* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 11 p3
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
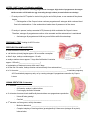
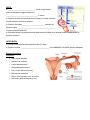
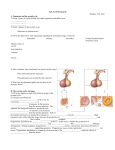
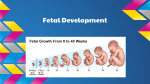
NOTES – UNIT 11 part 3: Fertilization and Birth: Recall that the corpus luteum is secreting progesterone & estrogen. High levels of progesterone & estrogen inhibit secretion of FSH while the egg is traveling through oviduct (no new follicles can develop). – IF embryo does NOT implant in uterine lining by the end of this phase, a new menstrual flow phase begins • Disintegration of the Corpus Luteum reduces progesterone & estrogen which reduces blood flow to the endometrium the endometrium breaks down & passes out of the uterus – IF embryo is present, embryo secretes HCG (hormone) which maintains the Corpus Luteum. Therefore, estrogen & progesterone continue to be secreted and the endometrium is maintained • And estrogen & progesterone inhibit any more follicles while fetus develops PREGNANCY TEST: looking for HCG in urine FERTILIZATION & IMPLANTATION ● most fertilization occurs in the ____________________________ ● cell division (mitosis) begins approx. 24 hours after conception ● after 3 days, embryo contains approx. 16 cells ● embryo reaches uterus approx. 7 days after fertilization & contains approx. 100 cells (_______________________) ● implantation of blastocyst occurs within next 5 days ● for the first 2-4 weeks, embryo obtains nutrients directly from endometrium (____________________) ● in 2nd trimester, _____________________________________________________ to maintain pregnancy -HCG maintained pregnancy early on by causing estrogen & progesterone secretion by Corpus Luteum HUMAN GESTATION: 3 trimesters ● 1st trimester: ________________________________________ – At 8 weeks, embryo is called a fetus – 5 cm long by the end of trimester ● 2nd trimester: hormone levels stabilize & placenta takes over progesterone production – Uterus & fetus growing! – Can feel __________________________________________ ● 3 trimester: as fetus grows, activity decreases rd – Mother’s abdominal ____________________________________________________ – Complex interplay of local regulators (prostaglandins) & hormones (estrogen & oxytocin) induces labor BIRTH: ● _______________________________ levels during the last weeks of pregnancy trigger formation of ___________________________________ in uterus ● Oxytocin secreted by fetus & posterior pituitary of mother stimulate smooth muscles of uterus to contract ● Oxytocin stimulates _________________________ secretion by placenta which __________________________________________ of uterus (positive feedback) ● Decreased levels of progesterone after birth remove inhibition from anterior pituitary which allows for prolactin secretion AFTER BIRTH: ● PROLACTIN stimulates milk production after 2-3 days ● Oxytocin controls ________________________________ from MAMMARY GLANDS (positive feedback) Ectopic Pregnancy: Symptoms: • Light vaginal bleeding • Nausea and vomiting • Lower abdominal pain • Sharp abdominal cramps • Pain on one side of your body • Dizziness or weakness • Pain in your shoulder, neck, or rectum • Will have a positive pregnancy test