BLOOD SUPPLY OF EYE - Home
... Abbreviations: A = arachnoid; C = choroid; CRA = central retinal artery; Col. Br. = Collateral branches; CRV = central retinal vein; D = dura; LC = lamina cribrosa; NFL = surface nerve fiber layer of the disc; OD = optic disc; ON = optic nerve; P = pia; PCA = posterior ciliary artery; PR and PLR = ...
... Abbreviations: A = arachnoid; C = choroid; CRA = central retinal artery; Col. Br. = Collateral branches; CRV = central retinal vein; D = dura; LC = lamina cribrosa; NFL = surface nerve fiber layer of the disc; OD = optic disc; ON = optic nerve; P = pia; PCA = posterior ciliary artery; PR and PLR = ...
Patterns of blood flow in episcleral vessels studied by low
... 16 angiograms were adequately imaged for flow direction to be documented. Twenty-five episcleral arteries flowed away from the limbus: 15 carried blood towards the limbus. Arteries flowing in opposing directions were found in nine out of 21 angiographic fields (Fig. 7). All veins drained away from t ...
... 16 angiograms were adequately imaged for flow direction to be documented. Twenty-five episcleral arteries flowed away from the limbus: 15 carried blood towards the limbus. Arteries flowing in opposing directions were found in nine out of 21 angiographic fields (Fig. 7). All veins drained away from t ...
MIDDLE MENINGEAL ARTERY Is typically the 3 rd
... fissure .this sinus connect cavernous sinus to superior dilatation of internal jugular vein. right and left inf. petrosal sinus connect together by basilar plexus. ...
... fissure .this sinus connect cavernous sinus to superior dilatation of internal jugular vein. right and left inf. petrosal sinus connect together by basilar plexus. ...
Human Blood Vessels - Austin Community College
... In this exercise the arteries and veins of the cat will be identified and compared with those of the human. To facilitate identification, the arteries and veins have been injected with colored latex: arteries red, veins blue. In tracing the blood vessels, it is necessary that each artery and vein be ...
... In this exercise the arteries and veins of the cat will be identified and compared with those of the human. To facilitate identification, the arteries and veins have been injected with colored latex: arteries red, veins blue. In tracing the blood vessels, it is necessary that each artery and vein be ...
Major arteries of the body
... All arteries, carry oxygenated blood, except the pulmonary and umbilical arteries, which carry deoxygenated blood to the lungs (postnatal) and to the placenta (prenatal) respectively The flow of blood depends on the pumping action of the heart There are no valves in the arteries. The branches of art ...
... All arteries, carry oxygenated blood, except the pulmonary and umbilical arteries, which carry deoxygenated blood to the lungs (postnatal) and to the placenta (prenatal) respectively The flow of blood depends on the pumping action of the heart There are no valves in the arteries. The branches of art ...
Amazing anatomy: roadmaps of venous collateral circulation in
... presentation is to review the most important pathways of collateral circulation in patients with obstruction of SVC, as well as to provide tips for easy identification. Four main systems of collateral venous circulation include: (1) azygos system of veins, which provides communication between SVC an ...
... presentation is to review the most important pathways of collateral circulation in patients with obstruction of SVC, as well as to provide tips for easy identification. Four main systems of collateral venous circulation include: (1) azygos system of veins, which provides communication between SVC an ...
thoracic wall - Yeditepe University Dentistry Anatomy
... Protect vital thoracic and abdominal organs (most air or fluid filled) from external forces. Resist the negative (sub-atmospheric) internal pressures generated by the elastic recoil of the lungs and inspiratory movements. Provide attachment for and support the weight of the upper limbs. Prov ...
... Protect vital thoracic and abdominal organs (most air or fluid filled) from external forces. Resist the negative (sub-atmospheric) internal pressures generated by the elastic recoil of the lungs and inspiratory movements. Provide attachment for and support the weight of the upper limbs. Prov ...
(updated) Heart-MBVS-veins-2016
... forward around the medial side of the thigh. Hooks through the lower part of the saphenous opening in the deep fascia to join the femoral vein about 1.5 in. (4 cm) below and lateral to the pubic tubercle. ...
... forward around the medial side of the thigh. Hooks through the lower part of the saphenous opening in the deep fascia to join the femoral vein about 1.5 in. (4 cm) below and lateral to the pubic tubercle. ...
Veins 1 Head and Thoracic Veins
... 5. In one type of heart failure, the RIGHT side of the heart does not pump out enough blood. As a result, blood tends to "backup" in the blood vessels that carry blood to the right side of the heart. What neck blood vessel is clearly visible on the neck when filled with blood as a result of this typ ...
... 5. In one type of heart failure, the RIGHT side of the heart does not pump out enough blood. As a result, blood tends to "backup" in the blood vessels that carry blood to the right side of the heart. What neck blood vessel is clearly visible on the neck when filled with blood as a result of this typ ...
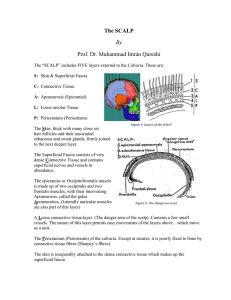
The SCALP
... branches of the external carotid. These five branches not only anastomose with each other but also with those of the opposite side. These anastomoses assume great importance after ligation of the common or external carotid artery of one side. ...
... branches of the external carotid. These five branches not only anastomose with each other but also with those of the opposite side. These anastomoses assume great importance after ligation of the common or external carotid artery of one side. ...
pertinent blood vessel routes
... PERTINENT BLOOD VESSEL ROUTES See pages at end of Blood Vessels and Circulation Chapter in Saladin. When thinking about blood vessel routes, think about the path blood takes as it flows through vessels to some destination in the body. This is like giving directions to someone on how to drive somewhe ...
... PERTINENT BLOOD VESSEL ROUTES See pages at end of Blood Vessels and Circulation Chapter in Saladin. When thinking about blood vessel routes, think about the path blood takes as it flows through vessels to some destination in the body. This is like giving directions to someone on how to drive somewhe ...
27-As of Mid& hindgut
... Portal- Systemic Anastomoses Under normal conditions, the portal venous blood traverse the liver and drains into the inferior vena cava of the systemic venous circulation by way of the hepatic veins. This is the direct route, however, other smaller communications exist between the portal and system ...
... Portal- Systemic Anastomoses Under normal conditions, the portal venous blood traverse the liver and drains into the inferior vena cava of the systemic venous circulation by way of the hepatic veins. This is the direct route, however, other smaller communications exist between the portal and system ...
3-Major Veins of the body
... and lies behind the medial border of the patella. Passes behind the knee and curves forward around the medial side of the thigh. Hooks through the lower part of the saphenous opening in the deep fascia to joins the femoral vein about 1.5 in. (4 cm) below and lateral to the pubic tubercle. ...
... and lies behind the medial border of the patella. Passes behind the knee and curves forward around the medial side of the thigh. Hooks through the lower part of the saphenous opening in the deep fascia to joins the femoral vein about 1.5 in. (4 cm) below and lateral to the pubic tubercle. ...
Blood Vessel Lab
... vessel in the text of the guide; that can be more confusing. You are responsible for identifying vessels on models, drawings, photographs and A.D.A.M. Interactive Anatomy. In addition, you must know the part or parts of the body that each vessel serves. Figure references refer to figures in your tex ...
... vessel in the text of the guide; that can be more confusing. You are responsible for identifying vessels on models, drawings, photographs and A.D.A.M. Interactive Anatomy. In addition, you must know the part or parts of the body that each vessel serves. Figure references refer to figures in your tex ...
Anatomy - venous and lymphatic drainage of pelvis
... These are venæ comitantes of the superior gluteal artery; They receive tributaries from the buttock corresponding with the branches of the artery, and enter the pelvis through the greater sciatic foramen, above the Piriformis, They frequently unite before ending in the hypogastric vein. ...
... These are venæ comitantes of the superior gluteal artery; They receive tributaries from the buttock corresponding with the branches of the artery, and enter the pelvis through the greater sciatic foramen, above the Piriformis, They frequently unite before ending in the hypogastric vein. ...
Major arteries of the body
... Define arterial anastomosis and describe its significance. Define end arteries and give examples. Describe the aorta and its divisions & list the branches from each part. List major arteries and their distribution in the head & neck, thorax, abdomen and upper & lower extremities. List main pulse poi ...
... Define arterial anastomosis and describe its significance. Define end arteries and give examples. Describe the aorta and its divisions & list the branches from each part. List major arteries and their distribution in the head & neck, thorax, abdomen and upper & lower extremities. List main pulse poi ...
2-Copy of MAJOR ARTERIES OF BODY-PROF AHMED
... Define arterial anastomosis and describe its significance. Define end arteries and give examples. Describe the aorta and its divisions & list the branches from each part. List major arteries and their distribution in the head & neck, thorax, abdomen and upper & lower extremities. List main pulse poi ...
... Define arterial anastomosis and describe its significance. Define end arteries and give examples. Describe the aorta and its divisions & list the branches from each part. List major arteries and their distribution in the head & neck, thorax, abdomen and upper & lower extremities. List main pulse poi ...
artery - KSUMSC
... close to their origin from the superficial veins. They contain valves which normally allow the blood to flow from the superficial to the deep veins. The perforating veins pass through the deep fascia at an oblique angle so during muscular contraction , they are compressed. This also prevents blood ...
... close to their origin from the superficial veins. They contain valves which normally allow the blood to flow from the superficial to the deep veins. The perforating veins pass through the deep fascia at an oblique angle so during muscular contraction , they are compressed. This also prevents blood ...
the major blood vessels of the wing of the ostrich
... brachial artery or its branches, the radial and ulnar arteries. In the ostrich, no apastomoses between branches of the deep brachial and brachial arteries could be demonstrated. According to Baumel et al., (1979), Bhaduri et al., (1957), Cralley (1965), Gadhoke et al., (1975), Gobeil (1970) and Nish ...
... brachial artery or its branches, the radial and ulnar arteries. In the ostrich, no apastomoses between branches of the deep brachial and brachial arteries could be demonstrated. According to Baumel et al., (1979), Bhaduri et al., (1957), Cralley (1965), Gadhoke et al., (1975), Gobeil (1970) and Nish ...
Saladin 5e Extended Outline
... c. Small vessels called the vasa vasorum supply blood to at least the outer half of the wall of a larger vessel, while tissues on the inner half are thought to be nourished by diffusion from blood in the lumen. ...
... c. Small vessels called the vasa vasorum supply blood to at least the outer half of the wall of a larger vessel, while tissues on the inner half are thought to be nourished by diffusion from blood in the lumen. ...
21-Vascular anatomy of the lower limb2015-12-15 04
... close to their origin from the superficial veins. They contain valves which normally allow the blood to flow from the superficial to the deep veins. The perforating veins pass through the deep fascia at an oblique angle so during muscular contraction , they are compressed. This also prevents blood ...
... close to their origin from the superficial veins. They contain valves which normally allow the blood to flow from the superficial to the deep veins. The perforating veins pass through the deep fascia at an oblique angle so during muscular contraction , they are compressed. This also prevents blood ...
17-Art,Veins. OF L.L2014-12-23 00:294.5 MB
... 1. Nutrient artery to the tibia (the largest nutrient artery of the body). 2. Calcaneal arteries: supply the heel. 3. Peroneal (fibular) artery: The largest and most important branch. It supplies a nutrient artery to the fibula & Muscular branches to the muscles of the lateral and posterior compartm ...
... 1. Nutrient artery to the tibia (the largest nutrient artery of the body). 2. Calcaneal arteries: supply the heel. 3. Peroneal (fibular) artery: The largest and most important branch. It supplies a nutrient artery to the fibula & Muscular branches to the muscles of the lateral and posterior compartm ...
L18-Art,Veins. OF L.L2014-08-21 09:594.2 MB
... 1. Nutrient artery to the tibia (the largest nutrient artery of the body). 2. Calcaneal arteries: supply the heel. 3. Peroneal (fibular) artery: The largest and most important branch. It supplies a nutrient artery to the fibula & Muscular branches to the muscles of the lateral and posterior compartm ...
... 1. Nutrient artery to the tibia (the largest nutrient artery of the body). 2. Calcaneal arteries: supply the heel. 3. Peroneal (fibular) artery: The largest and most important branch. It supplies a nutrient artery to the fibula & Muscular branches to the muscles of the lateral and posterior compartm ...
William Harvey

William Harvey (1 April 1578 – 3 June 1657) was an English physician. He was the first known to describe completely and in detail the systemic circulation and properties of blood being pumped to the brain and body by the heart, though earlier writers, such as Jacques Dubois, had provided precursors of the theory. After his death the William Harvey Hospital was constructed in the town of Ashford, several miles from his birthplace of Folkestone.