a case report on abnormal course of vena saphena parva
... Short Saphenous Vein [8,9]. In our study we didn’t found giacomini vein but in our dissection the vein is purely deviating into the subustance of back of thigh. During the dilatation of veins or varicose veins it is very important to know the course of veins. In the lower limbs, venous blood flows f ...
... Short Saphenous Vein [8,9]. In our study we didn’t found giacomini vein but in our dissection the vein is purely deviating into the subustance of back of thigh. During the dilatation of veins or varicose veins it is very important to know the course of veins. In the lower limbs, venous blood flows f ...
Ultrasonographic anatomy of the lower extremity superficial veins
... (US) examination with color Doppler and spectral analysis has become increasingly important and is now used more frequently for the diagnosis and treatment of varicose veins. US is probably the simplest, most frequently used, and most effective method to evaluate the anatomy of varicose veins. In re ...
... (US) examination with color Doppler and spectral analysis has become increasingly important and is now used more frequently for the diagnosis and treatment of varicose veins. US is probably the simplest, most frequently used, and most effective method to evaluate the anatomy of varicose veins. In re ...
The Craniocervical Venous System in Relation to
... cerebral venous outflow into vertebral venous systems rather than into the internal jugular veins. We sought to determine venous connections between dural venous sinuses of the posterior cranial fossa and craniocervical vertebral venous systems. METHODS: Corrosion casts of the cranial and cervical v ...
... cerebral venous outflow into vertebral venous systems rather than into the internal jugular veins. We sought to determine venous connections between dural venous sinuses of the posterior cranial fossa and craniocervical vertebral venous systems. METHODS: Corrosion casts of the cranial and cervical v ...
Variation in the origin of inferior vesical artery from a variant
... most appropriate channels enlarge while others retract and disappear, thereby establishing the final arterial pattern [11, 12]. Before the obturator artery appears as an independent blood vessel from the ‘rete pelvicum’, the blood flow destined for this territory makes an unusual choice of source ch ...
... most appropriate channels enlarge while others retract and disappear, thereby establishing the final arterial pattern [11, 12]. Before the obturator artery appears as an independent blood vessel from the ‘rete pelvicum’, the blood flow destined for this territory makes an unusual choice of source ch ...
VII. The Veins
... larger and altogether more numerous than the arteries; hence, the entire capacity of the venous system is much greater than that of the arterial; the capacity of the pulmonary veins, however, only slightly exceeds that of the pulmonary arteries. The veins are cylindrical like the arteries; their wal ...
... larger and altogether more numerous than the arteries; hence, the entire capacity of the venous system is much greater than that of the arterial; the capacity of the pulmonary veins, however, only slightly exceeds that of the pulmonary arteries. The veins are cylindrical like the arteries; their wal ...
- Science Publishing Corporation
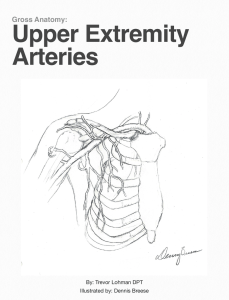
... In the present case superficial brachial artery was tortuous and running medial to the median nerve in the axilla. Deep brachial artery was giving branches as Profunda brachii and Superior ulnar collateral arteries. Superficial brachial artery was dividing into Radial and Ulnar arteries at the neck ...
... In the present case superficial brachial artery was tortuous and running medial to the median nerve in the axilla. Deep brachial artery was giving branches as Profunda brachii and Superior ulnar collateral arteries. Superficial brachial artery was dividing into Radial and Ulnar arteries at the neck ...
Cerebellar Arteries Originating from the Internal Carotid Artery
... origin and are responsible for the irrigation of the entire area of nervous tissue related to the specific artery (Fig 3). On the other hand, when the artery is of small caliber it irrigates only part of the territory , the rest being irrigated by a corresponding usually hypoplastic, artery, origina ...
... origin and are responsible for the irrigation of the entire area of nervous tissue related to the specific artery (Fig 3). On the other hand, when the artery is of small caliber it irrigates only part of the territory , the rest being irrigated by a corresponding usually hypoplastic, artery, origina ...
UE Arteries - AandPonline.com
... structures, the deep palmar arch for example, appear as both radial and ulnar artery structures. This is due to the fact that some arterial branches connect to both the ulnar and radial artery, and therefore are listed in duplicate based on their origin. That’s it! You have now mastered the arteries ...
... structures, the deep palmar arch for example, appear as both radial and ulnar artery structures. This is due to the fact that some arterial branches connect to both the ulnar and radial artery, and therefore are listed in duplicate based on their origin. That’s it! You have now mastered the arteries ...
Anatomy for the Phlebologist
... Anatomy of the great saphenous vein (GSV) The GSV originates in the medial foot and passes upward anterior to the medial malleolus, then crosses the medial tibia in a posterior direction to ascend in the medial line across the knee. Above the knee it continues anteromedially above the deep fascia t ...
... Anatomy of the great saphenous vein (GSV) The GSV originates in the medial foot and passes upward anterior to the medial malleolus, then crosses the medial tibia in a posterior direction to ascend in the medial line across the knee. Above the knee it continues anteromedially above the deep fascia t ...
Anatomical variations of the posterior circulation: case reports and a
... two vertebral arteries that meet together after a variable distance of a few millimetres. The assessment of the real frequency of fenestration of the basilar artery is difficult since the data vary according to type of series. However, the incidence of fenestration of the basilar artery is reported ...
... two vertebral arteries that meet together after a variable distance of a few millimetres. The assessment of the real frequency of fenestration of the basilar artery is difficult since the data vary according to type of series. However, the incidence of fenestration of the basilar artery is reported ...
2-Major Arteries of the Body
... places where we need a rich blood supply) providing backup routes for blood to flow if one artery is blocked, e.g. arteries of limbs. o The arteries whose terminal branches do not anastomose with branches of adjacent arteries are called “END ARTERIES”. End arteries are of two types: • Anatomic (True ...
... places where we need a rich blood supply) providing backup routes for blood to flow if one artery is blocked, e.g. arteries of limbs. o The arteries whose terminal branches do not anastomose with branches of adjacent arteries are called “END ARTERIES”. End arteries are of two types: • Anatomic (True ...
View PDF - OMICS Group
... Presence of bilateral accessory renal arteries can be explained in the light of embryogenic development and its molecular regulation. Each primitive dorsal aorta gives off ventral splanchnic arteries, lateral splanchnic arteries, somatic arteries and caudal continuation. The lateral splanchnic arter ...
... Presence of bilateral accessory renal arteries can be explained in the light of embryogenic development and its molecular regulation. Each primitive dorsal aorta gives off ventral splanchnic arteries, lateral splanchnic arteries, somatic arteries and caudal continuation. The lateral splanchnic arter ...
Bilateral Variations Of Renal Vessels
... cava, whereas the left renal vein which is three times longer than the right renal vein drains into the inferior vena cava by coursing anterior to the aorta. In addition, left renal vein also receives tributaries of left gonadal vein from below and left suprarenal vein from above.1 CASE REPORT Durin ...
... cava, whereas the left renal vein which is three times longer than the right renal vein drains into the inferior vena cava by coursing anterior to the aorta. In addition, left renal vein also receives tributaries of left gonadal vein from below and left suprarenal vein from above.1 CASE REPORT Durin ...
Pdf - McMed International
... During routine dissection, of the lower limb of a 70 year old donated embalmed male cadaver in the Department of Anatomy, at K.J. Somaiya Medical College, Sion, Mumbai, India, I observed two dorsalis pedis arteries arising from the anterior tibial artery. The anterior tibial artery divided into two ...
... During routine dissection, of the lower limb of a 70 year old donated embalmed male cadaver in the Department of Anatomy, at K.J. Somaiya Medical College, Sion, Mumbai, India, I observed two dorsalis pedis arteries arising from the anterior tibial artery. The anterior tibial artery divided into two ...
its pulse can be felt
... Small Saphenous Vein Tributaries: Numerous small veins from the back of the leg. Communicating veins with deep veins of the foot. Anastomotic branches that join the great saphenous ...
... Small Saphenous Vein Tributaries: Numerous small veins from the back of the leg. Communicating veins with deep veins of the foot. Anastomotic branches that join the great saphenous ...
terminal branch of Popliteal artery
... Small Saphenous Vein Tributaries: Numerous small veins from the back of the leg. Communicating veins with deep veins of the foot. Anastomotic branches that join the great saphenous ...
... Small Saphenous Vein Tributaries: Numerous small veins from the back of the leg. Communicating veins with deep veins of the foot. Anastomotic branches that join the great saphenous ...
Artery Vein - Stephen Tavoni
... interstitial fluid “pulls” end is a negative number. This fluid out of capillary. means that reabsorption, not filtration, is occurring and so fluid moves from the interstitial space into the capillary. ...
... interstitial fluid “pulls” end is a negative number. This fluid out of capillary. means that reabsorption, not filtration, is occurring and so fluid moves from the interstitial space into the capillary. ...
2-Major arteries of the body
... Define arterial anastomosis and describe its significance. Define end arteries and give examples. Describe the aorta and its divisions & list the branches from each part. List major arteries and their distribution in the head & neck, thorax, abdomen and upper & lower extremities. List main pulse poi ...
... Define arterial anastomosis and describe its significance. Define end arteries and give examples. Describe the aorta and its divisions & list the branches from each part. List major arteries and their distribution in the head & neck, thorax, abdomen and upper & lower extremities. List main pulse poi ...
2-MAJOR ARTERIES OF BODY-PROF AHMED
... Define arterial anastomosis and describe its significance. Define end arteries and give examples. Describe the aorta and its divisions & list the branches from each part. List major arteries and their distribution in the head & neck, thorax, abdomen and upper & lower extremities. List main pulse poi ...
... Define arterial anastomosis and describe its significance. Define end arteries and give examples. Describe the aorta and its divisions & list the branches from each part. List major arteries and their distribution in the head & neck, thorax, abdomen and upper & lower extremities. List main pulse poi ...
vascular prblems summer course 2014 New Microsoft
... • It is caused by pressure on the lower trunk of the plexus and circulatory impairment of the upper ...
... • It is caused by pressure on the lower trunk of the plexus and circulatory impairment of the upper ...
Why should we report posterior fossa emissary veins?
... (11). Assessing this vein preoperatively would allow one to modify the surgical procedure to reduce complications. The MEV may constitute a potential risk for spreading infectious processes from extracranial to intracranial areas. It may be thrombosed as a complication of acute otomastoiditis. The M ...
... (11). Assessing this vein preoperatively would allow one to modify the surgical procedure to reduce complications. The MEV may constitute a potential risk for spreading infectious processes from extracranial to intracranial areas. It may be thrombosed as a complication of acute otomastoiditis. The M ...
Veins - Dr. Par Mohammadian
... • Called capacitance vessels (blood reservoirs); contain up to 65% of blood supply • Blood pressure lower than in arteries (walls don’t burst!) => • Adaptations ensure return of blood to heart despite low pressure – Large-diameter lumens offer little resistance – Venous valves prevent backflow of bl ...
... • Called capacitance vessels (blood reservoirs); contain up to 65% of blood supply • Blood pressure lower than in arteries (walls don’t burst!) => • Adaptations ensure return of blood to heart despite low pressure – Large-diameter lumens offer little resistance – Venous valves prevent backflow of bl ...
Microsoft PowerPoint file
... The first of the heart's four chambers, the right atrium, receives purplish blood, short of oxygen and laden with carbon dioxide. This used blood arrives through the body's two major veins, the superior and inferior venae cavae, and from the many minute blood vessels that drain blood from the walls ...
... The first of the heart's four chambers, the right atrium, receives purplish blood, short of oxygen and laden with carbon dioxide. This used blood arrives through the body's two major veins, the superior and inferior venae cavae, and from the many minute blood vessels that drain blood from the walls ...
Where There Is Blood, There Is a Way
... A brief review of the developmental embryology will facilitate a better understanding of these collateral pathways. The developing visceral veins consist of the right and left vitelline veins from the yolk sac and the right and left umbilical veins from the placenta. These veins open into correspond ...
... A brief review of the developmental embryology will facilitate a better understanding of these collateral pathways. The developing visceral veins consist of the right and left vitelline veins from the yolk sac and the right and left umbilical veins from the placenta. These veins open into correspond ...
Superficial veins of the foot in the baboon Papio anubis
... leg. It was a single large vessel, which emptied into the deep veins above the popliteal fossa. In contrast, LSV was double and thin. The vessel’s width did not vary as it approached the saphenofemoral junction. We found only one type of SSV outflow into the popliteal vein and one type of LSV outflo ...
... leg. It was a single large vessel, which emptied into the deep veins above the popliteal fossa. In contrast, LSV was double and thin. The vessel’s width did not vary as it approached the saphenofemoral junction. We found only one type of SSV outflow into the popliteal vein and one type of LSV outflo ...
William Harvey

William Harvey (1 April 1578 – 3 June 1657) was an English physician. He was the first known to describe completely and in detail the systemic circulation and properties of blood being pumped to the brain and body by the heart, though earlier writers, such as Jacques Dubois, had provided precursors of the theory. After his death the William Harvey Hospital was constructed in the town of Ashford, several miles from his birthplace of Folkestone.