* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Anatomy Abdomen Forum 2012
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
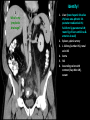
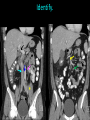
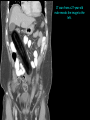
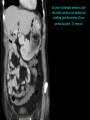
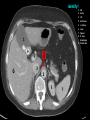
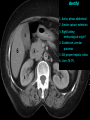
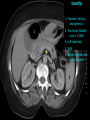
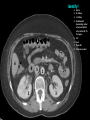
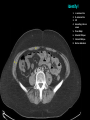
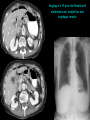
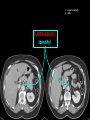
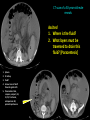
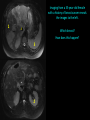
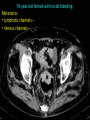
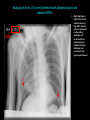
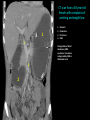
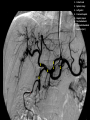
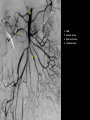
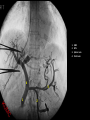
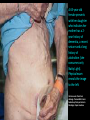
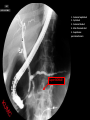
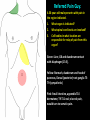
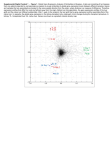
Abdomen Forum 2012 Surface Anatomy Guy: Document where the following organs/structures can be palpated: 1. Liver Rib5-10 right 2. Spleen under 9th,10th, 11th ribs. Begins about 1 midaxillary line. Posterior left 3. 2 3 4 Gallbladder 9th rib, midclavicular right Draw in: 1. Linea alba 2. Linea semilunaris 3. McBurney’s point 4. ASIS 5. Deep Inguinal ring 6. Superficial Inguinal ring Surface Anatomy Guy: Draw in the 4 lines to create the “9region pattern” Name the 9 regions. 1 2 What organs are found in each? 3 4 RH: R liver, kidney, Asc colon, GB? E: liver, kidney (R/L), GB, stomach, pancreas, Trans colon LH: Stomach, spleen, kidney, tip of liver RF: Asc colon, gutter, U: SI, Colon LF: Des colon, gutter, kidney RG: Asc colon, ASIS, Ing Lig, appendix, cecum P: appendix, cecum, SI, bladder, Genital organs, femoral vessels LG: des colon, ASIS, Ing Lig, sigmoid colon. Patient A – 42 yearold male presenting after trying to move his dishwasher Right: indirect inguinal hernia, most common, congenital, more in child and male. Lateral to inferior epigastric vessels via deep inguinal ring through entire inguinal canal. Same covering as spermatic cord. Enters the scrotum Compare and Contrast! Left: direct inguinal hernia, older male moving heavy things. Hernia out of Hesselbach’s triangle (rectus abdominis, inguinal ligament, inferior epigastric vessels) through superficial inguinal ring. Medial to inferior epigastric vessels. Cover by parietal peritoneum & transversalis fascia with external spermatic fascia Patient B – newborn male What fascial layers are cut in this procedure? Lymphatic drainage of the wound site? Vasetomy Skin Darto’s fascia ESF Cremaster ISF Superficial inguinal node Identify! 1 What's my lymphatic drainage? 2 3 5 4 6 1. Liver (most-hepatic LN-celiac LN; bare area-phrenic LNposterior mediastinal LN; Falciform lig-parasternal LN; round lig of liver-umbilicus & anterior ab wall) 2. Spleen, splenic artery 3. L. kidney (Lumbar LN), renal vein-IVC 4. Aorta 5. IVC 6. Ascending colon with contrast (Sup Men LN), cecum Identify. * CT scan from a 27-year-old male reveals the image to the left. Identify; What’s wrong? 58-year-old male with abdominal pain. CT scans reveal: 1 6 2 4 3 1: liver, cirrohsis 5 2: spleen, enlarged due to liver cirohisis 3: bladder 4: Psoas major 65-year-old female presents with the chief compliant of abdominal swelling and discomfort of two weeks duration. CT reveals: Identify! 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. GB Aorta IVC Gall stone L. kidney Liver Spleen R. Crus, diaphragm 9. Portal vein 1 4 8 9 6 3 2 5 7 Identify! 5 6 4 3 2 1 1. Aorta; plexus abdominal 2. Erector spinae; extension 3. Right kidney; embryological origin? 4. Duodenum, annular pancreas 5. GB; proper hepatic, celiac 6. Liver; T6-T9, Identify! 2 4 1 3 1. Pancreas; Celiac a. and splenic a. 2. Trav Colon; Middel colic a.?, SMA 3. Left renal vein. 4. SMA 5. Spleen; splenic vein to Portal vein? 5 Identify! 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 8 6 4 2 5 7 1 3 Aorta R. Kidney L. Kidney (Duodenum) descending, celiac artery and portal vein, Celiac LN, T5T9, vagus IVC Liver Psoas M Transverse colon Identify! 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 8 67 4 3 2 1 5 L. common iliac R. common iliac IVC Ascending colon or cecum Psoas Major External Oblique Internal Oblique Rectus abdominis Imaging of a 75-year-old female with abdominal pain, weight loss and dysphagia reveals: 3 2 4 1 5 6 Barium enema in a 1-year-old male with difficulty defecating reveals: 1. Celiac trunk (left) 2. SMA SUPER BONUS! Identify! Draw the celiac trunk, its major branches and anastomoses. Draw the IMA, its major branches and anastomoses. CT scan of a 50-year-old male reveals: Ascites! 1. Where is the fluid? 2. What layers must be traversed to drain this fluid? [Paracentesis] 1 1. 2. 3. 4. Spleen R. kidney Fluid? Arrow: liver or fluid? Paracolic gutter left. 5. Paracentesis: Skin, campers, scarpa’s, EO, IO, TA, Tran fascia, extraperinum fat, pariental peritonum 3 2 Imaging from a 55-year-old female with a history of breast cancer reveals the images to the left. 1 4 Which breast? How does this happen? 3 2 74-year-old female with rectal bleeding. Metastasis: • Lymphatic channels – • Venous channels – * Radiograph from a 73-year-old female with abdominal pain and elevated WBCs: Hint: 1. Right diaphragm is higher than the left. Infection based on high WBC. Infection of liver or peritoneal cavity pushing diaphragm up? Perforated bowel (ulcer)causing air leaked in between diaphragm and peritoneal cavity (pneumoperitoneum) CT scan from a 30-year-old female with complaints of vomiting and weight loss: 1 3 Stomach Duodenum Portal vein SMA Strangulation of distal duodenum, SMA syndrome. Duodenum compressed by SMA or abdominal aorta 4 2 1. 2. 3. 4. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 5 4 6 7 3 1 2 Celiac trunk Splenic artery Left gastric Common hepatic Hepatic proper Gastroduodenal pancreaticduodenal superior (ant.) 1 1. 2. 3. 4. 3 4 2 SMA Ileocolic artery Right colic artery Intestinal artery 1. 2. 3. 4. 4 1 3 2 SMV IMV Splenic vein Portal vein A 65-year-old female presents with her daughter who indicates her mother has a 2year history of dementia, a recent seizure and a long history of alcoholism [she consumes only Natty Light]. Physical exam reveals the image to the left: Varicose vein from liver damage. Paraumbilical vein backed up from portal vein blockage. Caput medusa. 1. Common hepatic duct 2. Cystic duct 3. Common bile duct 4. Main Pancreatic duct 5. Super bonus: pars interarticularis 1 2 3 Super BONUS! 4 Draw the pattern of sympathetic innervation to the ________________. Structure to be decided DURING the forum! Include pre and postganglionic neurons and GVAs! Referred Pain Guy: A 30-year-old male presents with pain in the region indicated. 1. What organ is indicated? 2. What spinal cord levels are involved? 3. Cell bodies in what location are responsible for relay of pain from this organ? 1 2 Green: Liver, GB and duodenum contact with diaphragm (C3-5), 3 4 Yellow: Stomach, duodenum and head of pancreas, Dorsal (posterior) root ganglia T5T9 (sympathetic) Pink: Small intestine, appendix T10 dermatone; T9-T11 real; visceral pain, would turn to somatic pain. Referred Pain Guy: A 16-year-old female presents with a fever and pain in the region indicated. 1. Which organ is implicated? 2. What spinal cord level is involved? 3. Is this somatic or visceral pain? 1 2 3 4 1 2 Referred Pain Guy: 3 4 A 36-year-old female presents with pain in the region indicated. 1. Which organ is implicated?