2.5.4. DNA Revision Qs
... 4 Heredity is the passing on of features from one generation to another by means of ________________________________________. ...
... 4 Heredity is the passing on of features from one generation to another by means of ________________________________________. ...
7th grade Ch. 5 section 2 and 3 Notes
... • Medical care and treatments can help people with some of these disorders. • Most genetic disorders do not prevent people from living active and productive lives. ...
... • Medical care and treatments can help people with some of these disorders. • Most genetic disorders do not prevent people from living active and productive lives. ...
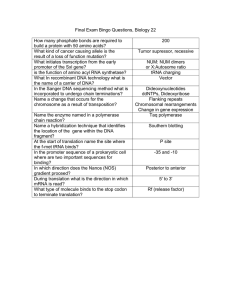
How many phosphate bonds are required to build a protein with 50
... What kind of cancer causing allele is the result of a loss of function mutation? What initiates transcription from the early promoter of the Sxl gene? is the function of amino acyl RNA synthetase? What In recombinant DNA technology what is the name of a carrier of DNA? In the Sanger DNA sequencing m ...
... What kind of cancer causing allele is the result of a loss of function mutation? What initiates transcription from the early promoter of the Sxl gene? is the function of amino acyl RNA synthetase? What In recombinant DNA technology what is the name of a carrier of DNA? In the Sanger DNA sequencing m ...
Genes and genomes
... A gene is a particular sequence (a string) of nucleotides on a particular site of a chromosome. It is made up of combinations of A, T, C, and G. These unique combinations code for a particular amino acid, much as letters join together to form words. ...
... A gene is a particular sequence (a string) of nucleotides on a particular site of a chromosome. It is made up of combinations of A, T, C, and G. These unique combinations code for a particular amino acid, much as letters join together to form words. ...
AP Biology
... 22. In colorectal cancer, tumor suppressor genes are not active. This is an important factor resulting in uncontrolled cell division. Two possible explanations for the inactive genes are: a mutation in the coding region, resulting in an inactive protein, or epigenetic silencing at the promoter of th ...
... 22. In colorectal cancer, tumor suppressor genes are not active. This is an important factor resulting in uncontrolled cell division. Two possible explanations for the inactive genes are: a mutation in the coding region, resulting in an inactive protein, or epigenetic silencing at the promoter of th ...
DNA and Protein Synthesis
... Protein Synthesis • The DNA code serves as a blueprint for making specific proteins. • Examples of proteins: hormones, enzymes, neurotransmitters, receptors, components of tissue. • Proteins are composed of amino acids. • Codons are a sequence of three bases that code for a specific amino acid. ...
... Protein Synthesis • The DNA code serves as a blueprint for making specific proteins. • Examples of proteins: hormones, enzymes, neurotransmitters, receptors, components of tissue. • Proteins are composed of amino acids. • Codons are a sequence of three bases that code for a specific amino acid. ...
Quiz 3-DNA.doc
... 7. How many amino acids are there? a. 20 b. 30 c. 40 d. 10 8. The disease that stops someone’s hemoglobin from getting to part of their body is called: a. Sickle-cell anemia b. Platelet dialysis c. Hemoglobina pseudomona d. Alzheimers 9. Only ___% of genes produce protein a. 1 b. 10 c. 20 d. 30 e. 4 ...
... 7. How many amino acids are there? a. 20 b. 30 c. 40 d. 10 8. The disease that stops someone’s hemoglobin from getting to part of their body is called: a. Sickle-cell anemia b. Platelet dialysis c. Hemoglobina pseudomona d. Alzheimers 9. Only ___% of genes produce protein a. 1 b. 10 c. 20 d. 30 e. 4 ...
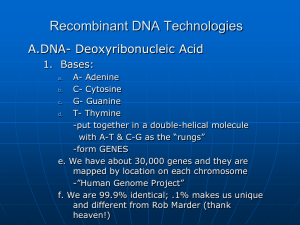
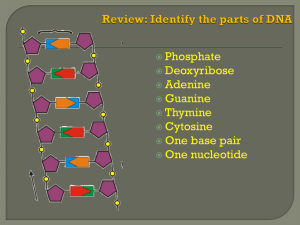
Recombinant DNA Technologies
... d. T- Thymine -put together in a double-helical molecule with A-T & C-G as the “rungs” -form GENES e. We have about 30,000 genes and they are mapped by location on each chromosome -”Human Genome Project” f. We are 99.9% identical; .1% makes us unique and different from Rob Marder (thank heaven!) a. ...
... d. T- Thymine -put together in a double-helical molecule with A-T & C-G as the “rungs” -form GENES e. We have about 30,000 genes and they are mapped by location on each chromosome -”Human Genome Project” f. We are 99.9% identical; .1% makes us unique and different from Rob Marder (thank heaven!) a. ...
Heredity
... Inherited traits-traits that are passed on from parents to offsprings. Genes-tiny message units Learned trait-a trait that is not passed on in DNA Dominant trait-a trait that will be expressed if it is inherited. Recessive trait-a trait that is not expressed if paired with a dominant trait Incomplet ...
... Inherited traits-traits that are passed on from parents to offsprings. Genes-tiny message units Learned trait-a trait that is not passed on in DNA Dominant trait-a trait that will be expressed if it is inherited. Recessive trait-a trait that is not expressed if paired with a dominant trait Incomplet ...
Genetics
... Trait that may not be expressed Lowercase letter t= short, b=white Only expressed when there is no dominant trait present ...
... Trait that may not be expressed Lowercase letter t= short, b=white Only expressed when there is no dominant trait present ...
DNA Connection
... • Nitrogen bases along a gene forms a genetic code that specifies what type of protein will be produced. • Proteins are long chains of individual amino acids. • A group 3 DNA bases codes for one specific amino acid. ...
... • Nitrogen bases along a gene forms a genetic code that specifies what type of protein will be produced. • Proteins are long chains of individual amino acids. • A group 3 DNA bases codes for one specific amino acid. ...
omic glossary
... the expression, localizations, functions, and interactions of the proteins expressed in the body and the determination of their role in physiological and pathophysiological functions. ...
... the expression, localizations, functions, and interactions of the proteins expressed in the body and the determination of their role in physiological and pathophysiological functions. ...
Chpt. 5 Review Questions
... • Genetic Engineering the process of transferring genes from one organism to another • Gene Therapy involves inserting copies of a gene directly into a person’s cells. ...
... • Genetic Engineering the process of transferring genes from one organism to another • Gene Therapy involves inserting copies of a gene directly into a person’s cells. ...
Notes from Lecture 1 - Tufts Computer Science
... Genes are the parts of the DNA that code for proteins. You can get different proteins from the same portion of DNA via splicing. ...
... Genes are the parts of the DNA that code for proteins. You can get different proteins from the same portion of DNA via splicing. ...
Allele: One of the variant forms of the DNA sequence at a particular
... Chromosome: A compact, threadlike organization in the nucleus of human cells that carries the DNA. Each human has two sets of 23 chromosomes, one of each parent. Gene: A gene is a segment of the DNA molecule that contains the “instructions” of how, when and where our bodies function. These instructi ...
... Chromosome: A compact, threadlike organization in the nucleus of human cells that carries the DNA. Each human has two sets of 23 chromosomes, one of each parent. Gene: A gene is a segment of the DNA molecule that contains the “instructions” of how, when and where our bodies function. These instructi ...
With the completion of the human genome sequence, we now have
... Since the completion of the human genome sequence, we now have access to more information than ever before about our genetic make-up. The human genome contains 3 billion base pairs of DNA, encoding an estimated 25,000 genes, which are the basic units of heredity. This course addresses questions such ...
... Since the completion of the human genome sequence, we now have access to more information than ever before about our genetic make-up. The human genome contains 3 billion base pairs of DNA, encoding an estimated 25,000 genes, which are the basic units of heredity. This course addresses questions such ...
The Human Genome Project CH 13 Sec 3 notes
... •Store large amount of information Steps in DNA Microarray •Use ________ from 2 different cells •Convert to complimentary _________________ •Label DNA with _________________________ –Ex: Green = normal, red = cancer •Place in microarray slide –incubate •Examine colors for gene expression –Yellow = s ...
... •Store large amount of information Steps in DNA Microarray •Use ________ from 2 different cells •Convert to complimentary _________________ •Label DNA with _________________________ –Ex: Green = normal, red = cancer •Place in microarray slide –incubate •Examine colors for gene expression –Yellow = s ...
Competency Goal # 3: DNA, Protein Synthesis, Genetics
... 26. _________________________________ The blending of two traits. 27. ___________________________ - alleles result in the expression of both traits. 28. __________________________ - Tools used by scientists to trace inherited genes through a family tree 29. ___________________________ - Traits which ...
... 26. _________________________________ The blending of two traits. 27. ___________________________ - alleles result in the expression of both traits. 28. __________________________ - Tools used by scientists to trace inherited genes through a family tree 29. ___________________________ - Traits which ...
Competency Goal # 3: DNA, Protein Synthesis
... 26. _________________________________ The blending of two traits. 27. ___________________________ - alleles result in the expression of both traits. 28. __________________________ - Tools used by scientists to trace inherited genes through a family tree 29. ___________________________ - Traits which ...
... 26. _________________________________ The blending of two traits. 27. ___________________________ - alleles result in the expression of both traits. 28. __________________________ - Tools used by scientists to trace inherited genes through a family tree 29. ___________________________ - Traits which ...
CentralDogmaNotes
... specific sequences of nucleotides • The DNA inherited by an organism leads to specific traits by dictating the synthesis of proteins • Gene expression, the process by which DNA directs protein synthesis, includes two stages: transcription and translation ...
... specific sequences of nucleotides • The DNA inherited by an organism leads to specific traits by dictating the synthesis of proteins • Gene expression, the process by which DNA directs protein synthesis, includes two stages: transcription and translation ...
Gene

A gene is a locus (or region) of DNA that encodes a functional RNA or protein product, and is the molecular unit of heredity. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as the gene–environment interactions. Some genetic traits are instantly visible, such as eye colour or number of limbs, and some are not, such as blood type, risk for specific diseases, or the thousands of basic biochemical processes that comprise life.Genes can acquire mutations in their sequence, leading to different variants, known as alleles, in the population. These alleles encode slightly different versions of a protein, which cause different phenotype traits. Colloquial usage of the term ""having a gene"" (e.g., ""good genes,"" ""hair colour gene"") typically refers to having a different allele of the gene. Genes evolve due to natural selection or survival of the fittest of the alleles.The concept of a gene continues to be refined as new phenomena are discovered. For example, regulatory regions of a gene can be far removed from its coding regions, and coding regions can be split into several exons. Some viruses store their genome in RNA instead of DNA and some gene products are functional non-coding RNAs. Therefore, a broad, modern working definition of a gene is any discrete locus of heritable, genomic sequence which affect an organism's traits by being expressed as a functional product or by regulation of gene expression.