document
... Enthalpy is a tricky thing to grasp, but we can look at it this way: • Enthalpy is the macroscopic energy change (in the form of heat) that accompanies changes at the atomic level (bond formation or breaking) • Enthalpy has the same sign convention as work, q and U – If energy is released as heat d ...
... Enthalpy is a tricky thing to grasp, but we can look at it this way: • Enthalpy is the macroscopic energy change (in the form of heat) that accompanies changes at the atomic level (bond formation or breaking) • Enthalpy has the same sign convention as work, q and U – If energy is released as heat d ...
Chemistry Unit Study Guide Key
... laws says that no matter can be created or destroyed. Therefore, each side of the equation must be the same. ...
... laws says that no matter can be created or destroyed. Therefore, each side of the equation must be the same. ...
elements
... physical and chemical properties. It cannot be broken down into a simpler substance and still retain all these properties of the element. ...
... physical and chemical properties. It cannot be broken down into a simpler substance and still retain all these properties of the element. ...
FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
... first law of thermodynamics can be applied to a system to evaluate the changes in its energy when it undergoes a change of state while interacting with its surroundings. The processes that are usually encountered in thermodynamic analysis of systems can be identified as any one or a combination of t ...
... first law of thermodynamics can be applied to a system to evaluate the changes in its energy when it undergoes a change of state while interacting with its surroundings. The processes that are usually encountered in thermodynamic analysis of systems can be identified as any one or a combination of t ...
Cosmetology Learning Module 12
... Chemistry Chemistry - Science that deals with the composition, structures, and properties of matter and how matter changes under different chemical conditions Organic Chemistry – is the study of substances that contain carbon All living things are made up of compounds that contain carbon Or ...
... Chemistry Chemistry - Science that deals with the composition, structures, and properties of matter and how matter changes under different chemical conditions Organic Chemistry – is the study of substances that contain carbon All living things are made up of compounds that contain carbon Or ...
Week - Mat-Su School District
... Description: This is an advanced Science course designed to prepare the student for either college Chemistry or AP Chemistry. The course covers the equivalent of one full year of general Chemistry, comparable to a first year course at a college or university. The course is a rigorous math-based cour ...
... Description: This is an advanced Science course designed to prepare the student for either college Chemistry or AP Chemistry. The course covers the equivalent of one full year of general Chemistry, comparable to a first year course at a college or university. The course is a rigorous math-based cour ...
File
... • In endothermic reactions energy is absorbed from the surroundings – Kinetic energy converts to potential energy when it is absorbed and is stored in bonds • Endothermic reactions feel cold because thermal energy is leaving the surroundings (i.e. your hands) • The endothermic reaction absorbs heat; ...
... • In endothermic reactions energy is absorbed from the surroundings – Kinetic energy converts to potential energy when it is absorbed and is stored in bonds • Endothermic reactions feel cold because thermal energy is leaving the surroundings (i.e. your hands) • The endothermic reaction absorbs heat; ...
Balancing chemical equations notes
... Reactants are the chemicals that are initially combined together. They are written on the left side of the reaction arrow. In the case above, Cu and HNO3 are reactants. Products are the chemicals produced by a reaction. They are written on the right side of the reaction arrow. In the case above, Cu( ...
... Reactants are the chemicals that are initially combined together. They are written on the left side of the reaction arrow. In the case above, Cu and HNO3 are reactants. Products are the chemicals produced by a reaction. They are written on the right side of the reaction arrow. In the case above, Cu( ...
Entropy and the end of it all
... implies the world will end with everything being heat, 'the heat death of the universe'. Everybody goes to hell, so to ...
... implies the world will end with everything being heat, 'the heat death of the universe'. Everybody goes to hell, so to ...
A.P. Chemistry Complexation Reactions
... A single element (A) replaces another element (B) in a compound A single element must be more reactive to replace another element. ...
... A single element (A) replaces another element (B) in a compound A single element must be more reactive to replace another element. ...
ppt
... specific heat of solution of KBrO3 (s) is an endothermic 0.25 kJ/g. Calculate the molar heat of solution and write the ...
... specific heat of solution of KBrO3 (s) is an endothermic 0.25 kJ/g. Calculate the molar heat of solution and write the ...
Notes on Heat, temperature and kinetic energy
... • During photosynthesis light energy is converted into chemical energy • Activation of a light stick converts chemical energy to light energy • During digestion, food (stored energy) is converted to chemical energy • When a falling object (kinetic energy) hits the ground some of the KE is converted ...
... • During photosynthesis light energy is converted into chemical energy • Activation of a light stick converts chemical energy to light energy • During digestion, food (stored energy) is converted to chemical energy • When a falling object (kinetic energy) hits the ground some of the KE is converted ...
The Use and Misuse of the LUWS of Thermodynamics
... From equations (I), (2a), and (2b), we can also derive the criteria of thermal, mechanical, and material equilibrium. If two parts of a body separated by a thermally conducting wall have different temperatures (Fig. la) then heat will flow spontaneously from the part with the higher T to the part wi ...
... From equations (I), (2a), and (2b), we can also derive the criteria of thermal, mechanical, and material equilibrium. If two parts of a body separated by a thermally conducting wall have different temperatures (Fig. la) then heat will flow spontaneously from the part with the higher T to the part wi ...
CHEMISTRY
... 2. Write a formula equation by substituting correct formulas for the names of reactants and products. ...
... 2. Write a formula equation by substituting correct formulas for the names of reactants and products. ...
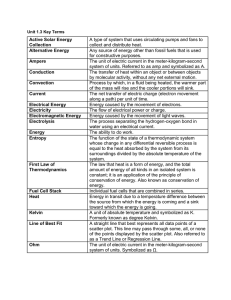
Unit 1.3 Key Terms Active Solar Energy Collection A type of system
... which all parts of the system have attained a uniform temperature which is the same as that of the system’s surroundings. A part of the physical world as described by its thermodynamic properties such as temperature, volume, pressure, concentration, surface tension, and viscosity. The study of the e ...
... which all parts of the system have attained a uniform temperature which is the same as that of the system’s surroundings. A part of the physical world as described by its thermodynamic properties such as temperature, volume, pressure, concentration, surface tension, and viscosity. The study of the e ...
Summary - Clarkson University
... EBf = EBi + ( −Q ) − ( −W ) E Af + EBf = E Ai + EBi E Af − E Ai = −( EBf − EBi ) ∆E A = − ∆EB F. Enthalpy In many applications we study processes conducted at constant pressure (dP=0). dE = dQ − dW dE = dQ − pdV considerin g only P - V work ...
... EBf = EBi + ( −Q ) − ( −W ) E Af + EBf = E Ai + EBi E Af − E Ai = −( EBf − EBi ) ∆E A = − ∆EB F. Enthalpy In many applications we study processes conducted at constant pressure (dP=0). dE = dQ − dW dE = dQ − pdV considerin g only P - V work ...
Section 11
... An engine cylinder has a crosssectional area of 0.010 m2. How much work can be done by a gas in the cylinder if the gas exerts a constant pressure of 7.5 x 105 Pa on the piston and moves the piston a distance of 0.040 m? ...
... An engine cylinder has a crosssectional area of 0.010 m2. How much work can be done by a gas in the cylinder if the gas exerts a constant pressure of 7.5 x 105 Pa on the piston and moves the piston a distance of 0.040 m? ...
CHEMICAL EQUATIONS, SYMBOLS, FORULAS 7
... kind of atom on the right side of the arrow for the equation to be balanced. ...
... kind of atom on the right side of the arrow for the equation to be balanced. ...
Let’s talk Chemistry!
... The ability to change or to move matter is referred to as Energy All changes of the state of matter require Energy Evaporation refers to the change of state from a Liquid to a gas The law of conservation of mass states that mass Cannot be created or destroyed ...
... The ability to change or to move matter is referred to as Energy All changes of the state of matter require Energy Evaporation refers to the change of state from a Liquid to a gas The law of conservation of mass states that mass Cannot be created or destroyed ...
Chemical thermodynamics

Chemical thermodynamics is the study of the interrelation of heat and work with chemical reactions or with physical changes of state within the confines of the laws of thermodynamics. Chemical thermodynamics involves not only laboratory measurements of various thermodynamic properties, but also the application of mathematical methods to the study of chemical questions and the spontaneity of processes.The structure of chemical thermodynamics is based on the first two laws of thermodynamics. Starting from the first and second laws of thermodynamics, four equations called the ""fundamental equations of Gibbs"" can be derived. From these four, a multitude of equations, relating the thermodynamic properties of the thermodynamic system can be derived using relatively simple mathematics. This outlines the mathematical framework of chemical thermodynamics.