* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Blood Vessels - IWS2.collin.edu
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
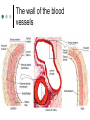
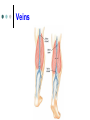
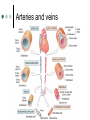
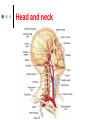
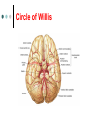
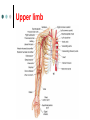
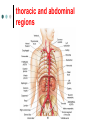
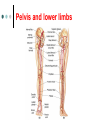
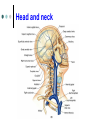
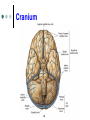
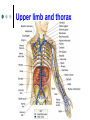
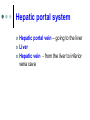
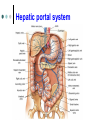
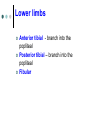
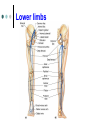
Exercise 36 Blood vessels The wall of the blood vessels Three distinct layers Tunica intima • Lines the lumen • Simple squamous epithelium • endothelium and endocardium Tunica media • Smooth muscle, • collagen and elastic fibers • Regulates the diameter of the blood vessels The wall of the blood vessels Tunica externa or adventitia • Areolar or fibrous connective tissue • Supports the vessel • Protects the vessel The wall of the blood vessels Arteries Blood vessels that conduct blood away from the heart and toward tissues. In the pulmonary circulation, pulmonary arteries conduct deoxygenated blood to the lungs. In the systemic circulation, the aorta and its branches conduct oxygenated blood toward the systemic tissues Arteries Small arteries are called arterioles. Arterioles conduct blood into a network of even smaller vessels, or capillaries. Arteries Subject to pressure fluctuations Thick walls Contain more smooth muscle and elastic tissues Narrower lumen than veins Arteries Can be classified as: Elastic Closer to the heart Large arteries More elastic fibers than smooth muscle Arteries Muscular Farther from the heart Smaller arteries More smooth muscle than elastic fibers Veins Blood vessels that conduct blood toward the heart. In the pulmonary circulation, the pulmonary veins return oxygenated blood from the lungs. In the systemic circulation the vena cava returns deoxygenated blood from the rest of the systemic loop. Venules are small veins. Veins Far from the heart Not subjected to pressure fluctuations Thin walls Larger lumen than arteries Presence of valves Skeletal muscle pump Veins Arteries and veins Aorta Ascending aorta – first portion Aortic arch Descending aorta – within the thorax Abdominal aorta – within the abdomen Aorta Ascending aorta Right and left coronary arteries originate from base of aortic sinus Aortic arch Brachiocephalic trunk – first branch • Right common carotid • Right subclavian Left common carotid – second branch Left subclavian – third branch Aorta Descending aorta Thoracic and abdominal aortas Head and neck Internal Carotid External carotid Vertebral Basilar – formed by the fusion of the vertebral arteries Head and neck Head and neck Circle of Willis Posterior cerebral Posterior communicating Middle cerebral Anterior cerebral Anterior communicating Circle of Willis Upper limb Axillary – continuation of the subclavian Brachial – continuation of the axillary Ulnar – branch of the brachial Radial – branch of the brachial Palmar Arch Upper limb thoracic and abdominal regions Intercostals Celiac trunk – gastric, hepatic, splenic Superior mesenteric – to the small intestine and proximal large intestine Suprarenal – to the adrenals Renal – to the kidneys thoracic and abdominal regions Gonadals Testicular Ovarian Inferior mesenteric – to the distal large intestine Common iliac – branches from the inferior end of the abdominal aorta thoracic and abdominal regions Pelvis and lower limbs Internal iliac – to pelvic structures External iliac- to the leg Femoral- to the thigh Popliteal – to popliteal region Anterior tibial – to the crural region Posterior tibial – to the sural region Fibular – to fibular region Pelvis and lower limbs Chapter 33 PART B Veins – head and neck Brachiocephalic – into sup.vena cava Subclavian – lateral branch of brachiocephalic Internal jugular – medial branch into the brachiocephalic vein External jugular – external vein of the neck that returns blood to the subclavian Head and neck Head and neck Sinuses – drain blood from the cranium Superior sagittal Inferior sagittal sinus Transverse Cranium Upper limb and thorax Axillary – it is a continuation of the subclavian Basilic – medial and empties into the brachial Brachial – continuation of axillary Cephalic – lateral and empties into the axillary Medial cubital – connects basilic to cephalic Upper limb and thorax Ulnar Median Radial Azygos – unpaired branch into the sup. Vena cava. Drains the right side of the thorax. Hemiazygos, and accessory hemiazygos -2 sets of multiple veins that empty into the azygos and drain the left side of the thorax. Intercostals Upper limb and thorax Abdominal veins Hepatic Renal Gonadal – testicular or ovarian Right side empties into inf. Vena cava Left side joins with left renal Common iliac – two branches that fuse to become inf. Vena cava Hepatic portal system Portal circulation is a set of vessels that begins and ends with capillary networks. It returns blood from the digestive system to the liver From the liver the blood flows to the inf. Vena cava Hepatic portal system Hepatic portal vein – going to the liver Liver Hepatic vein - from the liver to inferior vena cava Hepatic portal system Lower limbs Internal iliac External iliac Femoral Great saphenous – medial; into the femoral vein. Popliteal Small saphenous - lateral and posterior; into the popliteal. Lower limbs Anterior tibial - branch into the popliteal Posterior tibial – branch into the popliteal Fibular Lower limbs Vessels on the Cat Thoracic Cavity and Arm Arteries Aorta Brachiocephalic trunk Common carotid- right and left Subclavian – right and left Axillary Brachial Vessels on the Cat Thoracic Cavity and Arm Veins Brachiocephalic trunks Jugular –internal and external Subclavian Brachial Vessels on the Cat Abdominal Cavity and Leg Arteries Abdominal aorta Celiac trunk Superior mesenteric Renal Inferior mesenteric Iliac – common, external and internal Femoral Vessels on the Cat Abdominal Cavity and Leg Veins Inferior vena cava Hepatic portal vein Renal Iliac – common, internal and external Great saphenous Femoral