53 word equations
... also formed in the process. Energy from the Sun is required for the reaction. ...
... also formed in the process. Energy from the Sun is required for the reaction. ...
CO 2(g) - cloudfront.net
... The states of the reactants and products are written in parentheses to the right of each compound. ...
... The states of the reactants and products are written in parentheses to the right of each compound. ...
Single-Replacement Reactions
... Balance the atoms of an element one at a time by adding coefficients (the numbers in front) - save H and O until LAST! Check to make sure it is balanced. ...
... Balance the atoms of an element one at a time by adding coefficients (the numbers in front) - save H and O until LAST! Check to make sure it is balanced. ...
Science24-UnitA-Section3.4
... you get a chemical equation. Chemical equations are used to represent all reactions. In mathematics you work with equations. What you do to one side of the equation must be done to the other side to keep the equation balanced. Similarly, in chemical equations you need have the same number of atoms o ...
... you get a chemical equation. Chemical equations are used to represent all reactions. In mathematics you work with equations. What you do to one side of the equation must be done to the other side to keep the equation balanced. Similarly, in chemical equations you need have the same number of atoms o ...
Earth Science - Green Local Schools
... Be able to look at a periodic table and gather information about different elements Know how to determine how reactive an element is based on its electrons Chapter 5 – Structure of Matter Chemical bond Making a compound Ionic bond Covalent bond ...
... Be able to look at a periodic table and gather information about different elements Know how to determine how reactive an element is based on its electrons Chapter 5 – Structure of Matter Chemical bond Making a compound Ionic bond Covalent bond ...
Biochemistry 304 2014 Student Edition Thermodynamics Lecture
... objects due to a difference in the objects’ temperatures. By convention heat is positive when it is added to the system. Units: J Work Simplest representation of work involves the operation of force through a distance in such a way as to produce an increase in the potential or kinetic energy of an o ...
... objects due to a difference in the objects’ temperatures. By convention heat is positive when it is added to the system. Units: J Work Simplest representation of work involves the operation of force through a distance in such a way as to produce an increase in the potential or kinetic energy of an o ...
Review Notes - Biochemistry
... gained it will be _NEGATIVE_charged and when an electron is lost it will be _POSITIVE_ charged. ...
... gained it will be _NEGATIVE_charged and when an electron is lost it will be _POSITIVE_ charged. ...
The Language of Chemistry
... • A homogeneous mixture consists of two or more substances in the same phase. No amount of optical magnification will reveal a homogeneous mixture to have different properties in different regions. • A heterogeneous mixture does not have uniform composition. Its components are easily visually distin ...
... • A homogeneous mixture consists of two or more substances in the same phase. No amount of optical magnification will reveal a homogeneous mixture to have different properties in different regions. • A heterogeneous mixture does not have uniform composition. Its components are easily visually distin ...
Chapter 2 Introduction to Chemistry
... chemical reactions and to form new substances (i.e. flammability, rusting) – can only be observed during the change Chemical changes can’t be observed without altering the ...
... chemical reactions and to form new substances (i.e. flammability, rusting) – can only be observed during the change Chemical changes can’t be observed without altering the ...
File
... 20. The rows in the periodic table are called ____________________. They are organized by ______________________________________. 21. The columns in the periodic table are called ______________________. They are grouped by ____________________________________________________________. 22. Most of the ...
... 20. The rows in the periodic table are called ____________________. They are organized by ______________________________________. 21. The columns in the periodic table are called ______________________. They are grouped by ____________________________________________________________. 22. Most of the ...
CHM 101
... The reactants in a chemical change have 487 kJ of energy. The change they undergo has a H = -157 kJ. The activation energy for the reaction is 570 kJ. a. Draw the energy vs reaction progress graph on the axes above paying attention to all values. Label a point that represents all products and one t ...
... The reactants in a chemical change have 487 kJ of energy. The change they undergo has a H = -157 kJ. The activation energy for the reaction is 570 kJ. a. Draw the energy vs reaction progress graph on the axes above paying attention to all values. Label a point that represents all products and one t ...
File - Flipped Out Science with Mrs. Thomas!
... 5A describe the structure of atoms, including the masses, electrical charges, and locations, of protons and neutrons in the nucleus and electrons in the electron cloud 5B identify that protons determine an element’s identity and valence electrons determine its chemical properties, including reactivi ...
... 5A describe the structure of atoms, including the masses, electrical charges, and locations, of protons and neutrons in the nucleus and electrons in the electron cloud 5B identify that protons determine an element’s identity and valence electrons determine its chemical properties, including reactivi ...
File - Flipped Out Science with Mrs. Thomas!
... 5A describe the structure of atoms, including the masses, electrical charges, and locations, of protons and neutrons in the nucleus and electrons in the electron cloud 5B identify that protons determine an element’s identity and valence electrons determine its chemical properties, including reactivi ...
... 5A describe the structure of atoms, including the masses, electrical charges, and locations, of protons and neutrons in the nucleus and electrons in the electron cloud 5B identify that protons determine an element’s identity and valence electrons determine its chemical properties, including reactivi ...
Honors Chemistry- Chapter 16 Homework Packet Reaction Energy
... 10) (a) What does it mean when we say that a chemical reaction is spontaneous? ...
... 10) (a) What does it mean when we say that a chemical reaction is spontaneous? ...
Chemistry - El Camino College
... 2. _________ Bonds are strong chemical bonds between atoms that result from the _______ of electrons in their outer orbitals. Molecules with covalent bonds are represented 2 ways: a. ___________ formulas in which each pair of shared electrons is represented by a line (e.g.: O=C=O). b. __________ for ...
... 2. _________ Bonds are strong chemical bonds between atoms that result from the _______ of electrons in their outer orbitals. Molecules with covalent bonds are represented 2 ways: a. ___________ formulas in which each pair of shared electrons is represented by a line (e.g.: O=C=O). b. __________ for ...
Physical Behavior of Matter Review
... Chemical and physical changes can be exothermic or endothermic. • Table I shows heats of reaction (ΔH) for a number of combustion reactions, a bunch of synthesis reactions (often called the heat of formation), and some solubility changes (a physical change). • There is usually one question using th ...
... Chemical and physical changes can be exothermic or endothermic. • Table I shows heats of reaction (ΔH) for a number of combustion reactions, a bunch of synthesis reactions (often called the heat of formation), and some solubility changes (a physical change). • There is usually one question using th ...
Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics
... process the system changes in such a way that the system and surroundings can be put back in their original states by exactly reversing the process. Chemical Thermodynamics © 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ...
... process the system changes in such a way that the system and surroundings can be put back in their original states by exactly reversing the process. Chemical Thermodynamics © 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ...
Word
... another example. Here we are compressing the gas as we pump and so work is being done on the gas. If we do it quickly the thermal energy has no time to flow out and the internal energy of the gas increases. This is an example of an adiabatic process, where ___________ B. Activity Questions: ...
... another example. Here we are compressing the gas as we pump and so work is being done on the gas. If we do it quickly the thermal energy has no time to flow out and the internal energy of the gas increases. This is an example of an adiabatic process, where ___________ B. Activity Questions: ...
Fundamentals of chemical thermodynamics and bioenergetics
... When writing thermochemical equations, one must always specify the physical states of all reactants and products, because they help determine the actual enthalpy changes. For example, the thermochemical equation for the combustion of methane is: ...
... When writing thermochemical equations, one must always specify the physical states of all reactants and products, because they help determine the actual enthalpy changes. For example, the thermochemical equation for the combustion of methane is: ...
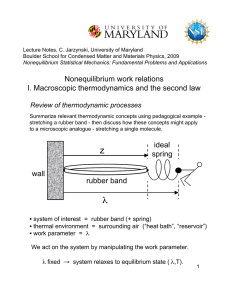
W - Boulder School for Condensed Matter and Materials Physics
... but keep in mind that the meaning of the quantities involved depends on how we define our system of interest. ...
... but keep in mind that the meaning of the quantities involved depends on how we define our system of interest. ...
Chemistry Quiz #2 Study Guide (Answers)
... sublimation, evaporation) • Exothermic Reaction – Energy (heat) leaving a reaction (condensation, solidification, deposition) 2. What is the Kinetic Molecular Theory? The theory that all molecules are in constant motion. ...
... sublimation, evaporation) • Exothermic Reaction – Energy (heat) leaving a reaction (condensation, solidification, deposition) 2. What is the Kinetic Molecular Theory? The theory that all molecules are in constant motion. ...
Chapter
... 2.2. Donnan potential and salt solubilities in pulp suspensions The concept of ion-exchanging (Donnan) equilibrium has been conventionally used to characterize electrolyte interactions with cellulose fibres (Towers, Scallan 1996). Because of its simplicity it is an attractive approach to modelling o ...
... 2.2. Donnan potential and salt solubilities in pulp suspensions The concept of ion-exchanging (Donnan) equilibrium has been conventionally used to characterize electrolyte interactions with cellulose fibres (Towers, Scallan 1996). Because of its simplicity it is an attractive approach to modelling o ...
Chemical thermodynamics

Chemical thermodynamics is the study of the interrelation of heat and work with chemical reactions or with physical changes of state within the confines of the laws of thermodynamics. Chemical thermodynamics involves not only laboratory measurements of various thermodynamic properties, but also the application of mathematical methods to the study of chemical questions and the spontaneity of processes.The structure of chemical thermodynamics is based on the first two laws of thermodynamics. Starting from the first and second laws of thermodynamics, four equations called the ""fundamental equations of Gibbs"" can be derived. From these four, a multitude of equations, relating the thermodynamic properties of the thermodynamic system can be derived using relatively simple mathematics. This outlines the mathematical framework of chemical thermodynamics.