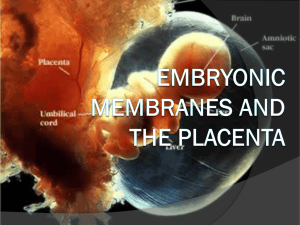
Chapter 29
... • Organs complete most of their development • Fetus looks distinctly human • Chance of survival if born near end of this trimester ...
... • Organs complete most of their development • Fetus looks distinctly human • Chance of survival if born near end of this trimester ...
Chapter 29 *Lecture PowerPoint Human Development
... • Organs complete most of their development • Fetus looks distinctly human • Chance of survival if born near end of this trimester ...
... • Organs complete most of their development • Fetus looks distinctly human • Chance of survival if born near end of this trimester ...
What is a fetal echocardiogram?
... assessed. Sometimes this information may not be important while in some cases it means that definite answers are not possible. The doctor will discuss this with you if necessary. Some fetal heart defects can be very hard to detect before a baby is born, but often these are less severe abnormalities. ...
... assessed. Sometimes this information may not be important while in some cases it means that definite answers are not possible. The doctor will discuss this with you if necessary. Some fetal heart defects can be very hard to detect before a baby is born, but often these are less severe abnormalities. ...
Fetal Pig Dissection Worksheet
... Where is the epiglottis & what is its function? Where is the pharynx located? Give the function of the larynx. What keeps the trachea from collapsing? Where is the diaphragm & give its function. Does the diaphragm function in the fetus? Explain Name the large tubes that enter the lungs. ...
... Where is the epiglottis & what is its function? Where is the pharynx located? Give the function of the larynx. What keeps the trachea from collapsing? Where is the diaphragm & give its function. Does the diaphragm function in the fetus? Explain Name the large tubes that enter the lungs. ...
Chapter 41 Animal Development
... – Chorionic villi contain fetal capillaries that bathe in maternal blood – Many small molecules can be exchanged between fetus and mother • Examples: O2, CO2, nutrients, and fetal urea ...
... – Chorionic villi contain fetal capillaries that bathe in maternal blood – Many small molecules can be exchanged between fetus and mother • Examples: O2, CO2, nutrients, and fetal urea ...
Ch. 42 - Development and Aging
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
- Academy Test Bank
... 64. In the female reproductive system, the ovaries contain eggs. When an egg ripens and leaves the ovary, it is drawn into the oviduct, or fallopian tube, where fertilization could take place if sperm are present. This results in a zygote. The oviduct is lined with cilia, which propel the egg. The u ...
... 64. In the female reproductive system, the ovaries contain eggs. When an egg ripens and leaves the ovary, it is drawn into the oviduct, or fallopian tube, where fertilization could take place if sperm are present. This results in a zygote. The oviduct is lined with cilia, which propel the egg. The u ...
Amnion - Epiblast / Extraembryonic Mesoderm
... Human Chorionic Gonadotropin – Corpus Luteum (declines after 8 weeks) Progesterone – High levels by the end of first trimester Estrogen – Synthesis involves enzymatic activity of fetal adrenal gland and liver Chorionic Somatomammotropin – Human Placental Lactogen – similar to GH (growth, lactation, ...
... Human Chorionic Gonadotropin – Corpus Luteum (declines after 8 weeks) Progesterone – High levels by the end of first trimester Estrogen – Synthesis involves enzymatic activity of fetal adrenal gland and liver Chorionic Somatomammotropin – Human Placental Lactogen – similar to GH (growth, lactation, ...
Human Health - SCHS EOC biology files
... Describe the basic anatomy and physiology of the human reproductive system. Describe the process of human development from fertilization to birth and major changes that occur in each trimester of pregnancy ...
... Describe the basic anatomy and physiology of the human reproductive system. Describe the process of human development from fertilization to birth and major changes that occur in each trimester of pregnancy ...
DERIVATIVES OF THE ENDODERMAL GERM LAYER
... that begins to be transported from mother to fetus at approximately 14 weeks. In this manner, the fetus gains passive immunity against various infectious diseases. Newborns begin to produce their own IgG, but adult levels are not attained until the age of 3 years. ...
... that begins to be transported from mother to fetus at approximately 14 weeks. In this manner, the fetus gains passive immunity against various infectious diseases. Newborns begin to produce their own IgG, but adult levels are not attained until the age of 3 years. ...
Embryology_Objectives heart 2008
... ligamentum teres hepatis and ligamentum venosum, respectively Cardinal: drain the body of the embryo proper Anterior, posterior, and common cardinal veins form a symmetrical system during the fourth week; additional veins form weeks 5-7 Umbilical veins: The ductus venosus bypasses the sinuso ...
... ligamentum teres hepatis and ligamentum venosum, respectively Cardinal: drain the body of the embryo proper Anterior, posterior, and common cardinal veins form a symmetrical system during the fourth week; additional veins form weeks 5-7 Umbilical veins: The ductus venosus bypasses the sinuso ...
Stage 2
... Unilateral traction is applied to the bottom (most anteriorly located) forelimb until its shoulder and elbow are past the pelvic inlet – It can usually be felt when the shoulder passes ...
... Unilateral traction is applied to the bottom (most anteriorly located) forelimb until its shoulder and elbow are past the pelvic inlet – It can usually be felt when the shoulder passes ...
Chapter 29 - Palm Beach State College
... • Organs complete most of their development • Fetus looks distinctly human • Chance of survival (with intensive care) if born near end of this trimester ...
... • Organs complete most of their development • Fetus looks distinctly human • Chance of survival (with intensive care) if born near end of this trimester ...
Learning Objectives Biology 253/Human Anatomy Body cavities are
... what are pleural reflections? -relate their positions to surface anatomy what is the hilus of the lung, and what passes through it? are the right and left lungs symmetrical? identify the lobes of the lungs what is the nerve supply to the respiratory diaphragm? -from what spinal level does it arise? ...
... what are pleural reflections? -relate their positions to surface anatomy what is the hilus of the lung, and what passes through it? are the right and left lungs symmetrical? identify the lobes of the lungs what is the nerve supply to the respiratory diaphragm? -from what spinal level does it arise? ...
Unit XVII: Reproduction
... - Development is the process by which the zygote becomes the organism - Zygote Mitosis Differentiation and Cell Specialization a) Embryo Development 1) Mitosis - cell division to make more cells ...
... - Development is the process by which the zygote becomes the organism - Zygote Mitosis Differentiation and Cell Specialization a) Embryo Development 1) Mitosis - cell division to make more cells ...
ch 29 Development Inheritance
... c. The syncytiotrophoblast cells secrete enzymes that enable the blastocyst to penetrate the uterine lining. d. The trophoblast also secretes human chorionic gonadotropin, which rescues the corpus luteum from degeneration and sustains its function. 2. The cells of the inner cell mass differentiate i ...
... c. The syncytiotrophoblast cells secrete enzymes that enable the blastocyst to penetrate the uterine lining. d. The trophoblast also secretes human chorionic gonadotropin, which rescues the corpus luteum from degeneration and sustains its function. 2. The cells of the inner cell mass differentiate i ...
1) A 12 foot tall human: a) Would need a disproportionally larger and
... 26) The oxygen dissociation curves above are for human adult and human fetal hemoglobin. Which curve is the fetal hemoglobin A or B? 27) When oxygen concentration is zero, hemoglobin percent saturation is: a) Also zero b) There is no way to know c) 50 28) The Bohr effect which happens when blood pH ...
... 26) The oxygen dissociation curves above are for human adult and human fetal hemoglobin. Which curve is the fetal hemoglobin A or B? 27) When oxygen concentration is zero, hemoglobin percent saturation is: a) Also zero b) There is no way to know c) 50 28) The Bohr effect which happens when blood pH ...
Fetal Membranes
... Is attached to the placenta usually near the center of the fetal surface of this organ ...
... Is attached to the placenta usually near the center of the fetal surface of this organ ...
Topic: Reproduction
... The exchange of substances such as nutrients, gases and wastes takes place in the (1) umbilical cord (2) placenta (3) amniotic fluid (4) vagina ...
... The exchange of substances such as nutrients, gases and wastes takes place in the (1) umbilical cord (2) placenta (3) amniotic fluid (4) vagina ...
Animal Jeopardy
... What are the major characteristics of the class? Endoskeleton and radial symmetry ...
... What are the major characteristics of the class? Endoskeleton and radial symmetry ...
Physiological changes in pregnancy
... the human chorionic gonadotrophine normally disappear from urine 7-10 days after delivery of placenta. ...
... the human chorionic gonadotrophine normally disappear from urine 7-10 days after delivery of placenta. ...
Endocrine System
... into the blood because they are ductless • Negative feedback system endocrine system gives itself messages to control the production and release of hormones ...
... into the blood because they are ductless • Negative feedback system endocrine system gives itself messages to control the production and release of hormones ...