* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Development - mcguireswr
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Umbilical cord wikipedia , lookup
Human cloning wikipedia , lookup
Birth defect wikipedia , lookup
Regeneration in humans wikipedia , lookup
Sexual reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Somatic cell nuclear transfer wikipedia , lookup
Drosophila embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
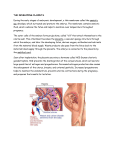
Development: Regardless of where the development takes place, the developing embryo has certain needs that must be met for survival •nourishment •proper temp •oxygen •protection •means of getting rid of wastes Pregnancy and Early Development Pregnancy, or gestation – Is the carrying of developing young within the female reproductive tract – Is measured as 40 weeks from the start of the last menstrual cycle in humans • Gestation is pregnancy – It begins at conception and continues until birth – Human gestation is 9 months – Mouse gestation is 1 month – Elephant gestation is 22 months • Structures develop that assist the developing embryo – The amnion, a fluid filled sac that encloses and protects the embryo – The yolk sac, which produces the embryo’s first blood and germ cells – The allantois, which forms part of the umbilical cord – The chorion, which becomes part of the placenta The Placenta oxygenated blood from mother’s artery deoxygenated blood to mother’s vein villus umbilical vein umbilical artery • The placenta allows for a variety of substances to pass from mother to fetus – Nutrients – Waste – Gas (oxygen & carbon dioxide) – Protective antibodies – German measles virus – HIV – Drugs (prescription and nonprescription) – Alcohol – Chemicals in tobacco smoke Prenatal Development • When the fertilized egg arrives in the uterus, it implants itself in the thickened, spongy uterine wall. • The gastrula forms, differentiation of cells and growth occurs. • The developing embryonic membranes become part of the placenta and umbilical cord. • After eight weeks of development the embryo is called the fetus. • The period of time between the fertilization of the egg and the birth of the offspring is called gestation – In humans the gestation period is nine months or approximately 266 days. Prenatal Development • During this time, it is essential that the expectant mother provide good prenatal care by eating nutritious foods, avoiding alcohol, tobacco, and drugs, and receiving proper medical attention regularly. • Using tobacco, alcohol and drugs may cause low birth rates, premature births, Fetal Alcohol Syndrome as well as other birth defects. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OsXK8Y4-PAs Over the counter drugs and pregnancy (3min) http://www.ksl.com/?nid=148&sid=14491332 Drug dependent babies (5min) http://rockcenter.nbcnews.com/_news/2012/07/05/12570381-prescription-drugaddiction-among-pregnant-women-becoming-monstrous-tidal-wave?lite Prescription drugs and pregnancy (12minutes) The Stages of Pregnancy • Pregnancy is divided into three trimesters The First Trimester • A human embryo @ about 6 weeks • A human embryo @ about 8 weeks A human fetus @ about 10 weeks • By the end of the first trimester (12 weeks) – The fetus looks like a miniature human being – The sex of the fetus can be determined by ultrasound A human fetus @ about 12 weeks The Second Trimester • The main developmental changes during the second and third trimesters involve an increase in size and general refinement of the human features • A fetus at 14 weeks, 2 weeks into the second trimester • At 20 weeks, the fetus – Is about 19 cm (7.6 in.) long and weighs about half a kilogram (1 lb) – Has the face of an infant The Third Trimester – Is a time of rapid growth – Includes many important physical changes At birth – A typical baby is about 50 cm (20 in.) long and weighs 2.7–4.5 kg (6–10 lb) 6 lbs. 13.5 oz 8 lbs. 3 oz The Human Zygote Fertilization 16 Cells Two Cells Morula Stage Four Cells Blastocyst Stage Implantation Human Gestation 3 Weeks Human Gestation 3 Months Summary of Human Development Childbirth • The birth of a child is brought about by a series of strong, rhythmic contractions of the uterus called labor • Hormones play a key role in inducing labor • There are three stages of labor • Dilation of the cervix is the first stage – Cervix reaches full dilation at 10cm – Longest stage of labor (6-12 hours or longer) • Expulsion is the second stage – Period from full dilation of the cervix to delivery of the infant – Uterine contractions occur every 2-3 minutes – Mother feels urge to push down with her abdominal muscles – Infant is forced down and out of uterus and vagina • The delivery of the placenta is the final stage of labor – Usually occurs within 15 minutes after the birth of the baby • Hormones continue to be important after the baby and placenta are delivered – Decreasing progesterone and estrogen levels allow the uterus to return to its pre-pregnancy state – Oxytocin and prolactin stimulate milk secretion http://www.doctoroz.com/videos/normal-labor-and-birthanimation normal labor and delivery Moving babies http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=w7qVJiYBlbo http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JKlPGzrrQZA&feature= related Postnatal Development • Following birth, the placenta is discarded from the mother’s body and the mother begins producing milk from mammary glands located in the breasts. • The mother’s breast milk is normally the best natural food for a newborn baby. Applications of reproductive technology: Reproductive technology has medical, agricultural, and ecological applications. This technology has also stirred ethical concerns as well, especially where this technology applies to humans 1. Genetic engineering in the field of agriculture • Crops resistant to insects, weed killer, frost 2. Cloning- used to make large numbers of identical copies of desired organisms 3. Artificial insemination. Can freeze sperm or embryos and use them at different locations or at different times • Scientist are also using these technologies to help engendered species 4. The use of reproductive hormones to control and combat pest populations of insects without using poisonous chemicals 5. Human reproductive problems: • Hormonal therapy • IVF (In-vitro fertilization) REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH • issues of human reproductive health – Contraception – Transmission of disease – Infertility Contraception : Is the deliberate prevention of pregnancy • prevents pregnancy in one of three ways – Blocking the release of gametes – Preventing fertilization – Preventing implantation Surgical Methods Vasectomy Cutting and tying of sperm ducts Tubal ligation Cutting and tying of oviducts Birth Control • Hormonal contraceptives (the pill, the patch, and the vaginal ring) – These hormones work to inhibit the body's natural cyclical hormones to prevent pregnancy. Pregnancy is prevented by a combination of factors. The hormonal contraceptive usually stops the body from ovulating. – No ovulation = no egg = no fertilization = no baby! – No hormones taken for 7 days = menstruation Barrier Method Male and female condoms prevent sperm from entering the vagina Diaphragm fitted over the cervix & along with use of spermacide to kill sperm No sperms= no fertilization= no baby! Sexually Transmitted Diseases • Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) – Are contagious diseases spread by sexual contact • Viral STDs, such as AIDS, genital herpes, and genital warts, cannot be cured but can be controlled by medications Human Reproductive Disorders • Sexually transmitted diseases may be transmitted by both males and females and may cause sterility or death if not treated by a competent physician. • Some sexually transmitted diseases in humans are syphilis, gonorrhea, genital herpes, and AIDS. REPRODUCTIVE TECHNOLOGIES • Reproductive technologies – Can help solve problems related to the inability to conceive a child • Infertility – Is the inability to have children after one year of trying – Problems in the man, such as underproduction of sperm or impotence • Female infertility can result from a lack of eggs or a failure to ovulate • There are technologies available to help treat the many forms of infertility In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) – Happens under artificial, laboratory conditions -Begins with the surgical removal of eggs and the collection of sperm - Involves fertilization of eggs in a petri dish • IVF – Offers choices that nature does not – Raises many moral and legal issues http://www.sumanasinc.com/webcontent/animations/content/invitrofe rtilization.html IVF • Show reproductive technologies ppt Basic Concepts of Embryonic Development • The key to development in all organisms is that each stage of development takes place in a highly organized fashion • About one week after conception – The embryo, which has become a blastocyst, implants itself in the uterine wall – The outer cell layer, the trophoblast, becomes part of the placenta Gastrulation produces a three-layered embryo • Gastrulation is the second major phase of embryonic development – It adds more cells to the embryo – It sorts all cells into three distinct cell layers – The embryo is transformed from the blastula into the gastrula • The three layers produced in gastrulation – Ectoderm, the outer layer – Endoderm, an embryonic digestive tract – Mesoderm, which partly fills the space between the ectoderm and endoderm Organs start to form after gastrulation • Embryonic tissue layers begin to differentiate into specific tissues and organ systems • In chordates – the notochord develops from the mesoderm – the neural tube develops from the ectoderm • The neural tube becomes the brain and spinal cord Changes in cell shape, cell migration, and programmed cell death give form to the developing animal • Tissues and organs take shape in a developing embryo as a result of – cell shape changes – cell migration Embryonic induction initiates organ formation • Induction is the mechanism by which one group of cells influences the development of tissues and organs from ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm – Adjacent cells and cell layers use chemical signals to influence differentiation – Chemical signals turn on a set of genes whose expression makes the receiving cells differentiate into a specific tissue http://player.discoveryeducation.com/?guidAssetId=B76C7495-F4F0-4CB4926E-BFD46A3060A8 Identical Twins “nature vs nuture” The amazing conception happened after two eggs were fertilized at the same time in the womb. Both Kylie and her partner Remi Horder, 17, are of mixed race. Their mothers are both white and their fathers are black. According to the Multiple Births Foundation, baby Kian must have inherited the black genes from both sides of the family, whilst Remee inherited the white ones. A mixed-race British mom, Kylie Hodgson, gave birth in 2005 to twins, one of each — one black, the other white. The odds of such a birth are about a million to one, experts said. Although occurrences of this nature sometimes occur when a woman conceives twins fathered by two different men, this was a much rarer case in which a single pairing produced twins with distinctly different physical attributes (e.g., skin tone, hair color, eye color) rather than a blending of their parents' characteristics. The parents, Kylie and her partner, Remi Horder, are of mixed race themselves, both having been born to white mothers and black fathers. Their twin girls — Kian and Remee — were both born with blue eyes, with Remee having blonde hair and Kian having black hair and somewhat darker skin than her sister. Since then, Remee's skin tone has become lighter, while Kian's has become darker and her eyes have turned brown. In the womb http://channel.nationalgeographic.com/channel/in-the-womb/videos/in-the-womb/ Life’s Greatest Miracle http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/body/life-greatest-miracle.html