* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Pregnancy PowerPoint
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Somatic cell nuclear transfer wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Umbilical cord wikipedia , lookup
Birth defect wikipedia , lookup
Sexual reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Drosophila embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
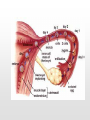
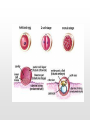
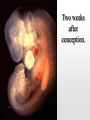
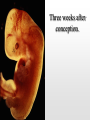
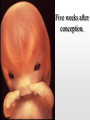
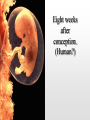
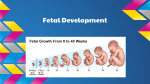
Biology 12 Unit 2: Reproduction and Development Pregnancy Fertilization • Fertilization takes place in the fallopian tube • When the sperm enters the egg, the ovum undergoes meiosis II • if an ovum is fertilized, the levels of estrogen and progesterone must remain high to maintain the endometrium and prevent further secretions of FSH • as the fertilized ovum develops it secretes chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) which maintains the corpus luteum until the placenta begins to secrete its own progesterone as it develops Clip Early Development • The fertilized ovum is called a zygote • The zygote travels down the fallopian tube, it continues to divide, becoming a hollow ball of cells (blastocyst) by the time it reaches the uterus. • Prior to implantation, the blastocyst undergoes gastrulation. • Gastrulation and cell migration set up the three germ layers - endoderm, ectoderm, and mesoderm • Implantation is when the zygote attaches to the endometrium. • As the embryo continues to grow by mitosis, part of the outer layer of cells (chorionic villi of the chorion) contribute the fetal portion of the placenta • The endometrium forms the maternal side of the placenta • A layer of tissue inside the chorion forms a fluid filled membrane called the amnion. • A third membrane called the allantois provides the blood vessels to the placenta. • The embryo is attached to the placenta by the umbilical cord. Early Development Clip Clip Early Human Development Two weeks after conception. Three weeks after conception. Five weeks after conception. Eight weeks after conception. (Human?) Twelve weeks after conception. First Trimester – Zygote becomes embryo when implanted – Amnion, chorion, and allantois develop early – Embryo grows to about 5.7 cm by end of trimester. – Heart, limbs , and brain have begun to develop – By nine weeks the embryo is called a fetus – The sucking reflex is present Second Trimester – The fetus will begin to kick – All organ systems will develop and continue to mature – Cartilage is replaced with bone – Hair and eyelids form – With modern medicine, some fetuses can survive after only 22 weeks. – The longer the pregnancy the greater the chances for survival. Third Trimester – The last trimester is marked by rapid growth and final maturation of the organs. – The fetus will grow to over 50 cm and up to 4 kg. – 9 months, 38 weeks, or approximately 266 days after implantation labor begins Time of Birth. Birth – Progesterone levels drop near the end of pregnancy. This may trigger labor. – Relaxin which is produced by the placenta causes the ligaments of the pelvis to relax. – Oxytocin produced by the anterior pituitary causes strong uterine contractions. – Oxytocin is controlled by a positive feedback loop. Lactation – Lower levels of progesterone after labor allow prolactin to be released from the anterior pituitary. – Prolactin stimulates mammary glands to produce breast milk. – To let down the milk, oxytocin must be released by the pituitary – During the first few days colostrum is let down instead of milk. Colostrum does not contain fat – Milk contains all substances the growing infant needs including antibodies