Introduction to Organic Mass Spectrometry
... Solvent evaporates, droplets split and/or ions evaporate to lower charge/area ratio Warm nebulizing gas accelerates drying Free ions are directed into the vacuum chamber ...
... Solvent evaporates, droplets split and/or ions evaporate to lower charge/area ratio Warm nebulizing gas accelerates drying Free ions are directed into the vacuum chamber ...
Test 2 - Northwest Florida State College
... {skip this #9 for Fall 2016 classes} 10) Find molar mass of an atom or compound. Be able to convert between grams and moles using a molar mass. ...
... {skip this #9 for Fall 2016 classes} 10) Find molar mass of an atom or compound. Be able to convert between grams and moles using a molar mass. ...
Activity Name: Polyatomic Ion Bingo
... Background Information: An ion is an atom or group of atoms that has a charge because of the loss or gain of electrons. A polyatomic ion is an ion that consists of at least two different elements. Polyatomic ions are common ingredients in many foods and household products. Phosphate, nitrate, sulfat ...
... Background Information: An ion is an atom or group of atoms that has a charge because of the loss or gain of electrons. A polyatomic ion is an ion that consists of at least two different elements. Polyatomic ions are common ingredients in many foods and household products. Phosphate, nitrate, sulfat ...
Mass Spectrometry and Organic
... a molecular Formula Take the Weight of ion, divide by 13 This answer is N, for (CH)N and any numerical remainder is added as H e.g.; 92 92/13 = 7 with remainder = 1; C7H8 weighs 92. This is our candidate formula Can evaluate other alternative candidate formulas possessing heteroatoms. For each membe ...
... a molecular Formula Take the Weight of ion, divide by 13 This answer is N, for (CH)N and any numerical remainder is added as H e.g.; 92 92/13 = 7 with remainder = 1; C7H8 weighs 92. This is our candidate formula Can evaluate other alternative candidate formulas possessing heteroatoms. For each membe ...
Infrared Spectroscopy and Mass Spectroscopy
... guessing a molecular Formula Take the Weight of ion, divide by 13 This answer is N, for (CH)N and any numerical remainder is added as H e.g.; 92 92/13 = 7 with remainder = 1; C7H8 weighs 92. This is our candidate formula Can evaluate other alternative candidate formulas possessing heteroatoms. For e ...
... guessing a molecular Formula Take the Weight of ion, divide by 13 This answer is N, for (CH)N and any numerical remainder is added as H e.g.; 92 92/13 = 7 with remainder = 1; C7H8 weighs 92. This is our candidate formula Can evaluate other alternative candidate formulas possessing heteroatoms. For e ...
File
... • Acid – H+ ion (or H3O+) is only positive ion in soln –H+ ion is also called a PROTON –H3O+ is called a HYDRONIUM ion ...
... • Acid – H+ ion (or H3O+) is only positive ion in soln –H+ ion is also called a PROTON –H3O+ is called a HYDRONIUM ion ...
Mass Spectrum – Interpretation
... Fluorine has only one isotope (19F), so the mass spectrum of F2 will show only two peaks one at 19 and the other at 38 (which one is bigger cannot be predicted – depends on how stable the F2 + ion is - the diagram below is just a sketch). ...
... Fluorine has only one isotope (19F), so the mass spectrum of F2 will show only two peaks one at 19 and the other at 38 (which one is bigger cannot be predicted – depends on how stable the F2 + ion is - the diagram below is just a sketch). ...
Chemistry primer Atom = the smallest unit of an element Element
... (the more reliable ones for mineral identification) Hardness: Resistance to scratching. Greater hardness due to: strong bonds, tight structure, small ions Cleavage: Planes of weakness along which a mineral breaks. Reflect crystalline structure, Cleavage occurs along planes of weakness between atoms. ...
... (the more reliable ones for mineral identification) Hardness: Resistance to scratching. Greater hardness due to: strong bonds, tight structure, small ions Cleavage: Planes of weakness along which a mineral breaks. Reflect crystalline structure, Cleavage occurs along planes of weakness between atoms. ...
The Born-Haber Cycle
... Consider the strongly exothermic reaction between sodium metal and chlorine gas… ...
... Consider the strongly exothermic reaction between sodium metal and chlorine gas… ...
Unit 5 – Test Study Guide
... another energy level and many more inner core electrons the atoms is much bigger. This means the valence electrons are further away from the nucleus and they are less attracted to the nucleus due to all the inner core electrons. This makes the removal of an electron much easier resulting in a lower ...
... another energy level and many more inner core electrons the atoms is much bigger. This means the valence electrons are further away from the nucleus and they are less attracted to the nucleus due to all the inner core electrons. This makes the removal of an electron much easier resulting in a lower ...
Electronic Spectroscopy of Transition Metal Ions
... • there are many different arrangements of electrons in d orbitals so this gives rise to many possible states (RussellSaunders ‘terms’) that represent different energies for the system as a whole eg. d2 ion 1st electron: any of the 5 d-orbitals and spin up or down gives rise to 10 possibilities 2nd ...
... • there are many different arrangements of electrons in d orbitals so this gives rise to many possible states (RussellSaunders ‘terms’) that represent different energies for the system as a whole eg. d2 ion 1st electron: any of the 5 d-orbitals and spin up or down gives rise to 10 possibilities 2nd ...
Chemical Bonds
... 8.3 Lattice Enthalpies • Lattice enthalpy (∆ ∆HL)– enthalpy change when a mol of an ionic compound is separated into isolated gaseous ions (positive) MX(s) → M+(g) + X-(g) ∆HL>0 • At constant pressure the lattice enthalpy is numerically equal to the heat of formation of one mol of the ionic compound ...
... 8.3 Lattice Enthalpies • Lattice enthalpy (∆ ∆HL)– enthalpy change when a mol of an ionic compound is separated into isolated gaseous ions (positive) MX(s) → M+(g) + X-(g) ∆HL>0 • At constant pressure the lattice enthalpy is numerically equal to the heat of formation of one mol of the ionic compound ...
determining oxidation numbers
... 5. Other halogens have ONs = -1 except when bound to oxygen or another halogen higher in the column. 6. The ON for hydrogen is +1, except when bound to a metal, when it is -1. 7. Alkali metals always have an ON = +1. 8. Polyatomic ions all have specific total charges that will be the sum of the oxid ...
... 5. Other halogens have ONs = -1 except when bound to oxygen or another halogen higher in the column. 6. The ON for hydrogen is +1, except when bound to a metal, when it is -1. 7. Alkali metals always have an ON = +1. 8. Polyatomic ions all have specific total charges that will be the sum of the oxid ...
Modeling and experimental studies of radical formation in RF discharges with etching gases
... Modeling and Experimental Studies of Radical Formation in RF Discharges with Etching Gases Y. Yasaka T. Kawamura, Y. Takada, and A. Tsuji Dept. Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Kobe University, Kobe 657-8501, Japan Abstract: Modeling of plasma production combined with gas phase chemical reacti ...
... Modeling and Experimental Studies of Radical Formation in RF Discharges with Etching Gases Y. Yasaka T. Kawamura, Y. Takada, and A. Tsuji Dept. Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Kobe University, Kobe 657-8501, Japan Abstract: Modeling of plasma production combined with gas phase chemical reacti ...
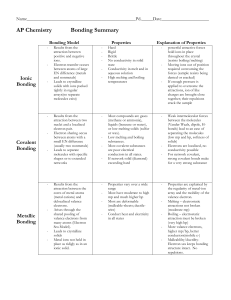
Types of Bonding Summary
... small EN difference (usually two nonmetals) Leads to separate molecules with specific shapes or to extended networks ...
... small EN difference (usually two nonmetals) Leads to separate molecules with specific shapes or to extended networks ...
Feasibility Study of using FAIMS to Detect Carbonyl Sulfide in Propane
... The UV ionization source is a direct ionization method whereby photons are emitted at energies of 9.6, 10.2, 10.6, 11.2, and 11.8eV and can only ionize chemical species with a first ionization potential less than the emitted energy. Important points to note are that there is no positive mode RIP pre ...
... The UV ionization source is a direct ionization method whereby photons are emitted at energies of 9.6, 10.2, 10.6, 11.2, and 11.8eV and can only ionize chemical species with a first ionization potential less than the emitted energy. Important points to note are that there is no positive mode RIP pre ...
API III User Training
... Must inject something, even if syringe pump is used Solution must contain only sample and volatile components Allows 2.5 minute analysis time ...
... Must inject something, even if syringe pump is used Solution must contain only sample and volatile components Allows 2.5 minute analysis time ...
AP Unit 1 Test Review
... Some binary compounds that form between fluorine and various nonmetals are listed in the table above. A student examines the data in the table and poses the following hypothesis: the number of F atoms that will bond to a nonmetal is always equal to 8 minus the number of valence electrons in the nonm ...
... Some binary compounds that form between fluorine and various nonmetals are listed in the table above. A student examines the data in the table and poses the following hypothesis: the number of F atoms that will bond to a nonmetal is always equal to 8 minus the number of valence electrons in the nonm ...
AP Chemistry Study Guide – Chapter 7, Atomic Structure
... Find wavelength, amplitude, and frequency of a sine wave Discuss the electromagnetic spectrum Convert between frequency and wavelength Calculate the energy of a wave Calculate the energy of an electron Calculate the energy released in a transition of an electron from an excited state to the ground s ...
... Find wavelength, amplitude, and frequency of a sine wave Discuss the electromagnetic spectrum Convert between frequency and wavelength Calculate the energy of a wave Calculate the energy of an electron Calculate the energy released in a transition of an electron from an excited state to the ground s ...
Request for Mass Spectrometric Analysis
... Incomplete forms will cause samples to be rejected. Max turnaround time: 2 weeks. Write legibly. If your sample has special requirements (keep frozen until analysis, sensitive to acid, etc) please describe in Extra Notes. Samples can be submitted directly to room 318 or placed on the labeled counter ...
... Incomplete forms will cause samples to be rejected. Max turnaround time: 2 weeks. Write legibly. If your sample has special requirements (keep frozen until analysis, sensitive to acid, etc) please describe in Extra Notes. Samples can be submitted directly to room 318 or placed on the labeled counter ...
Unit 2: Atoms and Ions Homework Booklet
... British coins are Alloys. A20p coin contains copper (84%) and nickel (16%), a 50p coin contains copper (75%) and nickel (25%) and a £1 coin contains copper (70%), nickel (5.5%) and zinc (24.5%). Present this information in the form of a table. ...
... British coins are Alloys. A20p coin contains copper (84%) and nickel (16%), a 50p coin contains copper (75%) and nickel (25%) and a £1 coin contains copper (70%), nickel (5.5%) and zinc (24.5%). Present this information in the form of a table. ...
Summer Assignment 2015
... 4. How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are in (a) a 138Ba atom, (b) an atom of phosphorus-31? 5. Give the complete chemical symbol for the atom that contains 82 protons, 82 electrons, and 126 neutrons. 6. Naturally occurring chlorine is 75.78% 35Cl, which has an atomic mass of 34.969 amu, and ...
... 4. How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are in (a) a 138Ba atom, (b) an atom of phosphorus-31? 5. Give the complete chemical symbol for the atom that contains 82 protons, 82 electrons, and 126 neutrons. 6. Naturally occurring chlorine is 75.78% 35Cl, which has an atomic mass of 34.969 amu, and ...
SCIENCE 10: Chemical Reactions – Atomic Structure
... The element copper forms two different compounds with chlorine. Chlorine always forms a 1- ion. Copper can form either a 1+ ion or a 2+ ion. CuCl = copper (I) chloride CuCl2 = copper (II) chloride Naming Ionic Compounds: (p.194) o Metal name first, non-metal name second o Change the ending of the ...
... The element copper forms two different compounds with chlorine. Chlorine always forms a 1- ion. Copper can form either a 1+ ion or a 2+ ion. CuCl = copper (I) chloride CuCl2 = copper (II) chloride Naming Ionic Compounds: (p.194) o Metal name first, non-metal name second o Change the ending of the ...
Atomic Radii Answers File
... A.R. increases going down a group. An extra shell is being added in successive elements and the electrons in the outer shell are “shielded” from the nucleus by the inner shells. There is a decreasing attractive pull on them from the nucleus. ...
... A.R. increases going down a group. An extra shell is being added in successive elements and the electrons in the outer shell are “shielded” from the nucleus by the inner shells. There is a decreasing attractive pull on them from the nucleus. ...
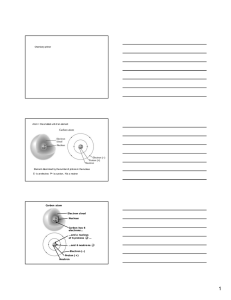
Ion source

An ion source is a device that creates atomic and molecular ions. Ion sources are used to form ions for mass spectrometers, optical emission spectrometers, particle accelerators, ion implanters and ion engines.