Steric protection of alkylidene is not needed:
... Reaction is driven by entropy: 1 molecule => 2 molecules Even 7-membered rings are possible By-product is easily removable gas No polymer by-products: intramolecular reactions are faster than intermolecular reactions - Also heavily substituted olefins can be converted ...
... Reaction is driven by entropy: 1 molecule => 2 molecules Even 7-membered rings are possible By-product is easily removable gas No polymer by-products: intramolecular reactions are faster than intermolecular reactions - Also heavily substituted olefins can be converted ...
dr. Zdenko Časar - Fakulteta za kemijo in kemijsko tehnologijo
... building blocks, which were till now prepared with limited number of synthetic methods. Moreover, halo substituted analogues like chiral (α-chloroalkyl) boronic esters are even more interesting chiral building blocks, which can be utilized in various coupling reactions and can undergo functional gro ...
... building blocks, which were till now prepared with limited number of synthetic methods. Moreover, halo substituted analogues like chiral (α-chloroalkyl) boronic esters are even more interesting chiral building blocks, which can be utilized in various coupling reactions and can undergo functional gro ...
MAGNESIUM STEARATE
... Given the doubts about the safety of magnesium stearate, itself a partially hydrogenated oil, the Three Treasures and Women’s Treasure remedies are now made without magnesium stearate and the only excipients used in their manufacture are potato starch and cellulose. The Little Treasures granules are ...
... Given the doubts about the safety of magnesium stearate, itself a partially hydrogenated oil, the Three Treasures and Women’s Treasure remedies are now made without magnesium stearate and the only excipients used in their manufacture are potato starch and cellulose. The Little Treasures granules are ...
Experiment #3: Asymmetric Synthesis – Use of a Chiral Manganese
... in 25 mL of distilled water. The solution is stirred as 11.4 g (12.2 mL, 0.10 mol) of 1,2diaminocyclohexane (a mixture of cis and trans isomers) is added slowly in one portion. (Note: The addition of the diamine is exothermic.) The solution is initially cloudy, but complete dissolution is observed w ...
... in 25 mL of distilled water. The solution is stirred as 11.4 g (12.2 mL, 0.10 mol) of 1,2diaminocyclohexane (a mixture of cis and trans isomers) is added slowly in one portion. (Note: The addition of the diamine is exothermic.) The solution is initially cloudy, but complete dissolution is observed w ...
alkene structure, naming, stereochemistry & preparation
... - The cis-/trans- notation for alkenes is being replaced by E(trans)-/Z(cis)- notation: 1st: Expand the C=C fragment and dissect it vertically 2nd: Identify and rank the groups at left; use the ...
... - The cis-/trans- notation for alkenes is being replaced by E(trans)-/Z(cis)- notation: 1st: Expand the C=C fragment and dissect it vertically 2nd: Identify and rank the groups at left; use the ...
A Straightforward Route to Enantiopure Pyrrolizidines and
... homogeneous catalysts for the production of oxygenates [26-33], including methanol, ethanol, and especially ethylene glycol. The principal shortcoming of all homogeneous CO hydrogenation reactions is their low catalytic activity, which results in the need to use high catalyst loadings and drastic re ...
... homogeneous catalysts for the production of oxygenates [26-33], including methanol, ethanol, and especially ethylene glycol. The principal shortcoming of all homogeneous CO hydrogenation reactions is their low catalytic activity, which results in the need to use high catalyst loadings and drastic re ...
Direct production of hydrogen peroxide from CO, O2, and H2O over
... Hydrogen peroxide is a clean oxidizing agent that is useful for highly selectively converting organic compounds into value-added products, as well as for industrial or municipal wastewater treatment and water disinfection.1 Currently, the commercial production of H2O2 is mainly based on a multistep ...
... Hydrogen peroxide is a clean oxidizing agent that is useful for highly selectively converting organic compounds into value-added products, as well as for industrial or municipal wastewater treatment and water disinfection.1 Currently, the commercial production of H2O2 is mainly based on a multistep ...
Lecture 31 Homogeneous catalysis
... The homogeneous catalyst precursors are added in the reaction system in different forms and are transformed into the active form insitu. During one catalytic cycle, the catalyst may pass through several intermediate forms and finally produce the products. After end of each catalytic cycle, the catal ...
... The homogeneous catalyst precursors are added in the reaction system in different forms and are transformed into the active form insitu. During one catalytic cycle, the catalyst may pass through several intermediate forms and finally produce the products. After end of each catalytic cycle, the catal ...
Document
... Carbocation Rearrangements in Hydrogen Halide Addition to Alkenes - In reactions involving carbocation intermediates, the carbocation may sometimes rearrange if a more stable carbocation can be formed by the rearrangement. These involve hydride and methyl shifts. H C ...
... Carbocation Rearrangements in Hydrogen Halide Addition to Alkenes - In reactions involving carbocation intermediates, the carbocation may sometimes rearrange if a more stable carbocation can be formed by the rearrangement. These involve hydride and methyl shifts. H C ...
Document
... Carbenes are very reactive; normally cannot be isolated and stored. Are intermediates in certain reactions. ...
... Carbenes are very reactive; normally cannot be isolated and stored. Are intermediates in certain reactions. ...
Organic Chemistry Fifth Edition
... Carbenes are very reactive; normally cannot be isolated and stored. Are intermediates in certain reactions. ...
... Carbenes are very reactive; normally cannot be isolated and stored. Are intermediates in certain reactions. ...
Postprint
... [L4Rh]+X- complex could convert in situ to an [L2Rh]+X- active catalyst. Overall having a 2:1 mono-dentate ligand/metal ratio was superior to the previously employed 3:1, since it removes the need to extrude a phosphine group during the catalytic cycle.5 In turn, this discovery was carried across to ...
... [L4Rh]+X- complex could convert in situ to an [L2Rh]+X- active catalyst. Overall having a 2:1 mono-dentate ligand/metal ratio was superior to the previously employed 3:1, since it removes the need to extrude a phosphine group during the catalytic cycle.5 In turn, this discovery was carried across to ...
Chapter 1 - chemistry
... Addition reactions of alkenes are an important method of introducing new functional groups into organic molecules. In alkenes one of the bonds in the double bond is somewhat weaker and is easier to break than a carboncarbon single bond. It is sometimes possible for a compound of general structure X- ...
... Addition reactions of alkenes are an important method of introducing new functional groups into organic molecules. In alkenes one of the bonds in the double bond is somewhat weaker and is easier to break than a carboncarbon single bond. It is sometimes possible for a compound of general structure X- ...
Hydrogenation for Low Trans and High Conjugated Fatty Acids
... 0.25 to 60 Hz had no effect on current efficiencies. The combination of increased oil feed flow rate and inserted nickel turbulence promoter into the oil stream increased the current efficiency of oil hydrogenation. An and others (1999) also reported the effects of cathode designs and reactor operat ...
... 0.25 to 60 Hz had no effect on current efficiencies. The combination of increased oil feed flow rate and inserted nickel turbulence promoter into the oil stream increased the current efficiency of oil hydrogenation. An and others (1999) also reported the effects of cathode designs and reactor operat ...
Combining transition metal catalysis and organocatalysis
... arylboronic acids with electron-withdrawing substituents at the aryl group •water-, acid-, and base-torelant •thermally stable and can be readily handled in air •strong Lewis acidity enhances the rate of the generation of acyloxyborane species and their reactivity with amines only catalytic amount o ...
... arylboronic acids with electron-withdrawing substituents at the aryl group •water-, acid-, and base-torelant •thermally stable and can be readily handled in air •strong Lewis acidity enhances the rate of the generation of acyloxyborane species and their reactivity with amines only catalytic amount o ...
... products. Despite the organoaluminium reagents are economically obtained in industrial scale, their use is rare. In this respect, the few successful catalysts developed for the enantioselective addition of trialkylaluminium to aldehydes can be grouped in two types. The first group are the titanium c ...
Slide 1
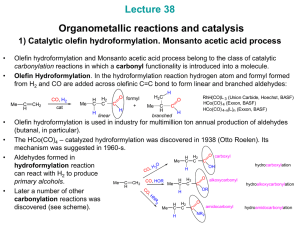
... Olefin hydroformylation and Monsanto acetic acid process belong to the class of catalytic carbonylation reactions in which a carbonyl functionality is introduced into a molecule. Olefin Hydroformylation. In the hydroformylation reaction hydrogen atom and formyl formed from H2 and CO are added across ...
... Olefin hydroformylation and Monsanto acetic acid process belong to the class of catalytic carbonylation reactions in which a carbonyl functionality is introduced into a molecule. Olefin Hydroformylation. In the hydroformylation reaction hydrogen atom and formyl formed from H2 and CO are added across ...
Contents - Personal WWW Pages
... Let us consider these advantages and disadvantages in a little more detail. Activity and Selectivity: these often have an inverse relation in both homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysis. i.e. faster reactions are often less selective. So, although homogeneous catalysis has a major advantage in the ...
... Let us consider these advantages and disadvantages in a little more detail. Activity and Selectivity: these often have an inverse relation in both homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysis. i.e. faster reactions are often less selective. So, although homogeneous catalysis has a major advantage in the ...
"Introduction" Kinetics in Process Chemistry: Case Studies Baran Group Meeting Mike DeMartino
... coupling reactions. There are advantages to using CDI: price -$8/mol (large-scale purchase), and the byproducts are the innocuous CO2 and imidazole. It is not without its problems though. The acyl imidazole is less reactive than, for instance, the corresponding acid chloride. As a result, particular ...
... coupling reactions. There are advantages to using CDI: price -$8/mol (large-scale purchase), and the byproducts are the innocuous CO2 and imidazole. It is not without its problems though. The acyl imidazole is less reactive than, for instance, the corresponding acid chloride. As a result, particular ...
Reductions of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives - IDC
... for the reduction of aldehydes and ketones to 1º and 2º-alcohols respectively has been noted. Of these, lithium aluminum hydride, often abbreviated LAH, is the most useful for reducing carboxylic acid derivatives. Thanks to its high reactivity, LAH easily reduces all classes of carboxylic acid deriv ...
... for the reduction of aldehydes and ketones to 1º and 2º-alcohols respectively has been noted. Of these, lithium aluminum hydride, often abbreviated LAH, is the most useful for reducing carboxylic acid derivatives. Thanks to its high reactivity, LAH easily reduces all classes of carboxylic acid deriv ...
montmorillonite catalysts for ethylene hydration
... hydration sphere around the cations in the interlamellar space; (iii) water hydrogen-bonded to the silicate surface. These are illustrated in Fig. 2. The Br6nsted acidity of the cation-exchanged clays can be accounted for by dissociation of coordinated water in the interlamellar space according to t ...
... hydration sphere around the cations in the interlamellar space; (iii) water hydrogen-bonded to the silicate surface. These are illustrated in Fig. 2. The Br6nsted acidity of the cation-exchanged clays can be accounted for by dissociation of coordinated water in the interlamellar space according to t ...
UN1001: Section 11: Hydrogen Effects
... Hydride-forming metals are susceptible to H- embrittlement . . .e.g., Zr-alloy pressure tubes (in CANDUs) and fuel sheathing (in all water- cooled reactors) pick up hydrogen (or deuterium in heavy water ) by general corrosion. The hydrogen (D) migrates through the metal lattice to cool regions and t ...
... Hydride-forming metals are susceptible to H- embrittlement . . .e.g., Zr-alloy pressure tubes (in CANDUs) and fuel sheathing (in all water- cooled reactors) pick up hydrogen (or deuterium in heavy water ) by general corrosion. The hydrogen (D) migrates through the metal lattice to cool regions and t ...
Ch13 Lecture
... • Lycopene, the red pigment in tomatoes and watermelons, has 13 double bonds. • Lycopene is an antioxidant, a compound that prevents unwanted oxidation from occurring. ...
... • Lycopene, the red pigment in tomatoes and watermelons, has 13 double bonds. • Lycopene is an antioxidant, a compound that prevents unwanted oxidation from occurring. ...
7. Alkenes: Reactions and Synthesis
... Requires Pt or Pd as powders on carbon and H2 Hydrogen is first adsorbed on catalyst Reaction is heterogeneous (process is not in solution) ...
... Requires Pt or Pd as powders on carbon and H2 Hydrogen is first adsorbed on catalyst Reaction is heterogeneous (process is not in solution) ...
Hydrogenation

Hydrogenation – to treat with hydrogen – is a chemical reaction between molecular hydrogen (H2) and another compound or element, usually in the presence of a catalyst such as nickel, palladium or platinum. The process is commonly employed to reduce or saturate organic compounds. Hydrogenation typically constitutes the addition of pairs of hydrogen atoms to a molecule, generally an alkene. Catalysts are required for the reaction to be usable; non-catalytic hydrogenation takes place only at very high temperatures. Hydrogenation reduces double and triple bonds in hydrocarbons.Because of the importance of hydrogen, many related reactions have been developed for its use. Most hydrogenations use gaseous hydrogen (H2), but some involve the alternative sources of hydrogen, not H2: these processes are called transfer hydrogenations. The reverse reaction, removal of hydrogen from a molecule, is called dehydrogenation. A reaction where bonds are broken while hydrogen is added is called hydrogenolysis, a reaction that may occur to carbon-carbon and carbon-heteroatom (oxygen, nitrogen or halogen) bonds. Hydrogenation differs from protonation or hydride addition: in hydrogenation, the products have the same charge as the reactants.Hydrogenation of unsaturated fats produces saturated fats. In the case of partial hydrogenation, trans fats may be generated as well.