* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ppt
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Electrolysis of water wikipedia , lookup
Calcium looping wikipedia , lookup
Process chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Spinodal decomposition wikipedia , lookup
Photoredox catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen-bond catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Multi-state modeling of biomolecules wikipedia , lookup
Heat transfer wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Rate equation wikipedia , lookup
Chemical equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Marcus theory wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Lewis acid catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Click chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical reaction wikipedia , lookup
Bioorthogonal chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Heat equation wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Chemical thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
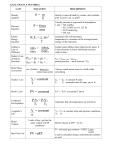
Lesson 4 – Representing Enthalpy Changes Method One THERMOCHEMICAL EQUATIONS WITH ENERGY TERMS a balanced chemical equation that includes the heat transferred to or from the surroundings Ex. H2 (g) + ½O2 (g) H2O(l) + 285.8 kJ MgCO3 (s) + 117.3 kJ MgO(s) + CO2(g) To write a thermochemical equation, you must know –the balanced chemical equation –the molar heat of reaction for one substance –if the reaction is endothermic or exothermic Sample Problem 1 From a calorimetry experiment, a student determines that the specific heat of solution of KBrO3 (s) is an endothermic 0.25 kJ/g. Calculate the molar heat of solution and write the thermochemical equation. Sample Problem 2 The combustion of magnesium releases 24.7 kJ per gram of magnesium. Calculate the molar heat of combustion of magnesium and write the thermochemical equation. Sample Problem 3 Use the following thermochemical equation to calculate the molar heat of combustion of hexane. 2C6H14 (l) + 19O2 (g) 12CO2 (g) + 14H2O (g) + 7086kJ Method Two THERMOCHEMICAL EQUATIONS WITH ΔH VALUES The enthalpy of reaction is indicated by a separate expression beside the chemical equation »Remember: exothermic reactions have -ΔH endothermic reactions have +ΔH Examples: H2 (g) + ½O2 (g) H2O(l) Horxn = -285.8 kJ MgCO3 (s) MgO(s) + CO2(g) Horxn = 117.3 kJ Method Three MOLAR ENTHALPY OF REACTION the quantity of heat transferred in a reaction per mole of a specified substance Hr (kJ/mol) to calculate the molar heat of reaction: Hr = specific heat of reaction x molar mass standard molar enthalpy of reaction (Hro): molar enthalpy that is determined at SATP Sample Problem 4 Ethane is the second largest component of natural gas. If its specific heat of combustion is -51.85 kJ/g, what is the molar heat of combustion of ethane? Method Four POTENTIAL ENERGY DIAGRAM a graphical representation of the energy transferred during a physical or chemical change exothermic reactions: products are lower in energy than reactants (energy lost to surroundings) endothermic reactions: products are higher in energy than reactants (energy absorbed from surroundings) Exothermic Reactions Endothermic Reactions Reactants Ep Products H Products Reaction Progress Ep H Reactants Reaction Progress