Unilateral Double Axillary and Double Brachial Arteries
... also recorded the bifurcation of brachial artery I into radial and ulnar arteries in cubital fossa,and further continuation of brachial artery II as common interosseous artery. Yoshinaga et al. (2003) observed the termination of deep brachial artery as inferior ulnar collateral artery in the middle ...
... also recorded the bifurcation of brachial artery I into radial and ulnar arteries in cubital fossa,and further continuation of brachial artery II as common interosseous artery. Yoshinaga et al. (2003) observed the termination of deep brachial artery as inferior ulnar collateral artery in the middle ...
Chapter VI - The Arteries
... the vessel runs backward its left side is in contact with the left lung and pleura. Passing downward on the left side of this part of the arch are four nerves; in order from before backward these are, the left phrenic, the lower of the superior cardiac branches of the left vagus, the superior cardia ...
... the vessel runs backward its left side is in contact with the left lung and pleura. Passing downward on the left side of this part of the arch are four nerves; in order from before backward these are, the left phrenic, the lower of the superior cardiac branches of the left vagus, the superior cardia ...
The persistence of the sciatic artery
... incidence of 0.06%. Cowie reported the first angiographically illustrated case in 1960. The persistent sciatic artery may be complete or incomplete. The complete type is a PSA which is the continuation of a large internal iliac artery, is accompanied by the sciatic nerve and continues as the poplite ...
... incidence of 0.06%. Cowie reported the first angiographically illustrated case in 1960. The persistent sciatic artery may be complete or incomplete. The complete type is a PSA which is the continuation of a large internal iliac artery, is accompanied by the sciatic nerve and continues as the poplite ...
tomeningeal artery through the superior orbital fissure. According to
... vessels separated by connective tissue and without a muscular layer [32]. Therefore, the macroscopic appearance of the venous channels of the lateral sellar compartment evolves from a network of venous channels of various size veins to a large venous cavity resulting from the coalescence of those ve ...
... vessels separated by connective tissue and without a muscular layer [32]. Therefore, the macroscopic appearance of the venous channels of the lateral sellar compartment evolves from a network of venous channels of various size veins to a large venous cavity resulting from the coalescence of those ve ...
Multiple arterial anomalies in upper limb Baral P, Vijayabhaskar P
... orthopaedic surgeons, plastic surgeons, radiologists and anatomists. In this paper, we are going to present a very rare anomaly regarding variation in arterial system of right upper limb which was observed during dissection of approximately 55 years old female cadaver in dissection hall of anatomy a ...
... orthopaedic surgeons, plastic surgeons, radiologists and anatomists. In this paper, we are going to present a very rare anomaly regarding variation in arterial system of right upper limb which was observed during dissection of approximately 55 years old female cadaver in dissection hall of anatomy a ...
CN-Multiple arterial anomalies in upper limb.indd
... radial artery did not give any contribution to superficial palmar arch which is solely formed by the continuation of ulnar artery. This type of anomalies are very rare and is not reported in Nepalese cadaver at all. These anomalies are described in detail and their clinical relevance is highlighted. ...
... radial artery did not give any contribution to superficial palmar arch which is solely formed by the continuation of ulnar artery. This type of anomalies are very rare and is not reported in Nepalese cadaver at all. These anomalies are described in detail and their clinical relevance is highlighted. ...
ABNORMAL BRANCHING PATTERN OF THE AXILLARY ARTERY
... Therefore the variation observed in this case will be of clinical use in the following instances: In performing a brachial plexus block, it is important to feel the pulsation of the axillary artery before performing it.In such variation the relation of the artery to the brachial plexus may be disrup ...
... Therefore the variation observed in this case will be of clinical use in the following instances: In performing a brachial plexus block, it is important to feel the pulsation of the axillary artery before performing it.In such variation the relation of the artery to the brachial plexus may be disrup ...
a study of the variation of the popliteal artery branching pattern
... A wide range of variations can be seen in the vascular system of an adult human lower limb. One of the important blood vessels that has been mentioned in the literature is popliteal artery. Popliteal artery injury is frequently associated with lower limb trauma or surgical procedures involving the k ...
... A wide range of variations can be seen in the vascular system of an adult human lower limb. One of the important blood vessels that has been mentioned in the literature is popliteal artery. Popliteal artery injury is frequently associated with lower limb trauma or surgical procedures involving the k ...
Title page Title of Article: - The cadaveric study of profunda brachii
... The profunda brachii, largest branch of the brachial, shows considerable variations in its origin. In 55% of cases, it arises as a single trunk at the level of the tendon of teres major muscle. It may arise from the axillary artery (22%), as common trunk with the superior ulnar collateral artery in ...
... The profunda brachii, largest branch of the brachial, shows considerable variations in its origin. In 55% of cases, it arises as a single trunk at the level of the tendon of teres major muscle. It may arise from the axillary artery (22%), as common trunk with the superior ulnar collateral artery in ...
Title page Title of Article: - The anatomical study of dorsalis pedis
... The embryonic blood vessels acquire a plexiform appearance in the foot. The dorsalis pedis artery is a constant embryonic vessel that plays an important role in the normal arterial morphogenesis of the lower limb. The tiny blood vessels derived from the blood islands in the 3rd and 4th week of devel ...
... The embryonic blood vessels acquire a plexiform appearance in the foot. The dorsalis pedis artery is a constant embryonic vessel that plays an important role in the normal arterial morphogenesis of the lower limb. The tiny blood vessels derived from the blood islands in the 3rd and 4th week of devel ...
Normal and Variant Mesenteric Anatomy
... (the eventual omphalomesenteric or vitelline duct). These three distinct segments of the primitive gut have important implications for mesenteric vascular supply. At about the same time, the embryo becomes too large to meet its metabolic needs by simple diffusion alone. The circulatory system begins ...
... (the eventual omphalomesenteric or vitelline duct). These three distinct segments of the primitive gut have important implications for mesenteric vascular supply. At about the same time, the embryo becomes too large to meet its metabolic needs by simple diffusion alone. The circulatory system begins ...
Variations of the Ophthalmic and Middle Meningeal
... middle cranial fossa via the meningoorbital foramen, a small opening in the medial aspect of the sphenoid bone just lateral to the superior orbital fissure. It eventually anastomoses with the middle meningeal artery . These recurrent arterial branches are seldom identified even after subtraction . I ...
... middle cranial fossa via the meningoorbital foramen, a small opening in the medial aspect of the sphenoid bone just lateral to the superior orbital fissure. It eventually anastomoses with the middle meningeal artery . These recurrent arterial branches are seldom identified even after subtraction . I ...
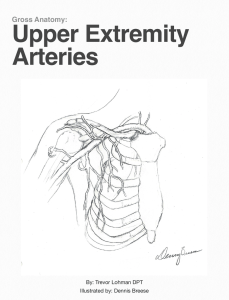
UE Arteries - AandPonline.com
... certain terms. You will find that certain structures, the deep palmar arch for example, appear as both radial and ulnar artery structures. This is due to the fact that some arterial branches connect to both the ulnar and radial artery, and therefore are listed in duplicate based on their origin. Tha ...
... certain terms. You will find that certain structures, the deep palmar arch for example, appear as both radial and ulnar artery structures. This is due to the fact that some arterial branches connect to both the ulnar and radial artery, and therefore are listed in duplicate based on their origin. Tha ...
Human Anatomy
... arterioles. They are directly continuous with the capillaries. Capillaries are hair-like vessels concerned with metabolism. The capillary wall consists of a single layer of flat endothelial cells permeable to substances and gases solved in liquids. The pre-capillaries, capillaries, postcapillaries, ...
... arterioles. They are directly continuous with the capillaries. Capillaries are hair-like vessels concerned with metabolism. The capillary wall consists of a single layer of flat endothelial cells permeable to substances and gases solved in liquids. The pre-capillaries, capillaries, postcapillaries, ...
2-Major Arteries of the Body
... places where we need a rich blood supply) providing backup routes for blood to flow if one artery is blocked, e.g. arteries of limbs. o The arteries whose terminal branches do not anastomose with branches of adjacent arteries are called “END ARTERIES”. End arteries are of two types: • Anatomic (True ...
... places where we need a rich blood supply) providing backup routes for blood to flow if one artery is blocked, e.g. arteries of limbs. o The arteries whose terminal branches do not anastomose with branches of adjacent arteries are called “END ARTERIES”. End arteries are of two types: • Anatomic (True ...
Blood vessels of the shin — anterior tibial artery
... such variation exists in 6% of cases. In our studies we have observed such type in 1 out of 50 limbs dissected (2%). The dorsal pedal artery may originate from the connection between the anterior tibial and the fibular arteries (1% — Perlinzski [1]). In our studies we did not find such variation. It ...
... such variation exists in 6% of cases. In our studies we have observed such type in 1 out of 50 limbs dissected (2%). The dorsal pedal artery may originate from the connection between the anterior tibial and the fibular arteries (1% — Perlinzski [1]). In our studies we did not find such variation. It ...
Unusual Branching Pattern of the External Carotid Artery in A Cadaver
... digastric muscle and stylohyoid muscle. The branches of the external carotid may arise irregularly or be diminished or increased in number. When increased in number (by two or more), they arise as a common stem or by the addition of branches not usually derived from this artery, such as the sternoma ...
... digastric muscle and stylohyoid muscle. The branches of the external carotid may arise irregularly or be diminished or increased in number. When increased in number (by two or more), they arise as a common stem or by the addition of branches not usually derived from this artery, such as the sternoma ...
Cerebellar Arteries Originating from the Internal Carotid Artery
... territory , the rest being irrigated by a corresponding usually hypoplastic, artery, originating from the vertebral or basilar artery (Fig 6). Although the clinical significance of these anomalous vessels is not yet completely defined, the areas they supply are important. One must be aware of their ...
... territory , the rest being irrigated by a corresponding usually hypoplastic, artery, originating from the vertebral or basilar artery (Fig 6). Although the clinical significance of these anomalous vessels is not yet completely defined, the areas they supply are important. One must be aware of their ...
study of arterial variations in the arm
... artery are the radial and middle collateral arteries, both of which help to form the anastomoses around the elbow. The radial collateral artery frollows the radial nerve through the lateral intermuscular septeum and anastomoses in front of the elbow with the radial recurrent artery. The middle colla ...
... artery are the radial and middle collateral arteries, both of which help to form the anastomoses around the elbow. The radial collateral artery frollows the radial nerve through the lateral intermuscular septeum and anastomoses in front of the elbow with the radial recurrent artery. The middle colla ...
BRANCHING PATTERN OF FETAL INTERNAL ILIAC ARTERY
... adult condition where there is no apparent separation of the adult internal iliac artery into an anterior and a posterior division. None of the specimens in this study revealed this type. Embryologically, the umbilical arteries arise when the embryo is less than 1.5 mm long, about the level where, t ...
... adult condition where there is no apparent separation of the adult internal iliac artery into an anterior and a posterior division. None of the specimens in this study revealed this type. Embryologically, the umbilical arteries arise when the embryo is less than 1.5 mm long, about the level where, t ...
A STUDY ON DIVISION OF BRACHIAL ARTERY AND ITS CLINICAL
... Icten et al found radial artery arising from the axillary artery bilaterally in a cadaver [21]. Okaro and jiburum had reported an incidence of radial artery arising from the axillary artery bilaterally in an adult Nigerian cadaver[22]. Balchandra et al reported a case of high origin of radial artery ...
... Icten et al found radial artery arising from the axillary artery bilaterally in a cadaver [21]. Okaro and jiburum had reported an incidence of radial artery arising from the axillary artery bilaterally in an adult Nigerian cadaver[22]. Balchandra et al reported a case of high origin of radial artery ...
PDF
... Fig 1. A, Left internal carotid angiogram demonstrates a carotid-cavernous fistula with main supply by the deep recurrent ophthalmic artery (arrows). There also is filling of the cavernous sinus through cavernous branches from the C-5 segment (curved arrow). B, Right internal carotid angiogram durin ...
... Fig 1. A, Left internal carotid angiogram demonstrates a carotid-cavernous fistula with main supply by the deep recurrent ophthalmic artery (arrows). There also is filling of the cavernous sinus through cavernous branches from the C-5 segment (curved arrow). B, Right internal carotid angiogram durin ...
The Craniocervical Venous System in Relation to
... sinuses of the posterior cranial fossa and the vertebral venous systems. This study revealed the nearly constant presence of the anterior condylar confluent (ACC) located on the external orifice of the canal of the hypoglossal nerve. The ACC offered multiple connections with the dural venous sinuses ...
... sinuses of the posterior cranial fossa and the vertebral venous systems. This study revealed the nearly constant presence of the anterior condylar confluent (ACC) located on the external orifice of the canal of the hypoglossal nerve. The ACC offered multiple connections with the dural venous sinuses ...
Fenestration of Axillary Vein by a Variant Axillary Artery
... a variation of axillary artery and vein. During routine educational dissections of axillary region, it was observed that a fenestrated axillary vein was perforated by a variant axillary artery in right arm of an old male cadaver. The axillary artery which was fenestrated through axillary vein had on ...
... a variation of axillary artery and vein. During routine educational dissections of axillary region, it was observed that a fenestrated axillary vein was perforated by a variant axillary artery in right arm of an old male cadaver. The axillary artery which was fenestrated through axillary vein had on ...
Standard Contour Nomenclature V1.4
... reason for this is that the FMA is a formal ontology which means that it embodies the relationships that exist between other anatomic structures. Relationships such as is_inferior_to and is_drained_by are catered for and can be manipulated by computers. Although developed independently, this nomencl ...
... reason for this is that the FMA is a formal ontology which means that it embodies the relationships that exist between other anatomic structures. Relationships such as is_inferior_to and is_drained_by are catered for and can be manipulated by computers. Although developed independently, this nomencl ...
Vascular remodelling in the embryo

Vascular remodelling is a process which begins at day 21 of human embryogenesis, when an immature heart begins contracting, pushing fluid through the early vasculature. This first passage of fluid initiates a signal cascade based on physical cues including shear stress and circumferential stress, which is necessary for the remodelling of the vascular network, arterial-venous identity, angiogenesis, and the regulation of genes through mechanotransduction. This embryonic process is necessary for the future stability of the mature vascular network.Vasculogenesis is the initial establishment of the components of the blood vessel network, or vascular tree. This is dictated by genetic factors and has no inherent function other than to lay down the preliminary outline of the circulatory system. Once fluid flow begins, biomechanical and hemodynamic inputs are applied to the system set up by vasculogenesis, and the active remodelling process can begin.Physical cues such as pressure, velocity, flow patterns, and shear stress are known to act on the vascular network in a number of ways, including branching morphogenesis, enlargement of vessels in high-flow areas, angiogenesis, and the development of vein valves. The mechanotransduction of these physical cues to endothelial and smooth muscle cells in the vascular wall can also trigger the promotion or repression of certain genes which are responsible for vasodilation, cell alignment, and other shear stress-mitigating factors. This relationship between genetics and environment is not clearly understood, but researchers are attempting to clarify it by combining reliable genetic techniques, such as genetically-ablated model organisms and tissues, with new technologies developed to measure and track flow patterns, velocity profiles, and pressure fluctuations in vivo.Both in vivo study and modelling are necessary tools to understand this complex process. Vascular remodelling is pertinent to wound healing and proper integration of tissue grafts and organ donations. Promoting an active remodelling process in some cases could help patients recover faster and retain functional use of donated tissues. However, outside of wound healing, chronic vascular remodelling in the adult is often symptomatic of cardiovascular disease. Thus, increased understanding of this biomedical phenomenon could aid in the development of therapeutics or preventative measures to combat diseases such as atherosclerosis.