Perinatal mortality Congenital malformations Birth trauma
... • Perinatal mortality: all fetal & neonatal deaths weighing 1000g or more between 28 weeks of gestation to first week of neonatal life(WHO) • Perinatal mortality rate: expressed in terms of perinatal deaths per 1000 total births ...
... • Perinatal mortality: all fetal & neonatal deaths weighing 1000g or more between 28 weeks of gestation to first week of neonatal life(WHO) • Perinatal mortality rate: expressed in terms of perinatal deaths per 1000 total births ...
- Surgery (Journal)
... The small intestine has fewer and less marked circular folds than are seen in adults. The mesentery contains very little fat and is much easier to manage when resecting intestine than in adults. The small intestine is between 300 and 350 cm long in a term baby. This is a measurement with the bowel u ...
... The small intestine has fewer and less marked circular folds than are seen in adults. The mesentery contains very little fat and is much easier to manage when resecting intestine than in adults. The small intestine is between 300 and 350 cm long in a term baby. This is a measurement with the bowel u ...
Abdominal examination
... fetal head and to listen to the fetal heart. The progress of labour is assessed as is descent and rotation of the presenting part. Abdominal examination is always carried out prior to auscultation and before fetal monitoring (CTG). It is also done before performing the vaginal examination. It is imp ...
... fetal head and to listen to the fetal heart. The progress of labour is assessed as is descent and rotation of the presenting part. Abdominal examination is always carried out prior to auscultation and before fetal monitoring (CTG). It is also done before performing the vaginal examination. It is imp ...
Unit XVII: Reproduction
... high levels of estrogen causes the pituitary to stop secreting FSH and to begin secreting luteinizing hormone LH high levels of LH cause the ovary to release the egg (usually occurs in the middle of the cycle) ...
... high levels of estrogen causes the pituitary to stop secreting FSH and to begin secreting luteinizing hormone LH high levels of LH cause the ovary to release the egg (usually occurs in the middle of the cycle) ...
extraembryonic splanchnopleura
... • eyelashes, brow, hair (several cm) are developed, nails overlap free end of fingers • skull bone are hard, major and minor fonticulus are palpable and separated from each other • newborn cries and moves ...
... • eyelashes, brow, hair (several cm) are developed, nails overlap free end of fingers • skull bone are hard, major and minor fonticulus are palpable and separated from each other • newborn cries and moves ...
Development of the placenta and its function Dr Samar Sarsam
... From 3rd week -the end of the 1st trimester , the villi are covered by a single layer of cytotrophoblast and an outer layer of syncytiotrophoblast (immediate contact with blood in the intervillous space) As pregnancy progresses ,villi become more numerous and smaller . The inner cytotrophoblast laye ...
... From 3rd week -the end of the 1st trimester , the villi are covered by a single layer of cytotrophoblast and an outer layer of syncytiotrophoblast (immediate contact with blood in the intervillous space) As pregnancy progresses ,villi become more numerous and smaller . The inner cytotrophoblast laye ...
ductus venosus
... 6. Some blood will enter the right ventricle from the right atrium and into the pulmonary trunk. From this point most of this blood will be shunted away from the pulmonary trunk and into the aorta via which fetal structure? Name the adult remnant of this structure. o Ductus arteriosus which becomes ...
... 6. Some blood will enter the right ventricle from the right atrium and into the pulmonary trunk. From this point most of this blood will be shunted away from the pulmonary trunk and into the aorta via which fetal structure? Name the adult remnant of this structure. o Ductus arteriosus which becomes ...
Topic 17: Reproduction
... embryo with food and oxygen In the lining implantation of the embryo takes place (where the emvbryo fixes itself to the lining of uterus If there is no fertilization the lining is broken down releasing blood , ...
... embryo with food and oxygen In the lining implantation of the embryo takes place (where the emvbryo fixes itself to the lining of uterus If there is no fertilization the lining is broken down releasing blood , ...
Week 10-19-15 lesson plans
... Objectives/Questions: Identify the fetal development from conception through pregnancy and birth, explain how a pregnant female transfers nutrients and other substances to her fetus, understand the stages of embryonic and fetal growth and development, explain how twins are formed and explain the sta ...
... Objectives/Questions: Identify the fetal development from conception through pregnancy and birth, explain how a pregnant female transfers nutrients and other substances to her fetus, understand the stages of embryonic and fetal growth and development, explain how twins are formed and explain the sta ...
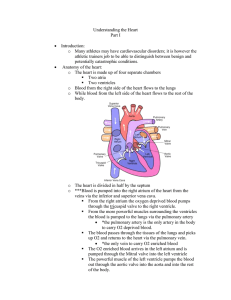
Cardiac Disorders
... The O2 enriched blood arrives in the left atrium and is pumped through the Mitral valve into the left ventricle The powerful muscle of the left ventricle pumps the blood out through the aortic valve into the aorta and into the rest of the body. ...
... The O2 enriched blood arrives in the left atrium and is pumped through the Mitral valve into the left ventricle The powerful muscle of the left ventricle pumps the blood out through the aortic valve into the aorta and into the rest of the body. ...
EMBRYOLOGY GENERAL EMBRYOLOGY SECOND WEEK
... 1-The head is about one third the crown-heel length(CHL) i.e of standing length. 2-Fine lanugo hair, eye brows & head hair are also visible. 3-By the end of 5th month the body weight is about 500 grams( 1/ 7 of birth wt). 4-Fetal movement is easily recognized by the pregnant mother. The weight of t ...
... 1-The head is about one third the crown-heel length(CHL) i.e of standing length. 2-Fine lanugo hair, eye brows & head hair are also visible. 3-By the end of 5th month the body weight is about 500 grams( 1/ 7 of birth wt). 4-Fetal movement is easily recognized by the pregnant mother. The weight of t ...
Development and Differentiation
... and the amniotic fluid is released (2-20 hrs). The cervix widens to approx. 10 cm. 2. Expulsion- contractions push baby into the birth canal. (0.5-2 hrs) ...
... and the amniotic fluid is released (2-20 hrs). The cervix widens to approx. 10 cm. 2. Expulsion- contractions push baby into the birth canal. (0.5-2 hrs) ...
Embryonic Development
... Organs start to form after gastrulation Embryonic tissue layers begin to differentiate into specific tissues and organ systems ...
... Organs start to form after gastrulation Embryonic tissue layers begin to differentiate into specific tissues and organ systems ...
Prenatal Development - Southern Illinois University School
... provides protective environment • Amniotic fluid protects embryo from being ...
... provides protective environment • Amniotic fluid protects embryo from being ...
Fetal Pig Information
... Fetal Pig Information Background The majority of mammals are placental mammals in which the developing young, or fetus, grows inside the female's uterus while attached to a membrane called the placenta. The placenta is the source of food and oxygen for the fetus, and it also serves to get rid of fet ...
... Fetal Pig Information Background The majority of mammals are placental mammals in which the developing young, or fetus, grows inside the female's uterus while attached to a membrane called the placenta. The placenta is the source of food and oxygen for the fetus, and it also serves to get rid of fet ...
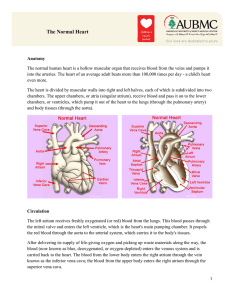
The Normal Heart
... The left atrium receives freshly oxygenated (or red) blood from the lungs. This blood passes through the mitral valve and enters the left ventricle, which is the heart's main pumping chamber. It propels the red blood through the aorta to the arterial system, which carries it to the body's tissues. A ...
... The left atrium receives freshly oxygenated (or red) blood from the lungs. This blood passes through the mitral valve and enters the left ventricle, which is the heart's main pumping chamber. It propels the red blood through the aorta to the arterial system, which carries it to the body's tissues. A ...
Unit 25.3: From Fertilization to Old Age
... normal fetal growth and development. During childbirth, contractions of the uterus push the child out of the body. • Growth and development are most rapid during infancy and slower throughout the rest of childhood until adolescence. Adolescence involves mental, emotional, and social changes in addit ...
... normal fetal growth and development. During childbirth, contractions of the uterus push the child out of the body. • Growth and development are most rapid during infancy and slower throughout the rest of childhood until adolescence. Adolescence involves mental, emotional, and social changes in addit ...
Reproductive System Pt 2 Development
... Similarities in embryonic development • Human embryonic development is very similar to embryonic development in other vertebrates such as reptiles, birds, fish and other mammals. • These similarities are REAL EVIDENCE that we share an evolutionary history with these organisms ...
... Similarities in embryonic development • Human embryonic development is very similar to embryonic development in other vertebrates such as reptiles, birds, fish and other mammals. • These similarities are REAL EVIDENCE that we share an evolutionary history with these organisms ...
Labor and Delivery Note (by Dr. Jen Pearson – to be used to
... Description of placental delivery and cord status (i.e. expressed, spontaneous, etc.) Medications given Estimated Blood Loss Status of perineum and further maternal anatomy and description of any repair required Complications Status of mother and baby Any other pertinent information from this stage ...
... Description of placental delivery and cord status (i.e. expressed, spontaneous, etc.) Medications given Estimated Blood Loss Status of perineum and further maternal anatomy and description of any repair required Complications Status of mother and baby Any other pertinent information from this stage ...
Reproductive System, Day 4 (Professor Powerpoint)
... At birth the placenta detaches from the uterus – it is expelled after birth Umbilical cord is cut – leaves “umbilicus” = belly button ...
... At birth the placenta detaches from the uterus – it is expelled after birth Umbilical cord is cut – leaves “umbilicus” = belly button ...
fertilization and name the site where fertilization
... Amniotic fluid (containing sloughed fetal cells) is withdrawn from amniotic sac; Cells are analyzed by Karyotyping to detect genetic (chromosome structure) abnormalities; Useful in detecting genetic disorders including Down Syndrome, spina bifida, hemophilia, Tay-Sachs disease, sickle-cell anemia, a ...
... Amniotic fluid (containing sloughed fetal cells) is withdrawn from amniotic sac; Cells are analyzed by Karyotyping to detect genetic (chromosome structure) abnormalities; Useful in detecting genetic disorders including Down Syndrome, spina bifida, hemophilia, Tay-Sachs disease, sickle-cell anemia, a ...
Normal placentae of domestic mammals
... of the mare (upper), cow (middle) and bitch (lower). The three main layers to the fetal membranes are the chorion, allantois and amnion, although they are fused to a greater (primate) or lesser (equid) degree. The amnion is a ...
... of the mare (upper), cow (middle) and bitch (lower). The three main layers to the fetal membranes are the chorion, allantois and amnion, although they are fused to a greater (primate) or lesser (equid) degree. The amnion is a ...
Chapter 22: Development and Aging
... atrium through an oval opening, the foramen ovale, and an arterial duct, the ductus arteriosus, shunts blood between the pulmonary trunk and aorta. These features enable blood to bypass the non-funtioning lungs. Two umbilical arteries that branch off the iliac arteries lead to the placenta. ...
... atrium through an oval opening, the foramen ovale, and an arterial duct, the ductus arteriosus, shunts blood between the pulmonary trunk and aorta. These features enable blood to bypass the non-funtioning lungs. Two umbilical arteries that branch off the iliac arteries lead to the placenta. ...
Reproductive System, Day 5 (Professor Powerpoint)
... The infant emerges from the vagina This stage usually lasts less than 2 hours If the vaginal canal is too small, there can be tearing A better alternative is an episiotomy = incisions to enlarge the opening (local anesthesia), will require sutures, but is easer to stitch a cut than a tear ...
... The infant emerges from the vagina This stage usually lasts less than 2 hours If the vaginal canal is too small, there can be tearing A better alternative is an episiotomy = incisions to enlarge the opening (local anesthesia), will require sutures, but is easer to stitch a cut than a tear ...