Ketones and Aldehydes Reading: Wade chapter 18, sections 18
... carbonyl to break and pushing the pi electrons onto oxygen. ...
... carbonyl to break and pushing the pi electrons onto oxygen. ...
Chapter 7 Hydrosilylation of Carbon
... [8]. Asymmetric hydrosilylation has thus become one of the most useful methods for the preparation of optically active alcohols from alkenes [9, 10]. Another important application of catalytic asymmetric hydrosilylation is the 1,4-hydrosilylation of 1,3-dienes which efficiently produces optically act ...
... [8]. Asymmetric hydrosilylation has thus become one of the most useful methods for the preparation of optically active alcohols from alkenes [9, 10]. Another important application of catalytic asymmetric hydrosilylation is the 1,4-hydrosilylation of 1,3-dienes which efficiently produces optically act ...
Formic acid oxidation reaction on a PdxNiy bimetallic nanoparticle
... unique ability to catalyze the oxidation of formic acid in fuel cells in 1987 [5]. Recently, many methods to synthesize Pd NPs have been reported. For example, Wang et al. [6] reported a facile method to synthesize Pd NPs supported on graphene ribbon (GR), in which Na2PdCl4 was employed as the precu ...
... unique ability to catalyze the oxidation of formic acid in fuel cells in 1987 [5]. Recently, many methods to synthesize Pd NPs have been reported. For example, Wang et al. [6] reported a facile method to synthesize Pd NPs supported on graphene ribbon (GR), in which Na2PdCl4 was employed as the precu ...
Heterogeneous Catalysis and Solid Catalysts
... is called homogeneously catalyzed. Metal salts of organic acids, organometallic complexes, and carbonyls of Co, Fe, and Rh are typical homogeneous catalysts. Examples of homogeneously catalyzed reactions are oxidation of toluene to benzoic acid in the presence of Co and Mn benzoatesandhydroformylati ...
... is called homogeneously catalyzed. Metal salts of organic acids, organometallic complexes, and carbonyls of Co, Fe, and Rh are typical homogeneous catalysts. Examples of homogeneously catalyzed reactions are oxidation of toluene to benzoic acid in the presence of Co and Mn benzoatesandhydroformylati ...
Chapter 1 Structure and Bonding
... Hyperconjugation makes substituted alkenes more stable by stabilizing p-orbitals cis alkenes are less stable than trans alkenes because of steric crowding cis cycloalkenes are more stable than trans for the small rings ...
... Hyperconjugation makes substituted alkenes more stable by stabilizing p-orbitals cis alkenes are less stable than trans alkenes because of steric crowding cis cycloalkenes are more stable than trans for the small rings ...
nucleophilic addition on ketones and ketimines - ISI
... The asymmetric allylation of ketones was also recently studied by the groups of Shibasaki22 and Yamamoto23 using soft transition metal–chiral diphosphine complexes as catalysts (Scheme 9). Shibasaki et al. used allyl boronates as nucleophiles for the allyl transfer on aliphatic and aromatic ketones ...
... The asymmetric allylation of ketones was also recently studied by the groups of Shibasaki22 and Yamamoto23 using soft transition metal–chiral diphosphine complexes as catalysts (Scheme 9). Shibasaki et al. used allyl boronates as nucleophiles for the allyl transfer on aliphatic and aromatic ketones ...
Naming Aldehydes & Ketones
... IUPAC Rules for Naming Ketones 3. If the chain is longer than four carbons, it is numbered so that the carbonyl group has the smallest number possible; this number is prefixed to the parent name of the ketone. 4. Other groups attached to the parent chain are named and numbered as we have done befor ...
... IUPAC Rules for Naming Ketones 3. If the chain is longer than four carbons, it is numbered so that the carbonyl group has the smallest number possible; this number is prefixed to the parent name of the ketone. 4. Other groups attached to the parent chain are named and numbered as we have done befor ...
Biomass Program
... product almost always occur when H2 and CO are converted to fuels and chemicals. Consequently, syngas conversion processes are more thermodynamically favorable at higher H2 and CO partial pressures. The optimum pressures depend on the specific synthesis process. With the exception of methane steam r ...
... product almost always occur when H2 and CO are converted to fuels and chemicals. Consequently, syngas conversion processes are more thermodynamically favorable at higher H2 and CO partial pressures. The optimum pressures depend on the specific synthesis process. With the exception of methane steam r ...
Factors influencing ring closure through olefin metathesis – A
... main group alkylating agents (such as WCl6/Bu4Sn, MoO3/SiO2, Re2O7/N2O3Cl2) were inefficient for RCM. An efficient RCM catalyst3 should be a good initiator of metathesis, should react exclusively or at least preferentially with olefins over the other polar groups present in the olefinic substrate an ...
... main group alkylating agents (such as WCl6/Bu4Sn, MoO3/SiO2, Re2O7/N2O3Cl2) were inefficient for RCM. An efficient RCM catalyst3 should be a good initiator of metathesis, should react exclusively or at least preferentially with olefins over the other polar groups present in the olefinic substrate an ...
O-VOCS - Tubitak Journals
... and it generates noxious byproducts (NO x ). Catalytic combustion appears to be the most promising solution for elimination of VOCs when they are at low concentrations. Catalytic combustion offers environmental advantages, since it operates at much lower temperatures, avoiding formation of nitrogen o ...
... and it generates noxious byproducts (NO x ). Catalytic combustion appears to be the most promising solution for elimination of VOCs when they are at low concentrations. Catalytic combustion offers environmental advantages, since it operates at much lower temperatures, avoiding formation of nitrogen o ...
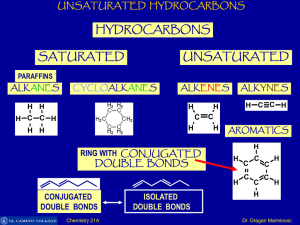
Unsaturated Hydrocarbons
... UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS All the C-atoms in benzene are sp2-hybridized. Two sp2-hybrid orbitals of each C-atom overlap with two sp2-hybrid orbital of two other C-atoms to form sigma bonds. In this way there are six sigma bonds are formed between six C-atoms which are 120o apart. Remaining six sp2-o ...
... UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS All the C-atoms in benzene are sp2-hybridized. Two sp2-hybrid orbitals of each C-atom overlap with two sp2-hybrid orbital of two other C-atoms to form sigma bonds. In this way there are six sigma bonds are formed between six C-atoms which are 120o apart. Remaining six sp2-o ...
homogeneous catalysis
... and industrial research laboratories the growth in research activity in this area in the past decade or so has been phenomenal. Written mainly from a pedagogical point of view, this book is not comprehensive but selective. The material presented was selected on the basis of two criteria. We have tri ...
... and industrial research laboratories the growth in research activity in this area in the past decade or so has been phenomenal. Written mainly from a pedagogical point of view, this book is not comprehensive but selective. The material presented was selected on the basis of two criteria. We have tri ...
RheniumCatalyzed Deoxydehydration of Diols and Polyols
... (Scheme 1). The virtues of the reaction are the simultaneous removal of two oxygen atoms and the formation of a carbon– carbon double bond that can be readily functionalized. ...
... (Scheme 1). The virtues of the reaction are the simultaneous removal of two oxygen atoms and the formation of a carbon– carbon double bond that can be readily functionalized. ...
hydrogen storage
... sample. The amount of adsorbed hydrogen from the gas phase at 77 K and electrochemically at RT is 1.5 × 10-3 mass%·m-2 g. Together with the maximum specific surface area of carbon (1315 m2 g-1), the maximum measured absorption capacity of the nanostructured material is 2 mass%. The experimental resu ...
... sample. The amount of adsorbed hydrogen from the gas phase at 77 K and electrochemically at RT is 1.5 × 10-3 mass%·m-2 g. Together with the maximum specific surface area of carbon (1315 m2 g-1), the maximum measured absorption capacity of the nanostructured material is 2 mass%. The experimental resu ...
Catalysts Containing Depleted Uranium Compounds
... are easy for recycling, whereas reaction products can be readily purified. It has been revealed that complexes of U4+ è U6+ are bright coloured, readily forming acilated ions, not forming complexes with ketones and aromatic esters. A possible mechanism for acylation reaction involving uranium salts ...
... are easy for recycling, whereas reaction products can be readily purified. It has been revealed that complexes of U4+ è U6+ are bright coloured, readily forming acilated ions, not forming complexes with ketones and aromatic esters. A possible mechanism for acylation reaction involving uranium salts ...
Unsaturated hydrocarbons Alkenes
... The second class of simple hydrocarbons the alkenes, consists of molecules that contain at least one doublebonded carbon pair. The chemical formula for the simple alkenes follows the expression: ...
... The second class of simple hydrocarbons the alkenes, consists of molecules that contain at least one doublebonded carbon pair. The chemical formula for the simple alkenes follows the expression: ...
Amines
... t Protonation of amines with acids leads to aminium salts l Aminium salts are formed from 1o, 2 o or 3o amines l An aminium ion bears at least one hydrogen ...
... t Protonation of amines with acids leads to aminium salts l Aminium salts are formed from 1o, 2 o or 3o amines l An aminium ion bears at least one hydrogen ...
lecture 12 catalysis_transformation of alkenes_alkynes
... SAMPLE PROBLEM: Assume 2-pentene and 2-hexene undergo metathesis. AT equilibrium what are all the possible alkenes that would be present, neglecting stereochemistry about the double bond? Remember to consider self metathesis reactions. ...
... SAMPLE PROBLEM: Assume 2-pentene and 2-hexene undergo metathesis. AT equilibrium what are all the possible alkenes that would be present, neglecting stereochemistry about the double bond? Remember to consider self metathesis reactions. ...
Synthesis of a TREN in Which the Aryl Substituents are... Atom Macrocycle ̈ller *
... reduced. Eight of the proposed catalytic intermediates in the Mocatalyzed TREN-based system were characterized by X-ray crystallography. The proposed reaction mechanism also has been scrutinized through extensive calculations.2 All steric and electronic modifications of the successful “HIPT catalysts ...
... reduced. Eight of the proposed catalytic intermediates in the Mocatalyzed TREN-based system were characterized by X-ray crystallography. The proposed reaction mechanism also has been scrutinized through extensive calculations.2 All steric and electronic modifications of the successful “HIPT catalysts ...
Ring-Opening Metathesis Polymerization of Norbornene by Cp
... dihydrogen affords a species that catalyzes the polymerization of cyclopentene.19 They also discovered that Ir2Cl2(COE)2 (COE ) cyclooctadiene) reacts with a mixture of silver trifluoroacetate and trifluoroacetic acid to afford a product that could polymerize C5 to C8 cycloalkenes.20 Demonceau and c ...
... dihydrogen affords a species that catalyzes the polymerization of cyclopentene.19 They also discovered that Ir2Cl2(COE)2 (COE ) cyclooctadiene) reacts with a mixture of silver trifluoroacetate and trifluoroacetic acid to afford a product that could polymerize C5 to C8 cycloalkenes.20 Demonceau and c ...
C 1 hapter
... The hydroboration reaction is a classical method for synthesising organoboron compounds and one of the most studied reactions in organic synthesis. Introduced by H. C. Brown [1] in 1959, it is based on the syn addition of borane reagent H-BR’2 to alkenes or alkynes. In fact, it is considered to be t ...
... The hydroboration reaction is a classical method for synthesising organoboron compounds and one of the most studied reactions in organic synthesis. Introduced by H. C. Brown [1] in 1959, it is based on the syn addition of borane reagent H-BR’2 to alkenes or alkynes. In fact, it is considered to be t ...
heterogeneous chiral catalyst derived from hydrolyzed
... and c, a chiral (asymmetric) centre is produced in (C abcd). In other words, it is a compound or group that has two enantiotopic atoms, faces or groups. For example, CH2XY has two enantiotopic H atoms. Asymmetric synthesis is only possible when the starting materials or conditions are optically acti ...
... and c, a chiral (asymmetric) centre is produced in (C abcd). In other words, it is a compound or group that has two enantiotopic atoms, faces or groups. For example, CH2XY has two enantiotopic H atoms. Asymmetric synthesis is only possible when the starting materials or conditions are optically acti ...
Chemistry 0310 - Organic Chemistry 1 Chapter 12. Reactions of
... - Syn-Hydroxylations of alkenes are most conveniently performed with catalytic OsO4 and NMO (N-methylmorpholine N-oxide) as co-oxidant. Attack occurs from the less-hindered face of the alkene, and a vicinal syn-diol is isolated after reductive workup. - Oxidative cleavage of 1,2-disubstituted alken ...
... - Syn-Hydroxylations of alkenes are most conveniently performed with catalytic OsO4 and NMO (N-methylmorpholine N-oxide) as co-oxidant. Attack occurs from the less-hindered face of the alkene, and a vicinal syn-diol is isolated after reductive workup. - Oxidative cleavage of 1,2-disubstituted alken ...
Palladium and Ruthenium Catalyzed Reactions By Bryan Jaksic
... catalyzed by a Pd(0)L2 species which are generated in situ from a palladium precatalyst and are often co-catalyzed by CuI although use of the latter is undesirable as it induces homocoupling in certain instances. The rate and quantity of active species generated is not known for the commonly used pr ...
... catalyzed by a Pd(0)L2 species which are generated in situ from a palladium precatalyst and are often co-catalyzed by CuI although use of the latter is undesirable as it induces homocoupling in certain instances. The rate and quantity of active species generated is not known for the commonly used pr ...
Hydrogenation

Hydrogenation – to treat with hydrogen – is a chemical reaction between molecular hydrogen (H2) and another compound or element, usually in the presence of a catalyst such as nickel, palladium or platinum. The process is commonly employed to reduce or saturate organic compounds. Hydrogenation typically constitutes the addition of pairs of hydrogen atoms to a molecule, generally an alkene. Catalysts are required for the reaction to be usable; non-catalytic hydrogenation takes place only at very high temperatures. Hydrogenation reduces double and triple bonds in hydrocarbons.Because of the importance of hydrogen, many related reactions have been developed for its use. Most hydrogenations use gaseous hydrogen (H2), but some involve the alternative sources of hydrogen, not H2: these processes are called transfer hydrogenations. The reverse reaction, removal of hydrogen from a molecule, is called dehydrogenation. A reaction where bonds are broken while hydrogen is added is called hydrogenolysis, a reaction that may occur to carbon-carbon and carbon-heteroatom (oxygen, nitrogen or halogen) bonds. Hydrogenation differs from protonation or hydride addition: in hydrogenation, the products have the same charge as the reactants.Hydrogenation of unsaturated fats produces saturated fats. In the case of partial hydrogenation, trans fats may be generated as well.