CH402 Asymmetric catalytic reactions Prof M. Wills
... Asymmetric catalysis – Ketone reduction The reduction of a ketone to a secondary alcohol is a perfect reaction for asymmetric catalysis: ...
... Asymmetric catalysis – Ketone reduction The reduction of a ketone to a secondary alcohol is a perfect reaction for asymmetric catalysis: ...
catalysis lecture
... Homogeneous Catalysis Homogeneous catalysts are more attractive for study in research labs because: a) the mechanism is accessible to detailed study (i.e., the rate data is easier to interpret) b) the species in solution are more easily characterized ...
... Homogeneous Catalysis Homogeneous catalysts are more attractive for study in research labs because: a) the mechanism is accessible to detailed study (i.e., the rate data is easier to interpret) b) the species in solution are more easily characterized ...
Organic Reactions
... • Isomers have the same molecular formula, empirical formula, and % composition. They test this definition a lot. • If you’re not sure about an isomer, count the carbons, hydrogens, and oxygens; make sure they’re the same as the molecule in question. ...
... • Isomers have the same molecular formula, empirical formula, and % composition. They test this definition a lot. • If you’re not sure about an isomer, count the carbons, hydrogens, and oxygens; make sure they’re the same as the molecule in question. ...
Homogeneously catalysed hydrogenation of unsaturated fatty acids
... y = x + - a+bx This equation, which represents a hyperbola, allows a simple representation of a complicated chemical reaction and is of practical importance for a systematic study of catalytic processes. It was found that the course of the hydrogenation of unsaturated acids under influence of Cu- an ...
... y = x + - a+bx This equation, which represents a hyperbola, allows a simple representation of a complicated chemical reaction and is of practical importance for a systematic study of catalytic processes. It was found that the course of the hydrogenation of unsaturated acids under influence of Cu- an ...
Current Research Click Here
... environmental point of view. Reagents such as PCC and the chemicals used in the Swern oxidation are not environmentally friendly. A recent report in the literature uses a Pd resin with the same functional group as the oxidation catalyst TEMPO. We are investigating the reaction of this new resin for ...
... environmental point of view. Reagents such as PCC and the chemicals used in the Swern oxidation are not environmentally friendly. A recent report in the literature uses a Pd resin with the same functional group as the oxidation catalyst TEMPO. We are investigating the reaction of this new resin for ...
Catalytic Hydrogenation of Alkenes: Relative Stability of
... steric interference with the bulky base. An E2 reaction that generates the thermodynamically less favored isomer is said to follow the Hofmann rule. ...
... steric interference with the bulky base. An E2 reaction that generates the thermodynamically less favored isomer is said to follow the Hofmann rule. ...
Nomenclature
... Catalytic Hydrogenation • When unsaturated vegetable oil is treated with hydrogen, some or all of the π bonds add H2. This increases the melting point of the oil. • Margarine is prepared by partially hydrogenating vegetable oils to give a product with a consistency that more closely resembles butte ...
... Catalytic Hydrogenation • When unsaturated vegetable oil is treated with hydrogen, some or all of the π bonds add H2. This increases the melting point of the oil. • Margarine is prepared by partially hydrogenating vegetable oils to give a product with a consistency that more closely resembles butte ...
Rxns of Alkynes
... b. for terminal alkynes, use isoamyl borane c. easly get aldehyde 5. Hydrogenation a. usually can’t stop at alkene b. can stop only if using “poison” catalyst (Lindlar catalyst) c. get cis alkene for syn addition with Lindlar d. to get trans, use Na or Li in liquid ammonia (-78ºC) e. this is radical ...
... b. for terminal alkynes, use isoamyl borane c. easly get aldehyde 5. Hydrogenation a. usually can’t stop at alkene b. can stop only if using “poison” catalyst (Lindlar catalyst) c. get cis alkene for syn addition with Lindlar d. to get trans, use Na or Li in liquid ammonia (-78ºC) e. this is radical ...
Syn Addition
... Alkene must be 2-butene. But wait that could be either cis or trans! We want meso. Have to worry about stereochemistry ...
... Alkene must be 2-butene. But wait that could be either cis or trans! We want meso. Have to worry about stereochemistry ...
Materials Seminar Professor Carsten Sievers Georgia Institute of Technology
... (HDO) of bio-oils and the direct conversion of methane to higher alcohols. HDO is a promising route for converting complex mixtures of oxygenates in bio-oils to biofuels. The process provides oils with reduced reactivity and corrosiveness and increases the energy density of the product. In HDO, oxyg ...
... (HDO) of bio-oils and the direct conversion of methane to higher alcohols. HDO is a promising route for converting complex mixtures of oxygenates in bio-oils to biofuels. The process provides oils with reduced reactivity and corrosiveness and increases the energy density of the product. In HDO, oxyg ...
Document
... Reduction of an Alkyne to a Cis Alkene • Palladium metal is too reactive to allow hydrogenation of an alkyne to stop after one equivalent of H2 adds. • To stop at a cis alkene, a less active Pd catalyst is used— Pd adsorbed onto CaCO3 with added lead(II) acetate and quinoline. This is called Lindla ...
... Reduction of an Alkyne to a Cis Alkene • Palladium metal is too reactive to allow hydrogenation of an alkyne to stop after one equivalent of H2 adds. • To stop at a cis alkene, a less active Pd catalyst is used— Pd adsorbed onto CaCO3 with added lead(II) acetate and quinoline. This is called Lindla ...
Hydrocarbons
... Saturated – this term is used to describe an organic molecule who has no double or triple bonds Unsaturated– this term is used to describe an organic molecule who has a double or triple bond between their carbons Polyunsaturated – when an organic molecule has many double or triple bonds Melting/boil ...
... Saturated – this term is used to describe an organic molecule who has no double or triple bonds Unsaturated– this term is used to describe an organic molecule who has a double or triple bond between their carbons Polyunsaturated – when an organic molecule has many double or triple bonds Melting/boil ...
ch07 by Dr. Dina
... The greater the number of attached alkyl groups (i.e. the more highly substituted the carbon atoms of the double bond), the greater the alkene’s stability [ more branches more stable] ...
... The greater the number of attached alkyl groups (i.e. the more highly substituted the carbon atoms of the double bond), the greater the alkene’s stability [ more branches more stable] ...
Exam 2 Review A
... You should be familiar with the detailed mechanisms of the SN1 and SN2 reactions. Rate determining steps are important to consider, as are the transition states associated with these steps. Compare and contrast the SN1 and SN2 reactions with respect to kinetics, nature of the electrophile [structure ...
... You should be familiar with the detailed mechanisms of the SN1 and SN2 reactions. Rate determining steps are important to consider, as are the transition states associated with these steps. Compare and contrast the SN1 and SN2 reactions with respect to kinetics, nature of the electrophile [structure ...
Exam 2 Review A
... You should be familiar with the detailed mechanisms of the SN1 and SN2 reactions. Rate determining steps are important to consider, as are the transition states associated with these steps. Compare and contrast the SN1 and SN2 reactions with respect to kinetics, nature of the electrophile [structure ...
... You should be familiar with the detailed mechanisms of the SN1 and SN2 reactions. Rate determining steps are important to consider, as are the transition states associated with these steps. Compare and contrast the SN1 and SN2 reactions with respect to kinetics, nature of the electrophile [structure ...
Exam 2 Review A
... You should be familiar with the detailed mechanisms of the SN1 and SN2 reactions. Rate determining steps are important to consider, as are the transition states associated with these steps. Compare and contrast the SN1 and SN2 reactions with respect to kinetics, nature of the electrophile [structure ...
... You should be familiar with the detailed mechanisms of the SN1 and SN2 reactions. Rate determining steps are important to consider, as are the transition states associated with these steps. Compare and contrast the SN1 and SN2 reactions with respect to kinetics, nature of the electrophile [structure ...
Chapter 1--Title
... The greater the number of attached alkyl groups (i.e. the more highly substituted the carbon atoms of the double bond), the greater the alkene’s stability ...
... The greater the number of attached alkyl groups (i.e. the more highly substituted the carbon atoms of the double bond), the greater the alkene’s stability ...
Addition Reactions
... acid-catalyzed hydration of an alkene is regioselective; hydrogen adds preferentially to the sp2 carbon with less # of hydrogens. ...
... acid-catalyzed hydration of an alkene is regioselective; hydrogen adds preferentially to the sp2 carbon with less # of hydrogens. ...
Document
... •Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1973 (shared with Ernst Otto Fischer) for their pioneering work, performed independently, on the chemistry of the organometallic, so called sandwich compounds. ...
... •Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1973 (shared with Ernst Otto Fischer) for their pioneering work, performed independently, on the chemistry of the organometallic, so called sandwich compounds. ...
Hydrogenation catalysts from used nickel metal hydride batteries
... The ethanol used was absolute ethanol and was used as supplied. The hydrogen gas was instrument grade and was used as supplied by AGA. The gas burette on the hydrogenation apparatus was a 100 ml burette fitted with a greased tap originally made for volumetric analysis. The burette was connected via ...
... The ethanol used was absolute ethanol and was used as supplied. The hydrogen gas was instrument grade and was used as supplied by AGA. The gas burette on the hydrogenation apparatus was a 100 ml burette fitted with a greased tap originally made for volumetric analysis. The burette was connected via ...
Table
... With HNO3: Nitration Ø-NO2 With RX: Alkylation Ø-R Preparation Alkenes and alkynes Organic Halides 1. Addition reactions with halogens or hydrogen halides Alkanes and Aromatics Organic Halides 1. Substitution Reactions with halogens or hydrogen halides Pathway to other groups: Alkyl halides ...
... With HNO3: Nitration Ø-NO2 With RX: Alkylation Ø-R Preparation Alkenes and alkynes Organic Halides 1. Addition reactions with halogens or hydrogen halides Alkanes and Aromatics Organic Halides 1. Substitution Reactions with halogens or hydrogen halides Pathway to other groups: Alkyl halides ...
1072. A General Synthesis of Ethers.
... solution, hydrogenation of a ketal gives the same results as that of the carbonyl compound. Enolethers such as 1-methoxycyclopentene also give a mixture of alkane and saturated ether, but in a ratio different from that found for direct hydrogenation of cyclopentanone in acid methanol. This could be ...
... solution, hydrogenation of a ketal gives the same results as that of the carbonyl compound. Enolethers such as 1-methoxycyclopentene also give a mixture of alkane and saturated ether, but in a ratio different from that found for direct hydrogenation of cyclopentanone in acid methanol. This could be ...
Cis/Trans
... – *Hydration is often confused with hydrogenation – *conversion of alkenes to alcohols is important in the metabolism of carbohs, fats, proteins. Enzymes are the catalysts. ...
... – *Hydration is often confused with hydrogenation – *conversion of alkenes to alcohols is important in the metabolism of carbohs, fats, proteins. Enzymes are the catalysts. ...
Organometallic Compounds and Catalysis: Synthesis
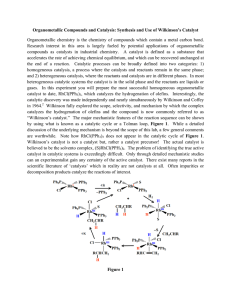
... Organometallic Compounds and Catalysis: Synthesis and Use of Wilkinson’s Catalyst Organometallic chemistry is the chemistry of compounds which contain a metal carbon bond. Research interest in this area is largely fueled by potential applications of organometallic compounds as catalysts in industria ...
... Organometallic Compounds and Catalysis: Synthesis and Use of Wilkinson’s Catalyst Organometallic chemistry is the chemistry of compounds which contain a metal carbon bond. Research interest in this area is largely fueled by potential applications of organometallic compounds as catalysts in industria ...
Chapter 7 Alkenes and Alkynes I
... The greater the number of attached alkyl groups (i.e. the more highly substituted the carbon atoms of the double bond), the greater the alkene’s stability ...
... The greater the number of attached alkyl groups (i.e. the more highly substituted the carbon atoms of the double bond), the greater the alkene’s stability ...
Hydrogenation

Hydrogenation – to treat with hydrogen – is a chemical reaction between molecular hydrogen (H2) and another compound or element, usually in the presence of a catalyst such as nickel, palladium or platinum. The process is commonly employed to reduce or saturate organic compounds. Hydrogenation typically constitutes the addition of pairs of hydrogen atoms to a molecule, generally an alkene. Catalysts are required for the reaction to be usable; non-catalytic hydrogenation takes place only at very high temperatures. Hydrogenation reduces double and triple bonds in hydrocarbons.Because of the importance of hydrogen, many related reactions have been developed for its use. Most hydrogenations use gaseous hydrogen (H2), but some involve the alternative sources of hydrogen, not H2: these processes are called transfer hydrogenations. The reverse reaction, removal of hydrogen from a molecule, is called dehydrogenation. A reaction where bonds are broken while hydrogen is added is called hydrogenolysis, a reaction that may occur to carbon-carbon and carbon-heteroatom (oxygen, nitrogen or halogen) bonds. Hydrogenation differs from protonation or hydride addition: in hydrogenation, the products have the same charge as the reactants.Hydrogenation of unsaturated fats produces saturated fats. In the case of partial hydrogenation, trans fats may be generated as well.