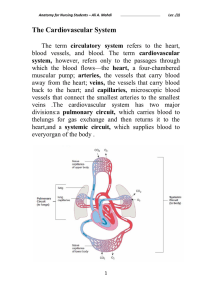
The Cardiovascular System
... The atria (sing. Atrium) exhibit thin flaccid walls correspondingto their light workload—all they do is pump blood into theventricles immediately below. They are separated from eachother by a wall, the interatrial septum.A thicker wall, the interventricularseptum, separates the right and left ventri ...
... The atria (sing. Atrium) exhibit thin flaccid walls correspondingto their light workload—all they do is pump blood into theventricles immediately below. They are separated from eachother by a wall, the interatrial septum.A thicker wall, the interventricularseptum, separates the right and left ventri ...
4. Cardiovascular System - yeditepe anatomy fhs 121
... Continuous inferiorly w/ central tendon of the diaphragm Attached anteriorly to the sternum by sternopericardial ligaments Site of continuity pericardiacophrenic ligament Inner surface lined by parietal layer of the serous pericardium Protects the heart against sudden overfilling. ...
... Continuous inferiorly w/ central tendon of the diaphragm Attached anteriorly to the sternum by sternopericardial ligaments Site of continuity pericardiacophrenic ligament Inner surface lined by parietal layer of the serous pericardium Protects the heart against sudden overfilling. ...
Rat LAB
... PULMONARY ARTERIES carry LOW OXYGEN blood to the from the heart to the lungs and the PULMONARY VEINS return blood return HIGH OXYGEN blood to the heart. The SYSTEMIC CIRCULATION carries oxygenated blood from heart to the muscles and body organs and brings deoxygenated blood back to the heart, just l ...
... PULMONARY ARTERIES carry LOW OXYGEN blood to the from the heart to the lungs and the PULMONARY VEINS return blood return HIGH OXYGEN blood to the heart. The SYSTEMIC CIRCULATION carries oxygenated blood from heart to the muscles and body organs and brings deoxygenated blood back to the heart, just l ...
Fetal Pig dissection lab
... Now cut the skin midsagittally and anteriorly to a point just behind the small, hairy papilla on the upper part of the throat. This is the “hair on its chinny, chin, chin”. Note that the tough skin is relatively thin so If you are trying to cut into something stiff and hard (bone) or brown and fibro ...
... Now cut the skin midsagittally and anteriorly to a point just behind the small, hairy papilla on the upper part of the throat. This is the “hair on its chinny, chin, chin”. Note that the tough skin is relatively thin so If you are trying to cut into something stiff and hard (bone) or brown and fibro ...
Cardiovascular System_Lecture III - Medical
... The pulmonary arteries carry blood from the heart to the lungs. They are the only arteries (other than umbilical arteries in the fetus) that carry deoxygenated blood. In the human heart, the pulmonary trunk begins at the base of the right ventricle. It is short and wide - approximately 5 cm (2 inche ...
... The pulmonary arteries carry blood from the heart to the lungs. They are the only arteries (other than umbilical arteries in the fetus) that carry deoxygenated blood. In the human heart, the pulmonary trunk begins at the base of the right ventricle. It is short and wide - approximately 5 cm (2 inche ...
The heart develops from mesoderm
... As the heart tube enlarges, it forms 4 primordia: the sinus venosus, common atrium, embryonic ventricle and bulbus cordis. These primordia are parts of the heart tube that have enlarged more than the other parts in between them so that they appear as heart vesicles. The sinus venosus, common atrium ...
... As the heart tube enlarges, it forms 4 primordia: the sinus venosus, common atrium, embryonic ventricle and bulbus cordis. These primordia are parts of the heart tube that have enlarged more than the other parts in between them so that they appear as heart vesicles. The sinus venosus, common atrium ...
Anatomy and Physiology II MED 165 Blood Vessels System
... What are three layers of all arteries and veins? What tissue is found in the three layers? Which direction do arteries transport blood? Is arterial blood oxygenated, deoxygenated or it depends on the type of circulation? What are the two types of arteries? What is the thickest tissue layer in an art ...
... What are three layers of all arteries and veins? What tissue is found in the three layers? Which direction do arteries transport blood? Is arterial blood oxygenated, deoxygenated or it depends on the type of circulation? What are the two types of arteries? What is the thickest tissue layer in an art ...
12-Aortic Arches2009-01-26 02:4412.5 MB
... The narrowing is distal to the ductus arteriosus. The ductus usually remains open to communicate pulmonary artery with the descending aorta Even with an open ductus arteriosus blood flow to the lower body can be impaired. Allows development of collateral circulation during the fetal period. ...
... The narrowing is distal to the ductus arteriosus. The ductus usually remains open to communicate pulmonary artery with the descending aorta Even with an open ductus arteriosus blood flow to the lower body can be impaired. Allows development of collateral circulation during the fetal period. ...
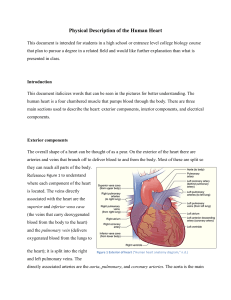
Physical Description of the Human Heart
... arteries and veins that branch off to deliver blood to and from the body. Most of these are split so they can reach all parts of the body. Reference Figure 1 to understand where each component of the heart is located. The veins directly associated with the heart are the superior and inferior vena ca ...
... arteries and veins that branch off to deliver blood to and from the body. Most of these are split so they can reach all parts of the body. Reference Figure 1 to understand where each component of the heart is located. The veins directly associated with the heart are the superior and inferior vena ca ...
Slide ()
... directly sutured to the RPA in a patient with tricuspid and pulmonary atresia. The right ventricle (RV), left ventricle (LV), mitral valve (MV), right pulmonary artery (RPA), and aorta (Ao) are labeled. B. The fenestrated lateral tunnel Fontan in which a synthetic material (eg, Gore-Tex) is used to ...
... directly sutured to the RPA in a patient with tricuspid and pulmonary atresia. The right ventricle (RV), left ventricle (LV), mitral valve (MV), right pulmonary artery (RPA), and aorta (Ao) are labeled. B. The fenestrated lateral tunnel Fontan in which a synthetic material (eg, Gore-Tex) is used to ...
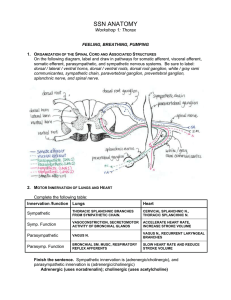
Anatomy Workshop #1
... Esophageal varices are often associated with what condition? Portal hypertension caused by diseased liver. Finish the sentence. Cervical spinal nerves exit just (above/below) the corresponding vertebrae; thoracic spinal nerves exit just (above/below) the corresponding vertebrae. Cervical spinal nerv ...
... Esophageal varices are often associated with what condition? Portal hypertension caused by diseased liver. Finish the sentence. Cervical spinal nerves exit just (above/below) the corresponding vertebrae; thoracic spinal nerves exit just (above/below) the corresponding vertebrae. Cervical spinal nerv ...
Thorax Forum Questions 2010ish
... 2. You have to perform a pericardiocentesis, what landmarks are you going to use to guide the needle? What is your approach? (not in your text) Infrasternal angle under the xiphoid process may be the safest; follow the bottom of the ribs upward to locate the xiphoid process 3. What is a stent and ho ...
... 2. You have to perform a pericardiocentesis, what landmarks are you going to use to guide the needle? What is your approach? (not in your text) Infrasternal angle under the xiphoid process may be the safest; follow the bottom of the ribs upward to locate the xiphoid process 3. What is a stent and ho ...
Thorax Worksheet
... The right main stem bronchus is shorter, wider, and MORE VERTICAL than the left. It is the probable resting place for large aspirated objects. Specifically, the right lower lobar bronchus is the most vertical division of the right main stem bronchus, and small aspirated objects will likely rest here ...
... The right main stem bronchus is shorter, wider, and MORE VERTICAL than the left. It is the probable resting place for large aspirated objects. Specifically, the right lower lobar bronchus is the most vertical division of the right main stem bronchus, and small aspirated objects will likely rest here ...
Rat Dissection-Circulation
... 4. Find the heart in the center of the thoracic cavity. Determine the apex (the pointed, ventral end) and the base (the broad, dorsal end). The apex is usually free within the pericardium, and the base contains the great vessels and the attachment of the pericardium. The pericardium or pericardial s ...
... 4. Find the heart in the center of the thoracic cavity. Determine the apex (the pointed, ventral end) and the base (the broad, dorsal end). The apex is usually free within the pericardium, and the base contains the great vessels and the attachment of the pericardium. The pericardium or pericardial s ...
Unit 11 Respiratory System
... alveoli) is a cupshaped pouch filled with fluid called surfactant. This is where oxygen and carbon dioxide enter and leave the blood from the capillaries. ...
... alveoli) is a cupshaped pouch filled with fluid called surfactant. This is where oxygen and carbon dioxide enter and leave the blood from the capillaries. ...