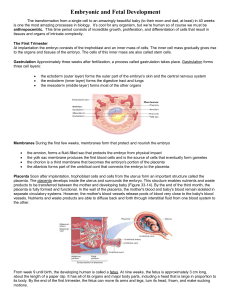
Chapter 28 - apsubiology.org
... amnion – epiblast cells form a transparent membrane filled with amniotic fluid – a maternal plasma filtrate amniotic fluid comes from maternal blood, and, later, fetal urine adds to it amniotic fluid acts as a liquid shock absorber to protect the ...
... amnion – epiblast cells form a transparent membrane filled with amniotic fluid – a maternal plasma filtrate amniotic fluid comes from maternal blood, and, later, fetal urine adds to it amniotic fluid acts as a liquid shock absorber to protect the ...
3.Lecturenotes(Placenta and fetal membrane)
... -The endometrial cells have accumulated lipids and glycogen, and are now called decidua. -The decidua underlying the chorion frondosum is known as the decidua basalis. A layer of decidual cells tightly adherent to the underlying chorion is known as the decidual plate. - The decidua atop the aembryon ...
... -The endometrial cells have accumulated lipids and glycogen, and are now called decidua. -The decidua underlying the chorion frondosum is known as the decidua basalis. A layer of decidual cells tightly adherent to the underlying chorion is known as the decidual plate. - The decidua atop the aembryon ...
CHAPTER 23: HUMAN GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT
... a thin protective membrane that forms about Day 8; b. ...
... a thin protective membrane that forms about Day 8; b. ...
3.4 Prenatal Development
... 3.4 Prenatal Development • A prenatal human is considered an embryo for the first eight weeks. ...
... 3.4 Prenatal Development • A prenatal human is considered an embryo for the first eight weeks. ...
Obstetric physical examination
... • Lateral palpation: (determine the position of the fetal back and small parts) • Hands are placed on each side of the umbilicus. The fetal spine will palpate as firm, flat and linear. The fetal extremities are palpable by their varying contour and movements. The purpose of this maneuver is to deter ...
... • Lateral palpation: (determine the position of the fetal back and small parts) • Hands are placed on each side of the umbilicus. The fetal spine will palpate as firm, flat and linear. The fetal extremities are palpable by their varying contour and movements. The purpose of this maneuver is to deter ...
chapter 23: human growth and development
... Developmental anatomy is the study of events from fertilization of the secondary oocyte to the formation of an adult organism. In this chapter we will study the sequence of events from fertilization to birth, which include fertilization, implantation, placental development, embryonic development, fe ...
... Developmental anatomy is the study of events from fertilization of the secondary oocyte to the formation of an adult organism. In this chapter we will study the sequence of events from fertilization to birth, which include fertilization, implantation, placental development, embryonic development, fe ...
Saladin, Human Anatomy 3e
... Nutrients diffuse from the maternal blood into embryonic blood vessels in the villi, and embryonic wastes diffuse the other way to be disposed of by the mother. Placental nutrition becomes dominant at the start of week 9 and continues until birth. 28. The placenta communicates with the embryo and fe ...
... Nutrients diffuse from the maternal blood into embryonic blood vessels in the villi, and embryonic wastes diffuse the other way to be disposed of by the mother. Placental nutrition becomes dominant at the start of week 9 and continues until birth. 28. The placenta communicates with the embryo and fe ...
Development - mcguireswr
... blending of their parents' characteristics. The parents, Kylie and her partner, Remi Horder, are of mixed race themselves, both having been born to white mothers and black fathers. Their twin girls — Kian and Remee — were both born with blue eyes, with Remee having blonde hair and Kian having black ...
... blending of their parents' characteristics. The parents, Kylie and her partner, Remi Horder, are of mixed race themselves, both having been born to white mothers and black fathers. Their twin girls — Kian and Remee — were both born with blue eyes, with Remee having blonde hair and Kian having black ...
Biology Chapter 43-2 Human Development
... In a process that last 2 to 16 hours, the baby is force toward the vagina as labor continues. The amniotic sac breaks releasing the fluid. As the baby meets the outside world, it may cough or cry to rid its lungs of the fluid. The umbilical cord is clamped and cut, leaving a small piece attached to ...
... In a process that last 2 to 16 hours, the baby is force toward the vagina as labor continues. The amniotic sac breaks releasing the fluid. As the baby meets the outside world, it may cough or cry to rid its lungs of the fluid. The umbilical cord is clamped and cut, leaving a small piece attached to ...
Pregnancy, Growth and Development
... implants – orients cell mass toward endometrium, and secretes enzymes which allow it to penetrate (digest) the endometrial wall. This nourishes the blastocyst for about a week after implantation. ...
... implants – orients cell mass toward endometrium, and secretes enzymes which allow it to penetrate (digest) the endometrial wall. This nourishes the blastocyst for about a week after implantation. ...
test1fall15.ede
... members should exhibit similar scores on intelligence tests when taking into account their kinship and child rearing context? a. biological siblings reared together in the same home b. adoptive siblings reared together in the same home c. fraternal twins reared together in the same home d. identical ...
... members should exhibit similar scores on intelligence tests when taking into account their kinship and child rearing context? a. biological siblings reared together in the same home b. adoptive siblings reared together in the same home c. fraternal twins reared together in the same home d. identical ...
Second Week of Development
... Stage of expulsion is the time (10 minutes to several hours) from complete cervical dilation to delivery of the baby Placental stage is the time (5-30 minutes or more) after delivery until the placenta or “afterbirth” is ...
... Stage of expulsion is the time (10 minutes to several hours) from complete cervical dilation to delivery of the baby Placental stage is the time (5-30 minutes or more) after delivery until the placenta or “afterbirth” is ...
Fertilization and Development
... • 3 functions of placenta: • It transports material between mother and fetus • It provides nutrients and energy to the fetus • It secretes HCG hormone • *** Sugar, water, oxygen, hormones, infectious agents, toxic substances and drugs can cross the placental barrier. ...
... • 3 functions of placenta: • It transports material between mother and fetus • It provides nutrients and energy to the fetus • It secretes HCG hormone • *** Sugar, water, oxygen, hormones, infectious agents, toxic substances and drugs can cross the placental barrier. ...
Section 15.2 Reproductive Control
... 1. Suckling stimulates nerve endings in the nipple and areola of the breast. 2. Nerves carry the stimulus to the hypothalamus. 3. The hypothalamus produces oxytocin which is released by the posterior pituitary gland. 4. Oxytocin causes the mammary lobules to contract. 5. Milk letdown (release of mil ...
... 1. Suckling stimulates nerve endings in the nipple and areola of the breast. 2. Nerves carry the stimulus to the hypothalamus. 3. The hypothalamus produces oxytocin which is released by the posterior pituitary gland. 4. Oxytocin causes the mammary lobules to contract. 5. Milk letdown (release of mil ...
Pregnancy PowerPoint
... – Heart, limbs , and brain have begun to develop – By nine weeks the embryo is called a fetus – The sucking reflex is present ...
... – Heart, limbs , and brain have begun to develop – By nine weeks the embryo is called a fetus – The sucking reflex is present ...
KEY CHAPTER 23 OBJECTIVES: PREGNANCY, GROWTH, AND
... Define the term cleavage and explain why the cells (blastomeres) are unable to grow between divisions. Period of Cleavage = the early series of mitotic divisions of the zygote. a. These divisions occur so rapidly, that the cells are unable to grow between divisions. b. The mass of successively small ...
... Define the term cleavage and explain why the cells (blastomeres) are unable to grow between divisions. Period of Cleavage = the early series of mitotic divisions of the zygote. a. These divisions occur so rapidly, that the cells are unable to grow between divisions. b. The mass of successively small ...
ECE/PSY171 Chapter 3 Prenatal Development What is the course of
... The Brain—By the time babies are born, they have approximately 100 billion neurons, or nerve cells, which handle information processing at the cellular level in the brain. As the human embryo develops inside its mother’s womb, the nervous system begins forming as a long, hollow tube located on the e ...
... The Brain—By the time babies are born, they have approximately 100 billion neurons, or nerve cells, which handle information processing at the cellular level in the brain. As the human embryo develops inside its mother’s womb, the nervous system begins forming as a long, hollow tube located on the e ...
Embryonic and Fetal Development
... stronger bones and muscles. The respiratory and circulatory systems undergo changes that will enable the baby to start breathing air and perform other vital functions outside the mother's uterus when it is born. As it fills more and more of the available space in the uterus, the fetus becomes less a ...
... stronger bones and muscles. The respiratory and circulatory systems undergo changes that will enable the baby to start breathing air and perform other vital functions outside the mother's uterus when it is born. As it fills more and more of the available space in the uterus, the fetus becomes less a ...
Casey Thomas EDCO240 Professor Julie Jay January 13, 2015
... Lastly is the fetal stage and it starts when cell differentiation is almost complete; the embryo is now known as a fetus. This begins during the ninth week and will last until birth. The early body structures and systems continue to develop and the neural tube develops into the brain and spinal cord ...
... Lastly is the fetal stage and it starts when cell differentiation is almost complete; the embryo is now known as a fetus. This begins during the ninth week and will last until birth. The early body structures and systems continue to develop and the neural tube develops into the brain and spinal cord ...
Embryonic Development
... 5. Gastrulation – formation of the trilaminar disk (3 primary germ layers) from the bilaminar disk (hypoblast and epiblast) i. Endoderm ii. Mesoderm iii. Ectoderm B. Embryo – 0 to 8 weeks C. Fetus – 9 weeks to birth D. Implantation 1. Fetal portion – chorion that develops from the trophoblast i. Cel ...
... 5. Gastrulation – formation of the trilaminar disk (3 primary germ layers) from the bilaminar disk (hypoblast and epiblast) i. Endoderm ii. Mesoderm iii. Ectoderm B. Embryo – 0 to 8 weeks C. Fetus – 9 weeks to birth D. Implantation 1. Fetal portion – chorion that develops from the trophoblast i. Cel ...
FETAL CIRCULATION
... The placenta is a vascular organ, genetically part maternal and part fetal. It enables maternal and fetal blood to flow close by one another, separated only by permeable membranes. Maternal and fetal blood do not mix, but the placenta allows for exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide; the fetal lungs ...
... The placenta is a vascular organ, genetically part maternal and part fetal. It enables maternal and fetal blood to flow close by one another, separated only by permeable membranes. Maternal and fetal blood do not mix, but the placenta allows for exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide; the fetal lungs ...
Chapter 4 Overview
... than 51/2 pounds (2,500 grams). Babies who weigh less than 3 pounds, 5 ounces (1,500 grams) are classified as very low birthweight (VLBW); those who weigh less than 2 pounds, 3 ounces (1,000 grams) are classified as extremely low birthweight (ELBW). 9. Low-birthweight infants who are born 3 or more ...
... than 51/2 pounds (2,500 grams). Babies who weigh less than 3 pounds, 5 ounces (1,500 grams) are classified as very low birthweight (VLBW); those who weigh less than 2 pounds, 3 ounces (1,000 grams) are classified as extremely low birthweight (ELBW). 9. Low-birthweight infants who are born 3 or more ...
Germ layers - Green Local Schools
... › 11 inches at seven months › Organ systems maturing › Fetuses born between 23–25 weeks will need ...
... › 11 inches at seven months › Organ systems maturing › Fetuses born between 23–25 weeks will need ...