Chemistry Study Guide
... Chemical Reactions- These are combinations of divisions of substances that result in one or more new substances with new physical and chemical properties. Chemical Equations- There should be the same number of atoms on each side of the equation. Multiply the atoms in each molecule by the number ...
... Chemical Reactions- These are combinations of divisions of substances that result in one or more new substances with new physical and chemical properties. Chemical Equations- There should be the same number of atoms on each side of the equation. Multiply the atoms in each molecule by the number ...
File
... Carbon dioxide and oxygen (air) gas-gas Water vapor in air (moist air) liquid-gas Carbon dioxide in water (soda water) gas-liquid Acetic acid in water (vinegar) liquid-liquid Sodium chloride in water (salt water) solid-liquid Copper in silver (sterling silver) solid-solid ...
... Carbon dioxide and oxygen (air) gas-gas Water vapor in air (moist air) liquid-gas Carbon dioxide in water (soda water) gas-liquid Acetic acid in water (vinegar) liquid-liquid Sodium chloride in water (salt water) solid-liquid Copper in silver (sterling silver) solid-solid ...
dx cx dx and x - Cameron University
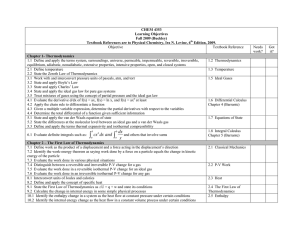
... 16.2 Determine the entropy change in a cyclic process ()S = 0, since S is a state function) 16.3 Determine the entropy change in a reversible adiabatic process 16.4 Determine the entropy change in a reversible phase change at constant temperature and pressure 16.5 Determine the entropy change in a r ...
... 16.2 Determine the entropy change in a cyclic process ()S = 0, since S is a state function) 16.3 Determine the entropy change in a reversible adiabatic process 16.4 Determine the entropy change in a reversible phase change at constant temperature and pressure 16.5 Determine the entropy change in a r ...
ppt
... Types of Chemical Reactions • Atoms and molecules react to create chemical reactions. • There are thousands of different chemical reactions, where atoms are never lost, just rearranged. ...
... Types of Chemical Reactions • Atoms and molecules react to create chemical reactions. • There are thousands of different chemical reactions, where atoms are never lost, just rearranged. ...
Name: Date: AP Chemistry/Chemistry 145 Summer Assignment
... and 25.98259 amu. The relative abundances of these three isotopes are 78.70%, 10.13 %, and 11.17% respectively. Calculate the average atomic mass. ...
... and 25.98259 amu. The relative abundances of these three isotopes are 78.70%, 10.13 %, and 11.17% respectively. Calculate the average atomic mass. ...
Ch. 8 Notes (Chemical Reactions) Teacher Relearn
... Example of a Balanced Chemical Equation: 2H2 (g) + O2 (g) 2H2O (g) left side of the arrow, and the Reactants are on the ______ right yields products are on the __________ side. The arrow means “________”, or “reacts to produce” when read aloud. ...
... Example of a Balanced Chemical Equation: 2H2 (g) + O2 (g) 2H2O (g) left side of the arrow, and the Reactants are on the ______ right yields products are on the __________ side. The arrow means “________”, or “reacts to produce” when read aloud. ...
Discover Chemical Changes - gk-12
... pieces and eventually down to atoms, becoming something different that what they were before. Rotting is also associated with the presence of mold, fungi that often grows on things that are decaying. Burning – the chemical process of combustion, which is an exothermic chemical reaction between a sub ...
... pieces and eventually down to atoms, becoming something different that what they were before. Rotting is also associated with the presence of mold, fungi that often grows on things that are decaying. Burning – the chemical process of combustion, which is an exothermic chemical reaction between a sub ...
Equilibrium Constant - Faculty Server Contact
... Equilibrium Constant To determine the amount of each compound that will be present at equilibrium you must know the equilibrium constant. To determine the equilibrium constant you must consider the ...
... Equilibrium Constant To determine the amount of each compound that will be present at equilibrium you must know the equilibrium constant. To determine the equilibrium constant you must consider the ...
CH 4: Matter and Energy
... • Potential energy, PE, is stored energy; it results from position or composition. • Kinetic energy, KE, is the energy matter has as a result of motion. • Energy can be converted between the two types. • A boulder at the top of the hill has potential energy; if you push it down the hill, the potenti ...
... • Potential energy, PE, is stored energy; it results from position or composition. • Kinetic energy, KE, is the energy matter has as a result of motion. • Energy can be converted between the two types. • A boulder at the top of the hill has potential energy; if you push it down the hill, the potenti ...
Oxidation-reduction reactions and electrochemistry
... This unit is primarily for science students who intend to major in Chemistry or proceed with Level 2 chemistry major units. During the semester the integrated laboratory/lecture programme is concerned with physical and inorganic chemistry. Content includes categories of chemical reaction in aqueous ...
... This unit is primarily for science students who intend to major in Chemistry or proceed with Level 2 chemistry major units. During the semester the integrated laboratory/lecture programme is concerned with physical and inorganic chemistry. Content includes categories of chemical reaction in aqueous ...
Energy, work and heat
... But it never goes away • Energy is conserved in any process – None is lost – None is gained – But it goes from one place to another ...
... But it never goes away • Energy is conserved in any process – None is lost – None is gained – But it goes from one place to another ...
Chapter 19 Reaction Rates And Equilibrium
... • If the number of moles on each side of the reaction are the same, change in pressure ...
... • If the number of moles on each side of the reaction are the same, change in pressure ...
Fundamentals of Chemistry
... atoms in which reactant compounds are converted into product compounds. • During a chem rxn, chemical bonds in the reactants are broken and chemical bonds in the products are created. • A rxn is accompanied by a change in energy (i.e. heat can be absorbed or given off), color, state of matter, etc. ...
... atoms in which reactant compounds are converted into product compounds. • During a chem rxn, chemical bonds in the reactants are broken and chemical bonds in the products are created. • A rxn is accompanied by a change in energy (i.e. heat can be absorbed or given off), color, state of matter, etc. ...
Chemistry! - Duplin County Schools
... • A chemical equation shows what happens during a chemical reaction • There is a reactant, an arrow, and a product in every chemical equation (RAP) • It is important for you to know if chemical equations are balanced or not ...
... • A chemical equation shows what happens during a chemical reaction • There is a reactant, an arrow, and a product in every chemical equation (RAP) • It is important for you to know if chemical equations are balanced or not ...
Chemical thermodynamics

Chemical thermodynamics is the study of the interrelation of heat and work with chemical reactions or with physical changes of state within the confines of the laws of thermodynamics. Chemical thermodynamics involves not only laboratory measurements of various thermodynamic properties, but also the application of mathematical methods to the study of chemical questions and the spontaneity of processes.The structure of chemical thermodynamics is based on the first two laws of thermodynamics. Starting from the first and second laws of thermodynamics, four equations called the ""fundamental equations of Gibbs"" can be derived. From these four, a multitude of equations, relating the thermodynamic properties of the thermodynamic system can be derived using relatively simple mathematics. This outlines the mathematical framework of chemical thermodynamics.