Review Chapter 19
... Catalytic Hydrogenation The conversion of p-bonds to s-bonds is a highly useful synthetic procedure where H2 is added across the p-bond. Although this conversion is exothermic, a catalyst is required to disrupt the di-hydrogen bond. By increasing hydrogen pressure, reaction temperature and the ...
... Catalytic Hydrogenation The conversion of p-bonds to s-bonds is a highly useful synthetic procedure where H2 is added across the p-bond. Although this conversion is exothermic, a catalyst is required to disrupt the di-hydrogen bond. By increasing hydrogen pressure, reaction temperature and the ...
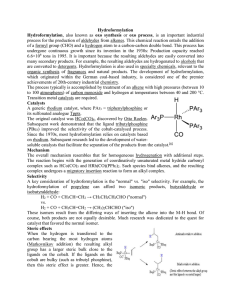
Hydroformylation Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or
... 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because the resulting aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in specialty chemicals, relevant to the organic s ...
... 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because the resulting aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in specialty chemicals, relevant to the organic s ...
File - chemistryworkshopjr
... Catalyzed reactions have a lower activation energy (rate-limiting free energy of activation) than the corresponding uncatalyzed reaction, resulting in a higher reaction rate at the same temperature and for the same reactant concentrations. However, the mechanistic explanation of catalysis is complex ...
... Catalyzed reactions have a lower activation energy (rate-limiting free energy of activation) than the corresponding uncatalyzed reaction, resulting in a higher reaction rate at the same temperature and for the same reactant concentrations. However, the mechanistic explanation of catalysis is complex ...
Cellulose und heterogene Katalyse – Eine
... Lignocellulose presents a potential future carbon source for production of fuels and chemicals. The high density of functional groups opens many possibilities for tailored transformations to new target molecules. With regard to catalysis, this overfunctionalization makes high demands on catalyst and ...
... Lignocellulose presents a potential future carbon source for production of fuels and chemicals. The high density of functional groups opens many possibilities for tailored transformations to new target molecules. With regard to catalysis, this overfunctionalization makes high demands on catalyst and ...
Alkanes and alkenes
... Alkanes are saturated compounds and contain single C-C bonds. They undergo substitution reactions. They have the general formula CnH2n+2 Alkenes are unsaturated compounds and contain double C=C bonds. They undergo addition reactions. They have the general formula CnH2n. Cracking is the process of br ...
... Alkanes are saturated compounds and contain single C-C bonds. They undergo substitution reactions. They have the general formula CnH2n+2 Alkenes are unsaturated compounds and contain double C=C bonds. They undergo addition reactions. They have the general formula CnH2n. Cracking is the process of br ...
Lecture6-Organometallic Chemistry
... are coordinatively unsaturated (having an open coordination site or being weakly coordinated) Square-planar 16-electron complexes are coordinatively unsaturated ML4 complexes of Pd(II), Pt(II) and Rh(I) [RhCl(PPh3)3] – hydrogenation catalyst ...
... are coordinatively unsaturated (having an open coordination site or being weakly coordinated) Square-planar 16-electron complexes are coordinatively unsaturated ML4 complexes of Pd(II), Pt(II) and Rh(I) [RhCl(PPh3)3] – hydrogenation catalyst ...
Reactions of Alkenes and Alkynes
... Oxidation of Alkenes: Epoxidation Synthesis of epoxides from alkenes • Peroxyacid transfers oxygen to alkene • Syn stereochemistry • Both C-O bonds form on the same face of the double ...
... Oxidation of Alkenes: Epoxidation Synthesis of epoxides from alkenes • Peroxyacid transfers oxygen to alkene • Syn stereochemistry • Both C-O bonds form on the same face of the double ...
Chapter 7 Alkenes and Alkynes I
... The second step of the E1 mechanism in which the carbocation forms is rate determining The transition state for this reaction has carbocation character Tertiary alcohols react the fastest because they have the most stable tertiary carbocation-like transition state in the second step Chapter 7 ...
... The second step of the E1 mechanism in which the carbocation forms is rate determining The transition state for this reaction has carbocation character Tertiary alcohols react the fastest because they have the most stable tertiary carbocation-like transition state in the second step Chapter 7 ...
Asymmetric catalytic routes to chiral building blocks of
... Enantiomerically pure P-hydroxy esters have served extensively as valuable chiral building blocks in synthetic organic and natural product chemistry.17 One of the most direct routes to enantiomerically-enriched P-hydroxy esters is through asymmetric hydrogenation of the corresponding P-keto esters, ...
... Enantiomerically pure P-hydroxy esters have served extensively as valuable chiral building blocks in synthetic organic and natural product chemistry.17 One of the most direct routes to enantiomerically-enriched P-hydroxy esters is through asymmetric hydrogenation of the corresponding P-keto esters, ...
Microsoft Word
... surface properties (such as surface area and crystal size) and catalytic activity (in the hydrogenation of o-nitrophenol at 308 K and H2-pressure of 1508 kPa) of Raney-Ni has been studied and the optimum conditions for the preparation of Raney-Ni catalyst for the hydrogenation reaction have been obt ...
... surface properties (such as surface area and crystal size) and catalytic activity (in the hydrogenation of o-nitrophenol at 308 K and H2-pressure of 1508 kPa) of Raney-Ni has been studied and the optimum conditions for the preparation of Raney-Ni catalyst for the hydrogenation reaction have been obt ...
Organometallic Compounds
... For example, in catalysis. (i) Upon isomerization (ii) Upon hydrogenation (iii) Upon hydroformylation (iv) Upon polymerization of alkenes (RCH=CH2) by using Ziegler-Natta catalyst. Ziegler-Natta catalyst consists of TiCl4 and Et3Al with Et2AlCl as co-catalyst. ...
... For example, in catalysis. (i) Upon isomerization (ii) Upon hydrogenation (iii) Upon hydroformylation (iv) Upon polymerization of alkenes (RCH=CH2) by using Ziegler-Natta catalyst. Ziegler-Natta catalyst consists of TiCl4 and Et3Al with Et2AlCl as co-catalyst. ...
Chapter 7 - Alkenes and Alkynes I less substituted alkene due to
... - The anticoplanar transition state is preferred, but the syn coplanar state can for with certain rigid molecules that can't assume an anti arrangement2 - If there is an E2 elimination where there are two anticoplanar β hydrogens, the major product will be one that follows Zaitsev's rule 1 To determ ...
... - The anticoplanar transition state is preferred, but the syn coplanar state can for with certain rigid molecules that can't assume an anti arrangement2 - If there is an E2 elimination where there are two anticoplanar β hydrogens, the major product will be one that follows Zaitsev's rule 1 To determ ...
Slides
... t You probably remember these from days of your youth. t Big Bang cannons have been in continuous production since ...
... t You probably remember these from days of your youth. t Big Bang cannons have been in continuous production since ...
Chapter 7
... • Geminal Dihalides can also be converted to alkynes via a double dehydrohalogenation • Geminal Dihalide- a hydrocarbon with two halogens on the same carbon • Geminal dihalides are made from the reaction of ketones with phosphorus pentachloride ...
... • Geminal Dihalides can also be converted to alkynes via a double dehydrohalogenation • Geminal Dihalide- a hydrocarbon with two halogens on the same carbon • Geminal dihalides are made from the reaction of ketones with phosphorus pentachloride ...
Chapter 7
... • Geminal Dihalides can also be converted to alkynes via a double dehydrohalogenation • Geminal Dihalide- a hydrocarbon with two halogens on the same carbon • Geminal dihalides are made from the reaction of ketones with phosphorus pentachloride ...
... • Geminal Dihalides can also be converted to alkynes via a double dehydrohalogenation • Geminal Dihalide- a hydrocarbon with two halogens on the same carbon • Geminal dihalides are made from the reaction of ketones with phosphorus pentachloride ...
Chapter 7
... • Geminal Dihalides can also be converted to alkynes via a double dehydrohalogenation • Geminal Dihalide- a hydrocarbon with two halogens on the same carbon • Geminal dihalides are made from the reaction of ketones with phosphorus pentachloride ...
... • Geminal Dihalides can also be converted to alkynes via a double dehydrohalogenation • Geminal Dihalide- a hydrocarbon with two halogens on the same carbon • Geminal dihalides are made from the reaction of ketones with phosphorus pentachloride ...
Highlights IACChE`s James Y. Oldshue Lecture Tuesday, November
... the interactions taking place in the gas-liquid-solid catalytic systems. One of the most common types of catalytic reactions carried out in the presence of solvents is the hydrogenation of organic compounds. In particular, the selective hydrogenation of aromatic ketones into the corresponding alcoho ...
... the interactions taking place in the gas-liquid-solid catalytic systems. One of the most common types of catalytic reactions carried out in the presence of solvents is the hydrogenation of organic compounds. In particular, the selective hydrogenation of aromatic ketones into the corresponding alcoho ...
Lecture 17-edited
... The reduction of carbon-carbon double bond is academically as well as industrially important transformation (Scheme 1). The order of hydrogenation of substituted double bond is 1,1-di > 1,2-di > 1,2-tri > 1,2-tetra substituted. Different metal catalysts have been used for the purpose. Among them, pl ...
... The reduction of carbon-carbon double bond is academically as well as industrially important transformation (Scheme 1). The order of hydrogenation of substituted double bond is 1,1-di > 1,2-di > 1,2-tri > 1,2-tetra substituted. Different metal catalysts have been used for the purpose. Among them, pl ...
Hydrogenation of Amino Acid Mixtures to Amino Alcohols
... serine and valine and their mixtures was studied to quantify reaction rates, understand interactions between the substrates and catalyst, and shed light onto the reaction mechanism. The understanding gained from this model system will aid in design of hydrogenation processes of more complex biorenew ...
... serine and valine and their mixtures was studied to quantify reaction rates, understand interactions between the substrates and catalyst, and shed light onto the reaction mechanism. The understanding gained from this model system will aid in design of hydrogenation processes of more complex biorenew ...
Summary of Organic Compounds -Functional Groups and Reactions
... Summary of Organic Compounds- Functional Groups and Reactions ...
... Summary of Organic Compounds- Functional Groups and Reactions ...
Catalytic hydrogenation
... (ketones, aldehydes) and C=N (imines) bond The catalytic hydrogenation of polar C=O and C=N bonds are key reactions in fine chemical and pharmaceutical synthesis. A very important group of catalysts operate by hydride transfer to the substrate in the outer coordination sphere of the complex. Hydroge ...
... (ketones, aldehydes) and C=N (imines) bond The catalytic hydrogenation of polar C=O and C=N bonds are key reactions in fine chemical and pharmaceutical synthesis. A very important group of catalysts operate by hydride transfer to the substrate in the outer coordination sphere of the complex. Hydroge ...
... Cologne, Germany. His research interests include the synthesis of chiral ferrocene ligands, ligand atnchorage to inorganic supports, their application in stereoselective palladium- and rhodiumcatalysed reactions, and stereoselective synthesis on arenetricarbonylchromiumcomplexes. Stefan Toma is Prof ...
Organometallic Catalysts
... The rate of hydrogenation depends on : (a) presence of a functional group in the vicinity of the C=C bond (b) degree of substitution of the C=C fragment ...
... The rate of hydrogenation depends on : (a) presence of a functional group in the vicinity of the C=C bond (b) degree of substitution of the C=C fragment ...
Iron-based process promises greener, cheaper and safer
... better catalyst than the industrial one based on The research takes advantage of Earth's extensive ruthenium. supply of iron – the fifth most abundant naturally occurring metal – substituting it in place of the rare The sustainable technology incubator GreenCentre elements of ruthenium, rhodium, pal ...
... better catalyst than the industrial one based on The research takes advantage of Earth's extensive ruthenium. supply of iron – the fifth most abundant naturally occurring metal – substituting it in place of the rare The sustainable technology incubator GreenCentre elements of ruthenium, rhodium, pal ...
Hydrogenation

Hydrogenation – to treat with hydrogen – is a chemical reaction between molecular hydrogen (H2) and another compound or element, usually in the presence of a catalyst such as nickel, palladium or platinum. The process is commonly employed to reduce or saturate organic compounds. Hydrogenation typically constitutes the addition of pairs of hydrogen atoms to a molecule, generally an alkene. Catalysts are required for the reaction to be usable; non-catalytic hydrogenation takes place only at very high temperatures. Hydrogenation reduces double and triple bonds in hydrocarbons.Because of the importance of hydrogen, many related reactions have been developed for its use. Most hydrogenations use gaseous hydrogen (H2), but some involve the alternative sources of hydrogen, not H2: these processes are called transfer hydrogenations. The reverse reaction, removal of hydrogen from a molecule, is called dehydrogenation. A reaction where bonds are broken while hydrogen is added is called hydrogenolysis, a reaction that may occur to carbon-carbon and carbon-heteroatom (oxygen, nitrogen or halogen) bonds. Hydrogenation differs from protonation or hydride addition: in hydrogenation, the products have the same charge as the reactants.Hydrogenation of unsaturated fats produces saturated fats. In the case of partial hydrogenation, trans fats may be generated as well.