* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Pulmonary semilunar valve
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
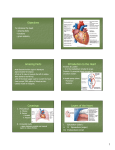
Heart Dissection Tutorial The hearts have already been cut open and are wrapped in a damp paper towel in zip lock bags. There are 2 at your lab table. Choose the period number on the bag for your specimen. The specimen should be returned the way you found it. DO NOT THROW IT Heart Dissection Tutorial You will not need the dissecting tools today. Your only tool is a straw (explained later) – do not destroy the straws! Do not remove any parts from the heart or tear it apart! Heart Dissection Tutorial WEAR EYE PROTECTION AND GLOVES! Heart Dissection Tutorial As you go through this tutorial, make note of any parts you had trouble finding and bring this next week when we will look at the hearts again. First determine the anterior and posterior sides of your sheep heart. This is the anterior side. Note the PULMONARY ARTERY shown here with arrow. Find this on your heart. Note the fat on the surface. Also note the blood vessels that are embedded in the external heart muscle. These are the coronary arteries and veins. The red one is called the WIDOW MAKER. WHY? These purplish structures are the auricles. They communicate with the atria chambers. Your heart does not have all of the aorta attached. You are responsible for knowing these branches off the aorta shown in the yellow boxes. Right side Right side Left side Left side Thicker wall Thicker wall When you have examined the outside of the heart, I will cut the heart in half as shown Right side Right side Left side Left side Thicker wall Thicker wall Examine your open heart. Try to keep in mind which is the anterior side vs. the posterior side. Note the difference in the thickness of the walls. The Left side has a thicker wall because it is the main pump having to move blood through the entire body. Right atrium Left atrium Tricuspid valve Bicuspid valve Chordae tendinae Right ventricle Papillary muscle Interventricular septum Left ventricle Now open the heart as shown and work with either the posterior or anterior side (choose the side you can see these structures in the bes)> Right atrium Left atrium Tricuspid valve Bicuspid valve Chordae tendinae Right ventricle Papillary muscle Interventricular septum Left ventricle Now find all of these labeled parts. Note the Chordae Tendinae. These are threadlike bands of fibrous tissue which attach on one end to the edges of the tricuspid and mitral valves of the heart and on the other end to the papillary muscles. the papillary muscles of the heart serve to limit the movements of the mitral and tricuspid valves. These muscles contract to tighten the chordae tendineae, which in turn prevent inversion of the valves. Pulmonary valve Aortic valve CLOSER LOOK ATof Area CHORDAE cutaway TENDINEAE AND Mitral PAPILLARY MUSCLE. valve Tricuspid valve Chordae tendineae attached to tricuspid valve flap Papillary muscle Figure 18.8c Now you are going to use your finger or the straw to trace a drop of blood through the heart naming all of the parts. Now you are going to use your finger to trace a drop of blood through the heart naming all of the parts. Begin at the posterior side of the heart and find the inferior and superior vena cavae. Put your fingers through these and note that your finger enters the right artrium. If you have problems finding the vena cavae, stick your finger into the posterior right atrium chamber and find the vena cavae as it exits this chamber. There are 2 vena cavae – find both. Now from the right atrium, find the tricuspid valve, and then the right ventricle . You will not be able to see the pulmonary semilunar valve, but it is embedded in the the heart tissue and it is not exposed. To find the exit from the right ventricle, go to the front of the heart and place your finger into the right ventricle at an angle. See if you can exit from this area into the pulmonary artery which is number 18 on this specimen. The blood exits the pulmonary artery, low in oxygen and now goes to lungs. From there it will drop of carbon dioxide and pick up oxygen. This oxygenated blood will now be channeled back to the heart via the pulmonary veins. See diagram below. The yellow arrows show the pulmonary artery. If your are having trouble finding the pulmonary artery, turn your heart to the anterior side and stick your finger down the pulmonary artery and watch where it comes into the right ventricle. The pulmonary semilunar valve is hidden under the heart tissue. This is the only valve that you will not be able to see. The blood has traveled to the lungs to pick up oxygen. This oxygenated blood will now be channeled back to the heart via the pulmonary veins. The pulmonary veins are going to be seen as one hole in the posterior side of the heart entering the left atrium. See circled area. Now from the left atrium, find the bicuspid valve (also called mitral), and then the left ventricle . The blood goes from the left ventricle through the semilunar aortic valve and then into the aorta. The aorta distributes oxygenated blood to all parts of the body. aorta 21 = aortic semilunar valve After the blood travels to the body cells, the deoxygenated blood is carried by the vena cavae into the right atrium and we are back to where we started. Now use your list to see if you can trace a drop of blood through the heart. When you are finished, go to the heart review (next slides) and LEARN THE PARTS!!! HEART ANATOMY REVIEW Name this specific valve circled in yellow. Bicuspid or mitral valve Name this chamber (yellow arrow). Right ventricle Name the chamber circled in yellow. Left ventricle Name this specific blood vessel highlighted in yellow. Pulmonary artery Name the specific blood vessel highlighted in yellow. aorta Name this specific part highlighted in yellow. Interventricular septum Name the valve that would be in the area circled by yellow. Aortic semilunar valve Name the blood vessel circled in yellow. Pulmonary artery After blood leaves the right ventricle, what valve does it pass through? Pulmonary semilunar valve What heart chamber does the vena cavae enter? What blood vessel carries blood from the lungs to the heart? Pulmonary vein What valve leads into the pulmonary artery? Pulmonary semilunar valve Name this string-like structure (pink arrow). . Chordae tendinae inferior and superior vena cavae right atrium tricuspid valve right ventricle pulmonary semilunar valve pulmonary artery lungs pulmonary veins left atrium bicuspid valve left ventricle aortic semilunar valve aorta body Name this bulging area (pink arrow). Papillary muscle Name the red blood vessels on surface of heart. Coronary arteries Name the blue blood vessels on surface of heart. Coronary veins Name the specific vessel # 1. Brachiocephalic artery 25. Name the specific vessel # 2. Left common carotid artery Name the specific vessel # 3. Left subclavian artery Name the specific valve # 19. Pulmonary semilunar valve THE END